Camille Chapdelaine
Backpropagation-Based Analytical Derivatives of EKF Covariance for Active Sensing
Mar 08, 2024



Abstract:To enhance accuracy of robot state estimation, active sensing (or perception-aware) methods seek trajectories that maximize the information gathered by the sensors. To this aim, one possibility is to seek trajectories that minimize the (estimation error) covariance matrix output by an extended Kalman filter (EKF), w.r.t. its control inputs over a given horizon. However, this is computationally demanding. In this article, we derive novel backpropagation analytical formulas for the derivatives of the covariance matrices of an EKF w.r.t. all its inputs. We then leverage the obtained analytical gradients as an enabling technology to derive perception-aware optimal motion plans. Simulations validate the approach, showcasing improvements in execution time, notably over PyTorch's automatic differentiation. Experimental results on a real vehicle also support the method.
White Paper Machine Learning in Certified Systems
Mar 18, 2021
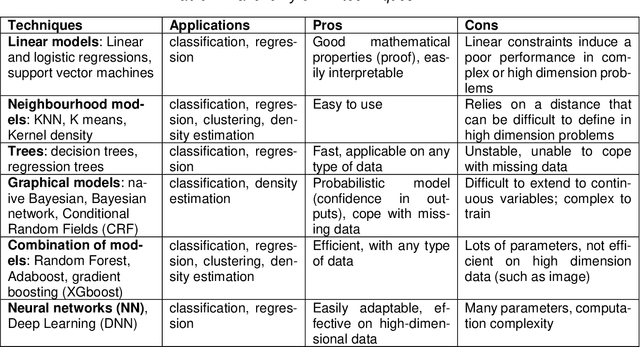

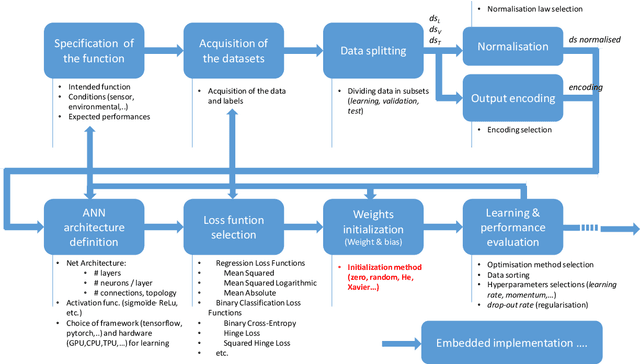
Abstract:Machine Learning (ML) seems to be one of the most promising solution to automate partially or completely some of the complex tasks currently realized by humans, such as driving vehicles, recognizing voice, etc. It is also an opportunity to implement and embed new capabilities out of the reach of classical implementation techniques. However, ML techniques introduce new potential risks. Therefore, they have only been applied in systems where their benefits are considered worth the increase of risk. In practice, ML techniques raise multiple challenges that could prevent their use in systems submitted to certification constraints. But what are the actual challenges? Can they be overcome by selecting appropriate ML techniques, or by adopting new engineering or certification practices? These are some of the questions addressed by the ML Certification 3 Workgroup (WG) set-up by the Institut de Recherche Technologique Saint Exup\'ery de Toulouse (IRT), as part of the DEEL Project.
Dataset Definition Standard (DDS)
Jan 07, 2021


Abstract:This document gives a set of recommendations to build and manipulate the datasets used to develop and/or validate machine learning models such as deep neural networks. This document is one of the 3 documents defined in [1] to ensure the quality of datasets. This is a work in progress as good practices evolve along with our understanding of machine learning. The document is divided into three main parts. Section 2 addresses the data collection activity. Section 3 gives recommendations about the annotation process. Finally, Section 4 gives recommendations concerning the breakdown between train, validation, and test datasets. In each part, we first define the desired properties at stake, then we explain the objectives targeted to meet the properties, finally we state the recommendations to reach these objectives.
Ensuring Dataset Quality for Machine Learning Certification
Nov 03, 2020



Abstract:In this paper, we address the problem of dataset quality in the context of Machine Learning (ML)-based critical systems. We briefly analyse the applicability of some existing standards dealing with data and show that the specificities of the ML context are neither properly captured nor taken into ac-count. As a first answer to this concerning situation, we propose a dataset specification and verification process, and apply it on a signal recognition system from the railway domain. In addi-tion, we also give a list of recommendations for the collection and management of datasets. This work is one step towards the dataset engineering process that will be required for ML to be used on safety critical systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge