Brian Kim
Bayesian Interpolating Neural Network (B-INN): a scalable and reliable Bayesian model for large-scale physical systems
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Neural networks and machine learning models for uncertainty quantification suffer from limited scalability and poor reliability compared to their deterministic counterparts. In industry-scale active learning settings, where generating a single high-fidelity simulation may require days or weeks of computation and produce data volumes on the order of gigabytes, they quickly become impractical. This paper proposes a scalable and reliable Bayesian surrogate model, termed the Bayesian Interpolating Neural Network (B-INN). The B-INN combines high-order interpolation theory with tensor decomposition and alternating direction algorithm to enable effective dimensionality reduction without compromising predictive accuracy. We theoretically show that the function space of a B-INN is a subset of that of Gaussian processes, while its Bayesian inference exhibits linear complexity, $\mathcal{O}(N)$, with respect to the number of training samples. Numerical experiments demonstrate that B-INNs can be from 20 times to 10,000 times faster with a robust uncertainty estimation compared to Bayesian neural networks and Gaussian processes. These capabilities make B-INN a practical foundation for uncertainty-driven active learning in large-scale industrial simulations, where computational efficiency and robust uncertainty calibration are paramount.
Deep Reinforcement Learning Based Routing for Heterogeneous Multi-Hop Wireless Networks
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:Routing in multi-hop wireless networks is a complex problem, especially in heterogeneous networks where multiple wireless communication technologies coexist. Reinforcement learning (RL) methods, such as Q-learning, have been introduced for decentralized routing by allowing nodes to make decisions based on local observations. However, Q-learning suffers from scalability issues and poor generalization due to the difficulty in managing the Q-table in large or dynamic network topologies, especially in heterogeneous networks (HetNets) with diverse channel characteristics. Thus, in this paper, we propose a novel deep Q-network (DQN)-based routing framework for heterogeneous multi-hop wireless networks to maximize the end-to-end rate of the route by improving scalability and adaptability, where each node uses a deep neural network (DNN) to estimate the Q-values and jointly select the next-hop relay and a communication technology for transmission. To achieve better performance with the DNN, selecting which nodes to exchange information is critical, as it not only defines the state and action spaces but also determines the input to the DNN. To this end, we propose neighbor node selection strategies based on channel gain and rate between nodes rather than a simple distance-based approach for an improved set of states and actions for DQN-based routing. During training, the model experiences diverse network topologies to ensure generalization and robustness, and simulation results show that the proposed neighbor node selection outperforms simple distance-based selection. Further, we observe that the DQN-based approach outperforms various benchmark schemes and performs comparably to the optimal approach.
Mathematical Derivation Graphs: A Task for Summarizing Equation Dependencies in STEM Manuscripts
Oct 26, 2024Abstract:Recent advances in natural language processing (NLP), particularly with the emergence of large language models (LLMs), have significantly enhanced the field of textual analysis. However, while these developments have yielded substantial progress in analyzing textual data, applying analysis to mathematical equations and their relationships within texts has produced mixed results. In this paper, we take the initial steps toward understanding the dependency relationships between mathematical expressions in STEM articles. Our dataset, sourced from a random sampling of the arXiv corpus, contains an analysis of 107 published STEM manuscripts whose inter-equation dependency relationships have been hand-labeled, resulting in a new object we refer to as a derivation graph that summarizes the mathematical content of the manuscript. We exhaustively evaluate analytical and NLP-based models to assess their capability to identify and extract the derivation relationships for each article and compare the results with the ground truth. Our comprehensive testing finds that both analytical and NLP models (including LLMs) achieve $\sim$40-50% F1 scores for extracting derivation graphs from articles, revealing that the recent advances in NLP have not made significant inroads in comprehending mathematical texts compared to simpler analytic models. While current approaches offer a solid foundation for extracting mathematical information, further research is necessary to improve accuracy and depth in this area.
Experimental Study of Adversarial Attacks on ML-based xApps in O-RAN
Sep 07, 2023Abstract:Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) is considered as a major step in the evolution of next-generation cellular networks given its support for open interfaces and utilization of artificial intelligence (AI) into the deployment, operation, and maintenance of RAN. However, due to the openness of the O-RAN architecture, such AI models are inherently vulnerable to various adversarial machine learning (ML) attacks, i.e., adversarial attacks which correspond to slight manipulation of the input to the ML model. In this work, we showcase the vulnerability of an example ML model used in O-RAN, and experimentally deploy it in the near-real time (near-RT) RAN intelligent controller (RIC). Our ML-based interference classifier xApp (extensible application in near-RT RIC) tries to classify the type of interference to mitigate the interference effect on the O-RAN system. We demonstrate the first-ever scenario of how such an xApp can be impacted through an adversarial attack by manipulating the data stored in a shared database inside the near-RT RIC. Through a rigorous performance analysis deployed on a laboratory O-RAN testbed, we evaluate the performance in terms of capacity and the prediction accuracy of the interference classifier xApp using both clean and perturbed data. We show that even small adversarial attacks can significantly decrease the accuracy of ML application in near-RT RIC, which can directly impact the performance of the entire O-RAN deployment.
Covert Communications via Adversarial Machine Learning and Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces
Dec 21, 2021

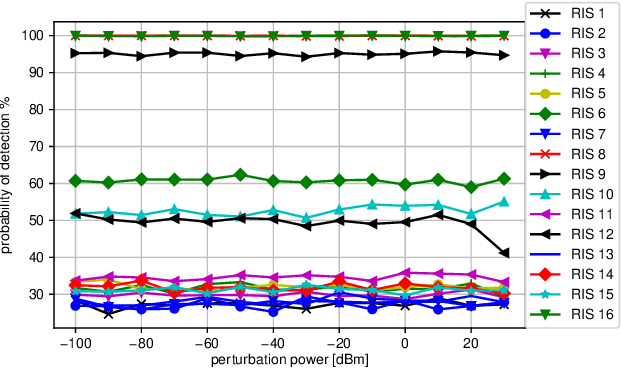
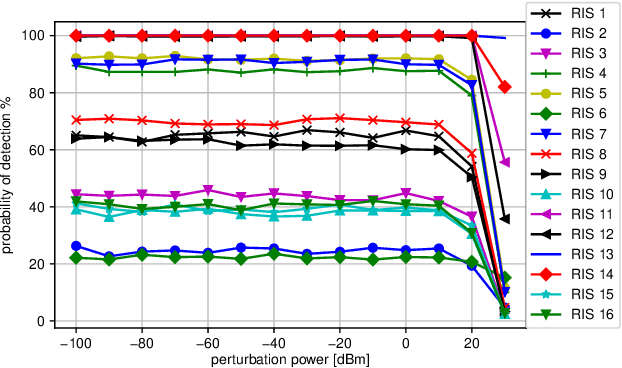
Abstract:By moving from massive antennas to antenna surfaces for software-defined wireless systems, the reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) rely on arrays of unit cells to control the scattering and reflection profiles of signals, mitigating the propagation loss and multipath attenuation, and thereby improving the coverage and spectral efficiency. In this paper, covert communication is considered in the presence of the RIS. While there is an ongoing transmission boosted by the RIS, both the intended receiver and an eavesdropper individually try to detect this transmission using their own deep neural network (DNN) classifiers. The RIS interaction vector is designed by balancing two (potentially conflicting) objectives of focusing the transmitted signal to the receiver and keeping the transmitted signal away from the eavesdropper. To boost covert communications, adversarial perturbations are added to signals at the transmitter to fool the eavesdropper's classifier while keeping the effect on the receiver low. Results from different network topologies show that adversarial perturbation and RIS interaction vector can be jointly designed to effectively increase the signal detection accuracy at the receiver while reducing the detection accuracy at the eavesdropper to enable covert communications.
Adversarial Attacks against Deep Learning Based Power Control in Wireless Communications
Oct 12, 2021



Abstract:We consider adversarial machine learning based attacks on power allocation where the base station (BS) allocates its transmit power to multiple orthogonal subcarriers by using a deep neural network (DNN) to serve multiple user equipments (UEs). The DNN that corresponds to a regression model is trained with channel gains as the input and returns transmit powers as the output. While the BS allocates the transmit powers to the UEs to maximize rates for all UEs, there is an adversary that aims to minimize these rates. The adversary may be an external transmitter that aims to manipulate the inputs to the DNN by interfering with the pilot signals that are transmitted to measure the channel gain. Alternatively, the adversary may be a rogue UE that transmits fabricated channel estimates to the BS. In both cases, the adversary carefully crafts adversarial perturbations to manipulate the inputs to the DNN of the BS subject to an upper bound on the strengths of these perturbations. We consider the attacks targeted on a single UE or all UEs. We compare these attacks with a benchmark, where the adversary scales down the input to the DNN. We show that the adversarial attacks are much more effective than the benchmark attack in terms of reducing the rate of communications. We also show that adversarial attacks are robust to the uncertainty at the adversary including the erroneous knowledge of channel gains and the potential errors in exercising the attacks exactly as specified.
Adversarial Attacks on Deep Learning Based mmWave Beam Prediction in 5G and Beyond
Mar 25, 2021



Abstract:Deep learning provides powerful means to learn from spectrum data and solve complex tasks in 5G and beyond such as beam selection for initial access (IA) in mmWave communications. To establish the IA between the base station (e.g., gNodeB) and user equipment (UE) for directional transmissions, a deep neural network (DNN) can predict the beam that is best slanted to each UE by using the received signal strengths (RSSs) from a subset of possible narrow beams. While improving the latency and reliability of beam selection compared to the conventional IA that sweeps all beams, the DNN itself is susceptible to adversarial attacks. We present an adversarial attack by generating adversarial perturbations to manipulate the over-the-air captured RSSs as the input to the DNN. This attack reduces the IA performance significantly and fools the DNN into choosing the beams with small RSSs compared to jamming attacks with Gaussian or uniform noise.
Channel Effects on Surrogate Models of Adversarial Attacks against Wireless Signal Classifiers
Dec 03, 2020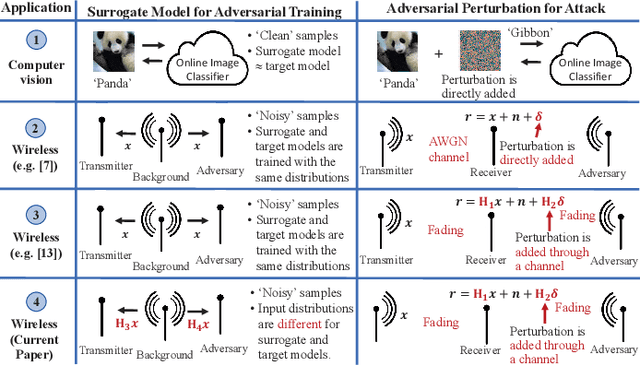
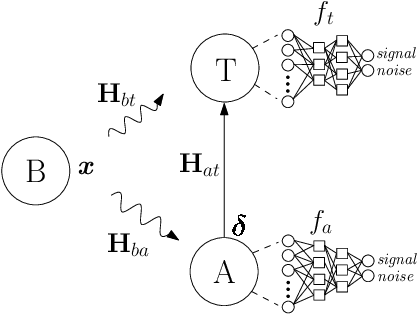
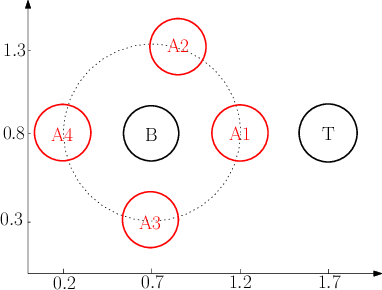
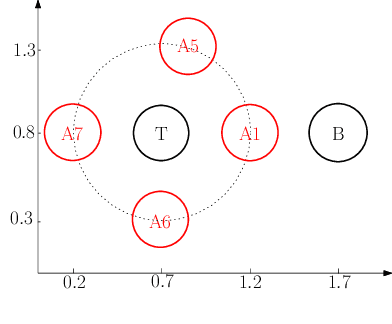
Abstract:We consider a wireless communication system that consists of a background emitter, a transmitter, and an adversary. The transmitter is equipped with a deep neural network (DNN) classifier for detecting the ongoing transmissions from the background emitter and transmits a signal if the spectrum is idle. Concurrently, the adversary trains its own DNN classifier as the surrogate model by observing the spectrum to detect the ongoing transmissions of the background emitter and generate adversarial attacks to fool the transmitter into misclassifying the channel as idle. This surrogate model may differ from the transmitter's classifier significantly because the adversary and the transmitter experience different channels from the background emitter and therefore their classifiers are trained with different distributions of inputs. This system model may represent a setting where the background emitter is a primary, the transmitter is a secondary, and the adversary is trying to fool the secondary to transmit even though the channel is occupied by the primary. We consider different topologies to investigate how different surrogate models that are trained by the adversary (depending on the differences in channel effects experienced by the adversary) affect the performance of the adversarial attack. The simulation results show that the surrogate models that are trained with different distributions of channel-induced inputs severely limit the attack performance and indicate that the transferability of adversarial attacks is neither readily available nor straightforward to achieve since surrogate models for wireless applications may significantly differ from the target model depending on channel effects.
Adversarial Attacks with Multiple Antennas Against Deep Learning-Based Modulation Classifiers
Jul 31, 2020


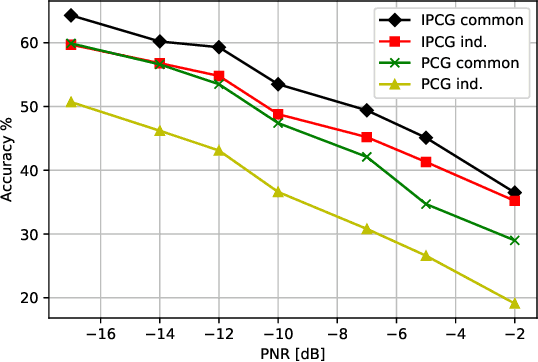
Abstract:We consider a wireless communication system, where a transmitter sends signals to a receiver with different modulation types while the receiver classifies the modulation types of the received signals using its deep learning-based classifier. Concurrently, an adversary transmits adversarial perturbations using its multiple antennas to fool the classifier into misclassifying the received signals. From the adversarial machine learning perspective, we show how to utilize multiple antennas at the adversary to improve the adversarial (evasion) attack performance. Two main points are considered while exploiting the multiple antennas at the adversary, namely the power allocation among antennas and the utilization of channel diversity. First, we show that multiple independent adversaries, each with a single antenna cannot improve the attack performance compared to a single adversary with multiple antennas using the same total power. Then, we consider various ways to allocate power among multiple antennas at a single adversary such as allocating power to only one antenna, and proportional or inversely proportional to the channel gain. By utilizing channel diversity, we introduce an attack to transmit the adversarial perturbation through the channel with the largest channel gain at the symbol level. We show that this attack reduces the classifier accuracy significantly compared to other attacks under different channel conditions in terms of channel variance and channel correlation across antennas. Also, we show that the attack success improves significantly as the number of antennas increases at the adversary that can better utilize channel diversity to craft adversarial attacks.
How to Make 5G Communications "Invisible": Adversarial Machine Learning for Wireless Privacy
May 15, 2020



Abstract:We consider the problem of hiding wireless communications from an eavesdropper that employs a deep learning (DL) classifier to detect whether any transmission of interest is present or not. There exists one transmitter that transmits to its receiver in the presence of an eavesdropper, while a cooperative jammer (CJ) transmits carefully crafted adversarial perturbations over the air to fool the eavesdropper into classifying the received superposition of signals as noise. The CJ puts an upper bound on the strength of perturbation signal to limit its impact on the bit error rate (BER) at the receiver. We show that this adversarial perturbation causes the eavesdropper to misclassify the received signals as noise with high probability while increasing the BER only slightly. On the other hand, the CJ cannot fool the eavesdropper by simply transmitting Gaussian noise as in conventional jamming and instead needs to craft perturbation signals built by adversarial machine learning to enable covert communications. Our results show that signals with different modulation types and eventually 5G communications can be effectively hidden from an eavesdropper even if it is equipped with a DL classifier to detect transmissions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge