Action Languages Based Actual Causality in Ethical Decision Making Contexts
Paper and Code
May 05, 2022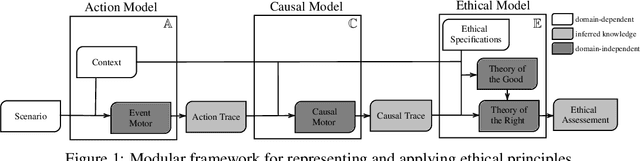
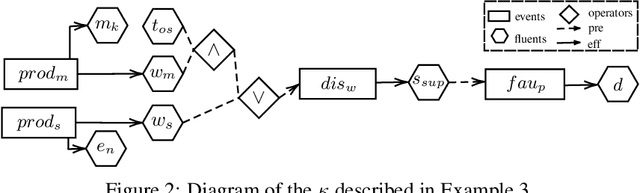
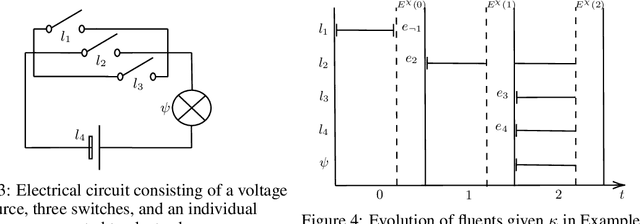
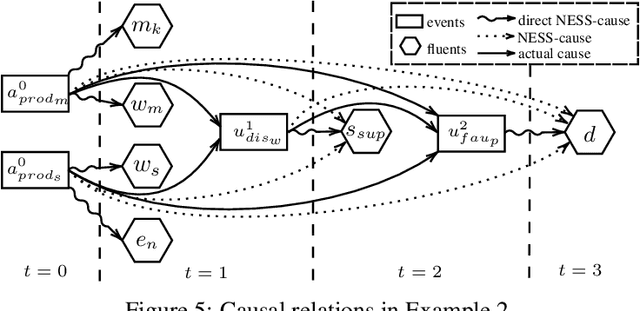
Moral responsibility is closely intermixed with causality, even if it cannot be reduced to it. Besides, rationally understanding the evolution of the physical world is inherently linked with the idea of causality. It follows that decision making applications based on automated planning, especially if they integrate references to ethical norms, have inevitably to deal with causality. Despite these considerations, much of the work in computational ethics relegates causality to the background, if not ignores it completely. This paper contribution is double. The first one is to link up two research topics$\unicode{x2014}$automated planning and causality$\unicode{x2014}$by proposing an actual causation definition suitable for action languages. This definition is a formalisation of Wright's NESS test of causation. The second is to link up computational ethics and causality by showing the importance of causality in the simulation of ethical reasoning and by enabling the domain to deal with situations that were previously out of reach thanks to the actual causation definition proposed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge