Cameron Birge
Rapid building damage assessment workflow: An implementation for the 2023 Rolling Fork, Mississippi tornado event
Jun 21, 2023


Abstract:Rapid and accurate building damage assessments from high-resolution satellite imagery following a natural disaster is essential to inform and optimize first responder efforts. However, performing such building damage assessments in an automated manner is non-trivial due to the challenges posed by variations in disaster-specific damage, diversity in satellite imagery, and the dearth of extensive, labeled datasets. To circumvent these issues, this paper introduces a human-in-the-loop workflow for rapidly training building damage assessment models after a natural disaster. This article details a case study using this workflow, executed in partnership with the American Red Cross during a tornado event in Rolling Fork, Mississippi in March, 2023. The output from our human-in-the-loop modeling process achieved a precision of 0.86 and recall of 0.80 for damaged buildings when compared to ground truth data collected post-disaster. This workflow was implemented end-to-end in under 2 hours per satellite imagery scene, highlighting its potential for real-time deployment.
Height Estimation of Children under Five Years using Depth Images
May 04, 2021

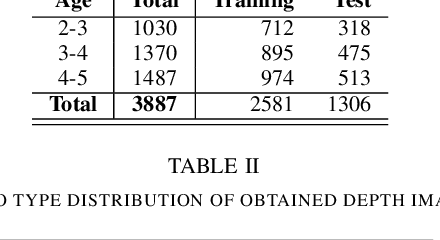
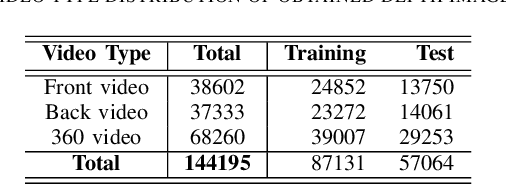
Abstract:Malnutrition is a global health crisis and is the leading cause of death among children under five. Detecting malnutrition requires anthropometric measurements of weight, height, and middle-upper arm circumference. However, measuring them accurately is a challenge, especially in the global south, due to limited resources. In this work, we propose a CNN-based approach to estimate the height of standing children under five years from depth images collected using a smart-phone. According to the SMART Methodology Manual [5], the acceptable accuracy for height is less than 1.4 cm. On training our deep learning model on 87131 depth images, our model achieved an average mean absolute error of 1.64% on 57064 test images. For 70.3% test images, we estimated height accurately within the acceptable 1.4 cm range. Thus, our proposed solution can accurately detect stunting (low height-for-age) in standing children below five years of age.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge