Cam Le
Landslide Detection and Segmentation Using Remote Sensing Images and Deep Neural Network
Dec 27, 2023

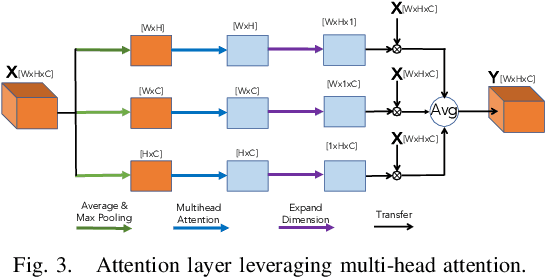
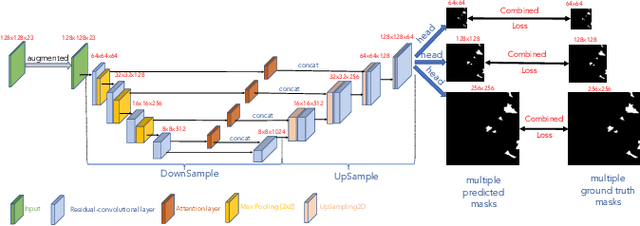
Abstract:Knowledge about historic landslide event occurrence is important for supporting disaster risk reduction strategies. Building upon findings from 2022 Landslide4Sense Competition, we propose a deep neural network based system for landslide detection and segmentation from multisource remote sensing image input. We use a U-Net trained with Cross Entropy loss as baseline model. We then improve the U-Net baseline model by leveraging a wide range of deep learning techniques. In particular, we conduct feature engineering by generating new band data from the original bands, which helps to enhance the quality of remote sensing image input. Regarding the network architecture, we replace traditional convolutional layers in the U-Net baseline by a residual-convolutional layer. We also propose an attention layer which leverages the multi-head attention scheme. Additionally, we generate multiple output masks with three different resolutions, which creates an ensemble of three outputs in the inference process to enhance the performance. Finally, we propose a combined loss function which leverages Focal loss and IoU loss to train the network. Our experiments on the development set of the Landslide4Sense challenge achieve an F1 score and an mIoU score of 84.07 and 76.07, respectively. Our best model setup outperforms the challenge baseline and the proposed U-Net baseline, improving the F1 score/mIoU score by 6.8/7.4 and 10.5/8.8, respectively.
Low-complexity deep learning frameworks for acoustic scene classification using teacher-student scheme and multiple spectrograms
May 16, 2023Abstract:In this technical report, a low-complexity deep learning system for acoustic scene classification (ASC) is presented. The proposed system comprises two main phases: (Phase I) Training a teacher network; and (Phase II) training a student network using distilled knowledge from the teacher. In the first phase, the teacher, which presents a large footprint model, is trained. After training the teacher, the embeddings, which are the feature map of the second last layer of the teacher, are extracted. In the second phase, the student network, which presents a low complexity model, is trained with the embeddings extracted from the teacher. Our experiments conducted on DCASE 2023 Task 1 Development dataset have fulfilled the requirement of low-complexity and achieved the best classification accuracy of 57.4%, improving DCASE baseline by 14.5%.
Deep Learning Based Multimodal with Two-phase Training Strategy for Daily Life Video Classification
Apr 30, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we present a deep learning based multimodal system for classifying daily life videos. To train the system, we propose a two-phase training strategy. In the first training phase (Phase I), we extract the audio and visual (image) data from the original video. We then train the audio data and the visual data with independent deep learning based models. After the training processes, we obtain audio embeddings and visual embeddings by extracting feature maps from the pre-trained deep learning models. In the second training phase (Phase II), we train a fusion layer to combine the audio/visual embeddings and a dense layer to classify the combined embedding into target daily scenes. Our extensive experiments, which were conducted on the benchmark dataset of DCASE (IEEE AASP Challenge on Detection and Classification of Acoustic Scenes and Events) 2021 Task 1B Development, achieved the best classification accuracy of 80.5%, 91.8%, and 95.3% with only audio data, with only visual data, both audio and visual data, respectively. The highest classification accuracy of 95.3% presents an improvement of 17.9% compared with DCASE baseline and shows very competitive to the state-of-the-art systems.
A Light-weight Deep Learning Model for Remote Sensing Image Classification
Feb 25, 2023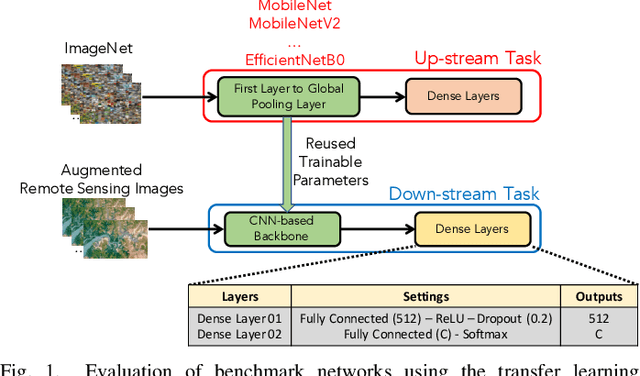
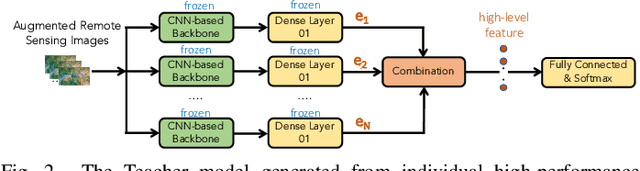
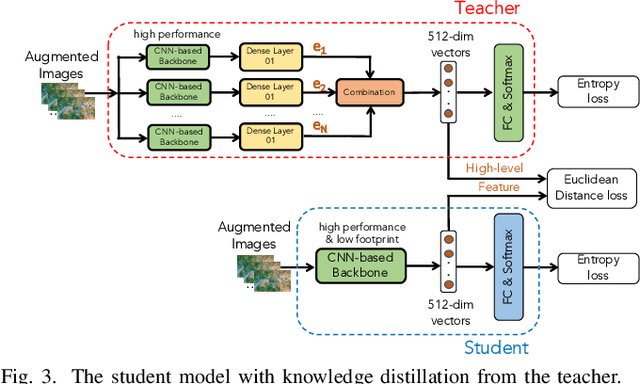
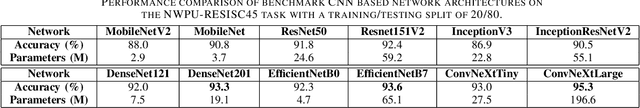
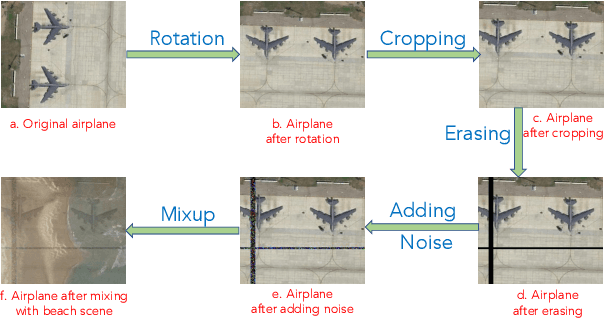
Abstract:In this paper, we present a high-performance and light-weight deep learning model for Remote Sensing Image Classification (RSIC), the task of identifying the aerial scene of a remote sensing image. To this end, we first valuate various benchmark convolutional neural network (CNN) architectures: MobileNet V1/V2, ResNet 50/151V2, InceptionV3/InceptionResNetV2, EfficientNet B0/B7, DenseNet 121/201, ConNeXt Tiny/Large. Then, the best performing models are selected to train a compact model in a teacher-student arrangement. The knowledge distillation from the teacher aims to achieve high performance with significantly reduced complexity. By conducting extensive experiments on the NWPU-RESISC45 benchmark, our proposed teacher-student models outperforms the state-of-the-art systems, and has potential to be applied on a wide rage of edge devices.
A Robust and Low Complexity Deep Learning Model for Remote Sensing Image Classification
Nov 05, 2022
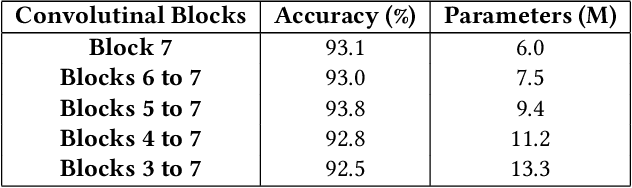
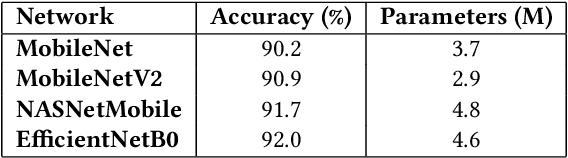
Abstract:In this paper, we present a robust and low complexity deep learning model for Remote Sensing Image Classification (RSIC), the task of identifying the scene of a remote sensing image. In particular, we firstly evaluate different low complexity and benchmark deep neural networks: MobileNetV1, MobileNetV2, NASNetMobile, and EfficientNetB0, which present the number of trainable parameters lower than 5 Million (M). After indicating best network architecture, we further improve the network performance by applying attention schemes to multiple feature maps extracted from middle layers of the network. To deal with the issue of increasing the model footprint as using attention schemes, we apply the quantization technique to satisfies the number trainable parameter of the model lower than 5 M. By conducting extensive experiments on the benchmark datasets NWPU-RESISC45, we achieve a robust and low-complexity model, which is very competitive to the state-of-the-art systems and potential for real-life applications on edge devices.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge