Brendan Russo
Deep Learning Serves Traffic Safety Analysis: A Forward-looking Review
Mar 07, 2022



Abstract:This paper explores Deep Learning (DL) methods that are used or have the potential to be used for traffic video analysis, emphasizing driving safety for both Autonomous Vehicles (AVs) and human-operated vehicles. We present a typical processing pipeline, which can be used to understand and interpret traffic videos by extracting operational safety metrics and providing general hints and guidelines to improve traffic safety. This processing framework includes several steps, including video enhancement, video stabilization, semantic and incident segmentation, object detection and classification, trajectory extraction, speed estimation, event analysis, modeling and anomaly detection. Our main goal is to guide traffic analysts to develop their own custom-built processing frameworks by selecting the best choices for each step and offering new designs for the lacking modules by providing a comparative analysis of the most successful conventional and DL-based algorithms proposed for each step. We also review existing open-source tools and public datasets that can help train DL models. To be more specific, we review exemplary traffic problems and mentioned requires steps for each problem. Besides, we investigate connections to the closely related research areas of drivers' cognition evaluation, Crowd-sourcing-based monitoring systems, Edge Computing in roadside infrastructures, ADS-equipped AVs, and highlight the missing gaps. Finally, we review commercial implementations of traffic monitoring systems, their future outlook, and open problems and remaining challenges for widespread use of such systems.
Network-level Safety Metrics for Overall Traffic Safety Assessment: A Case Study
Jan 27, 2022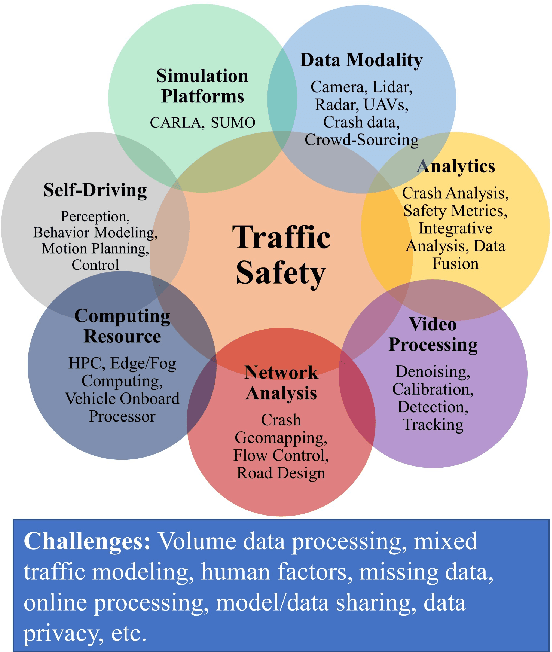
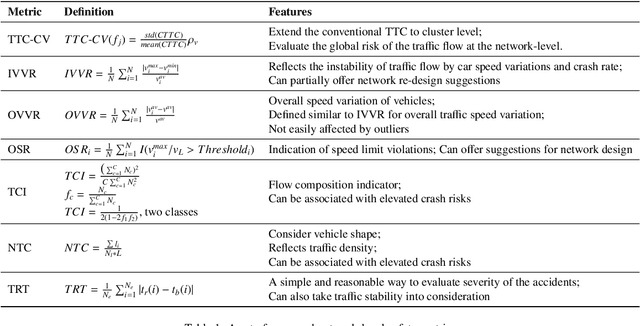
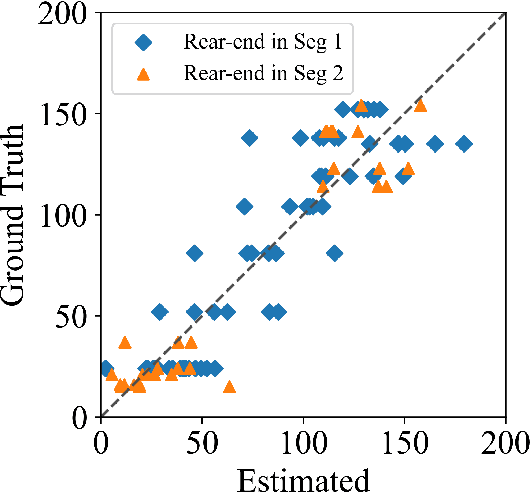
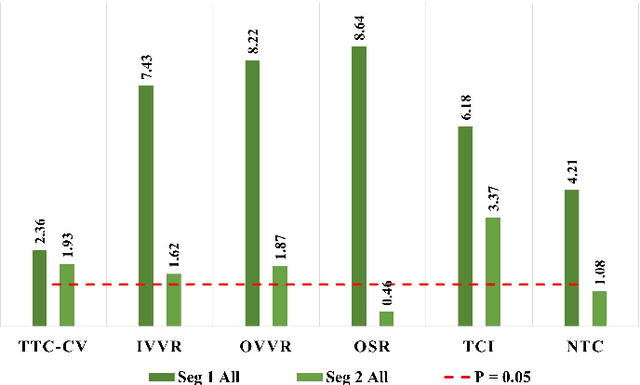
Abstract:Driving safety analysis has recently witnessed unprecedented results due to advances in computation frameworks, connected vehicle technology, new generation sensors, and artificial intelligence (AI). Particularly, the recent advances performance of deep learning (DL) methods realized higher levels of safety for autonomous vehicles and empowered volume imagery processing for driving safety analysis. An important application of DL methods is extracting driving safety metrics from traffic imagery. However, the majority of current methods use safety metrics for micro-scale analysis of individual crash incidents or near-crash events, which does not provide insightful guidelines for the overall network-level traffic management. On the other hand, large-scale safety assessment efforts mainly emphasize spatial and temporal distributions of crashes, while not always revealing the safety violations that cause crashes. To bridge these two perspectives, we define a new set of network-level safety metrics for the overall safety assessment of traffic flow by processing imagery taken by roadside infrastructure sensors. An integrative analysis of the safety metrics and crash data reveals the insightful temporal and spatial correlation between the representative network-level safety metrics and the crash frequency. The analysis is performed using two video cameras in the state of Arizona along with a 5-year crash report obtained from the Arizona Department of Transportation. The results confirm that network-level safety metrics can be used by the traffic management teams to equip traffic monitoring systems with advanced AI-based risk analysis, and timely traffic flow control decisions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge