Bram Vanderborght
Dual-Variable Force Characterisation method for Human-Robot Interaction in Wearable Robotics
Nov 18, 2025
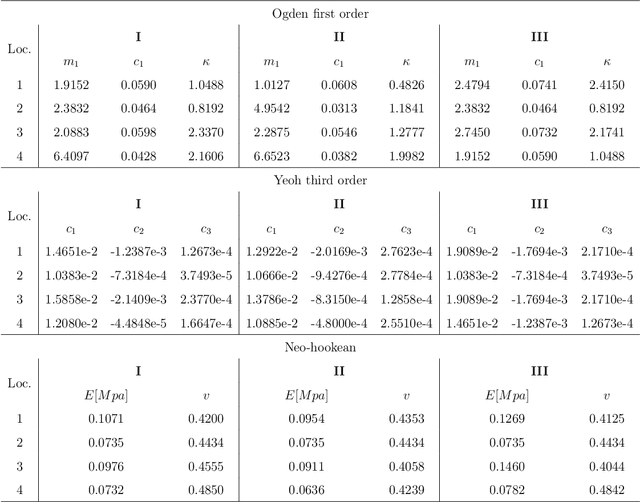
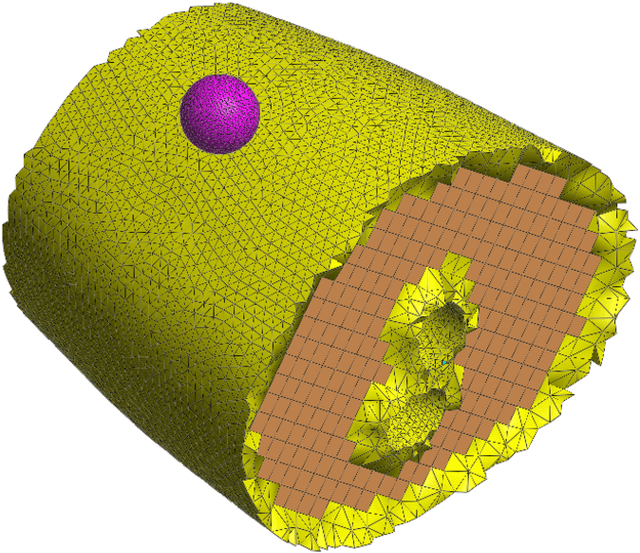
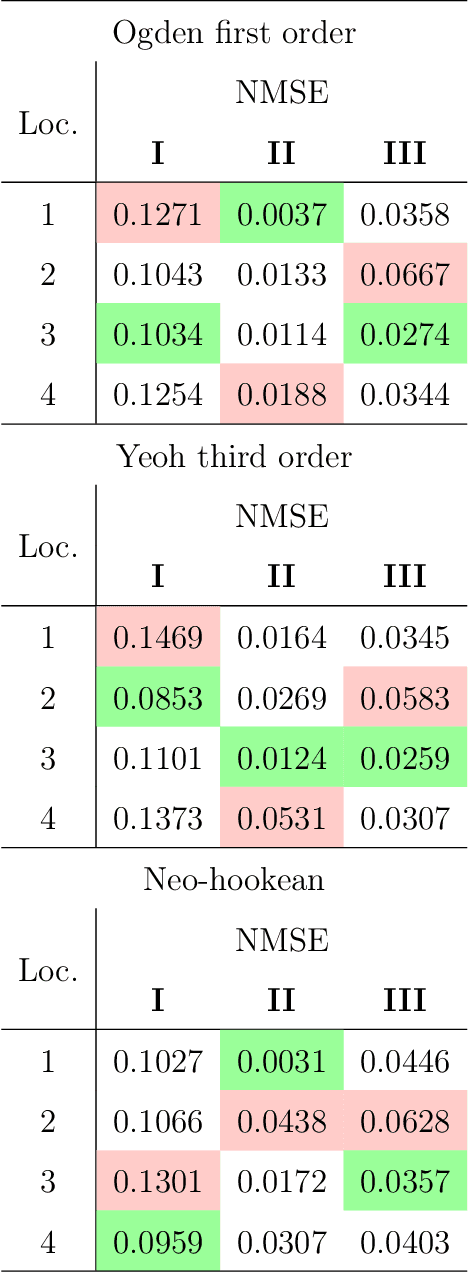
Abstract:Understanding the physical interaction with wearable robots is essential to ensure safety and comfort. However, this interaction is complex in two key aspects: (1) the motion involved, and (2) the non-linear behaviour of soft tissues. Multiple approaches have been undertaken to better understand this interaction and to improve the quantitative metrics of physical interfaces or cuffs. As these two topics are closely interrelated, finite modelling and soft tissue characterisation offer valuable insights into pressure distribution and shear stress induced by the cuff. Nevertheless, current characterisation methods typically rely on a single fitting variable along one degree of freedom, which limits their applicability, given that interactions with wearable robots often involve multiple degrees of freedom. To address this limitation, this work introduces a dual-variable characterisation method, involving normal and tangential forces, aimed at identifying reliable material parameters and evaluating the impact of single-variable fitting on force and torque responses. This method demonstrates the importance of incorporating two variables into the characterisation process by analysing the normalized mean square error (NMSE) across different scenarios and material models, providing a foundation for simulation at the closest possible level, with a focus on the cuff and the human limb involved in the physical interaction between the user and the wearable robot.
Optimistic Reinforcement Learning-Based Skill Insertions for Task and Motion Planning
Oct 15, 2025Abstract:Task and motion planning (TAMP) for robotics manipulation necessitates long-horizon reasoning involving versatile actions and skills. While deterministic actions can be crafted by sampling or optimizing with certain constraints, planning actions with uncertainty, i.e., probabilistic actions, remains a challenge for TAMP. On the contrary, Reinforcement Learning (RL) excels in acquiring versatile, yet short-horizon, manipulation skills that are robust with uncertainties. In this letter, we design a method that integrates RL skills into TAMP pipelines. Besides the policy, a RL skill is defined with data-driven logical components that enable the skill to be deployed by symbolic planning. A plan refinement sub-routine is designed to further tackle the inevitable effect uncertainties. In the experiments, we compare our method with baseline hierarchical planning from both TAMP and RL fields and illustrate the strength of the method. The results show that by embedding RL skills, we extend the capability of TAMP to domains with probabilistic skills, and improve the planning efficiency compared to the previous methods.
Automated Behavior Planning for Fruit Tree Pruning via Redundant Robot Manipulators: Addressing the Behavior Planning Challenge
Oct 14, 2025Abstract:Pruning is an essential agricultural practice for orchards. Proper pruning can promote healthier growth and optimize fruit production throughout the orchard's lifespan. Robot manipulators have been developed as an automated solution for this repetitive task, which typically requires seasonal labor with specialized skills. While previous research has primarily focused on the challenges of perception, the complexities of manipulation are often overlooked. These challenges involve planning and control in both joint and Cartesian spaces to guide the end-effector through intricate, obstructive branches. Our work addresses the behavior planning challenge for a robotic pruning system, which entails a multi-level planning problem in environments with complex collisions. In this paper, we formulate the planning problem for a high-dimensional robotic arm in a pruning scenario, investigate the system's intrinsic redundancies, and propose a comprehensive pruning workflow that integrates perception, modeling, and holistic planning. In our experiments, we demonstrate that more comprehensive planning methods can significantly enhance the performance of the robotic manipulator. Finally, we implement the proposed workflow on a real-world robot. As a result, this work complements previous efforts on robotic pruning and motivates future research and development in planning for pruning applications.
A Task-Efficient Reinforcement Learning Task-Motion Planner for Safe Human-Robot Cooperation
Oct 14, 2025Abstract:In a Human-Robot Cooperation (HRC) environment, safety and efficiency are the two core properties to evaluate robot performance. However, safety mechanisms usually hinder task efficiency since human intervention will cause backup motions and goal failures of the robot. Frequent motion replanning will increase the computational load and the chance of failure. In this paper, we present a hybrid Reinforcement Learning (RL) planning framework which is comprised of an interactive motion planner and a RL task planner. The RL task planner attempts to choose statistically safe and efficient task sequences based on the feedback from the motion planner, while the motion planner keeps the task execution process collision-free by detecting human arm motions and deploying new paths when the previous path is not valid anymore. Intuitively, the RL agent will learn to avoid dangerous tasks, while the motion planner ensures that the chosen tasks are safe. The proposed framework is validated on the cobot in both simulation and the real world, we compare the planner with hard-coded task motion planning methods. The results show that our planning framework can 1) react to uncertain human motions at both joint and task levels; 2) reduce the times of repeating failed goal commands; 3) reduce the total number of replanning requests.
Distributed Reinforcement Learning for Cooperative Multi-Robot Object Manipulation
Mar 21, 2020
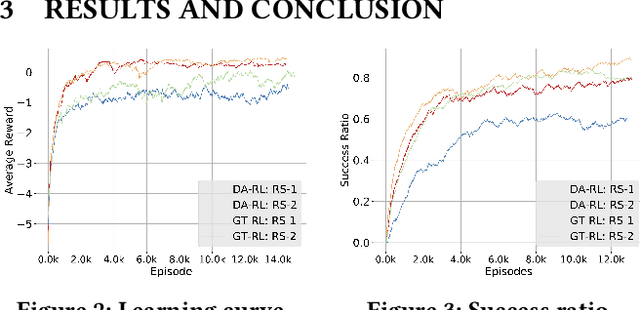
Abstract:We consider solving a cooperative multi-robot object manipulation task using reinforcement learning (RL). We propose two distributed multi-agent RL approaches: distributed approximate RL (DA-RL), where each agent applies Q-learning with individual reward functions; and game-theoretic RL (GT-RL), where the agents update their Q-values based on the Nash equilibrium of a bimatrix Q-value game. We validate the proposed approaches in the setting of cooperative object manipulation with two simulated robot arms. Although we focus on a small system of two agents in this paper, both DA-RL and GT-RL apply to general multi-agent systems, and are expected to scale well to large systems.
* 3 pages, 3 figures
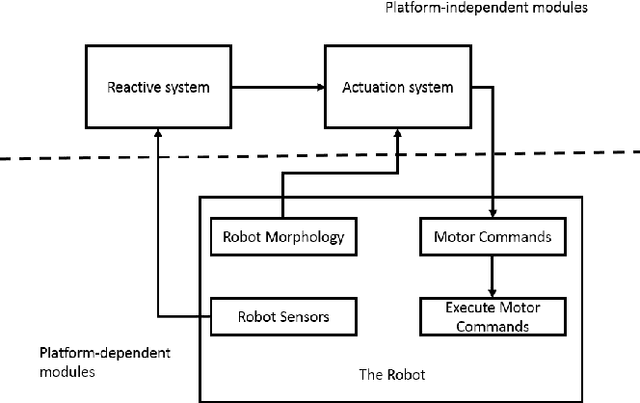
A platform-independent robot control architecture for multiple therapeutic scenarios
Jul 18, 2016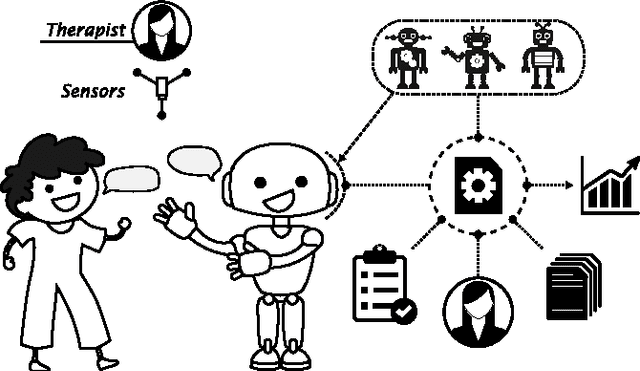
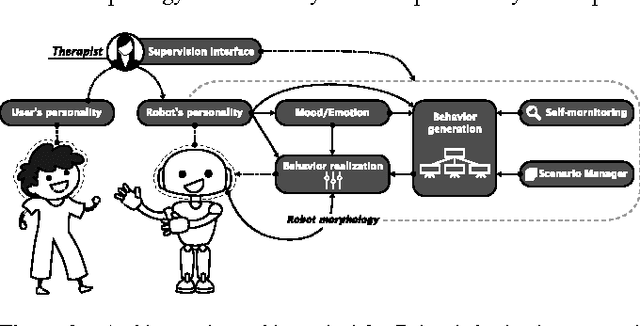
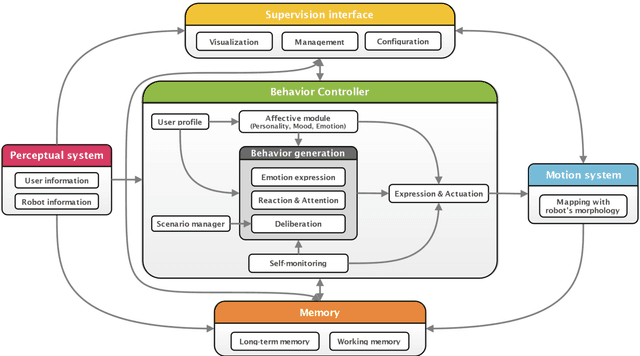
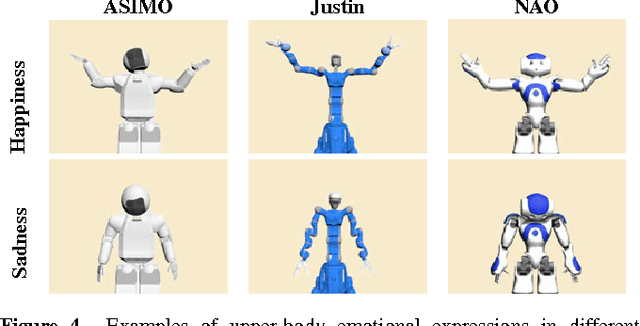
Abstract:While social robots are developed to provide assistance to users through social interactions, their behaviors are dominantly pre-programmed and remote-controlled. Despite the numerous robot control architectures being developed, very few offer reutilization opportunities in various therapeutic contexts. To bridge this gap, we propose a robot control architecture to be applied in different scenarios taking into account requirements from both therapeutic and robotic perspectives. As robot behaviors are kept at an abstract level and afterward mapped with the robot's morphology, the proposed architecture accommodates its applicability to a variety of social robot platforms.
A multilayer reactive system for robots interacting with children with autism
Jun 13, 2016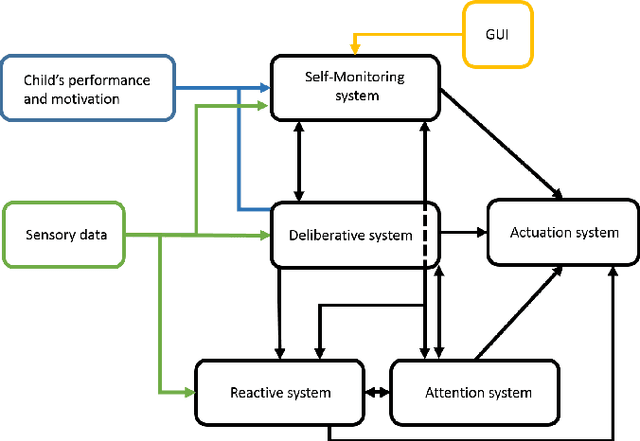
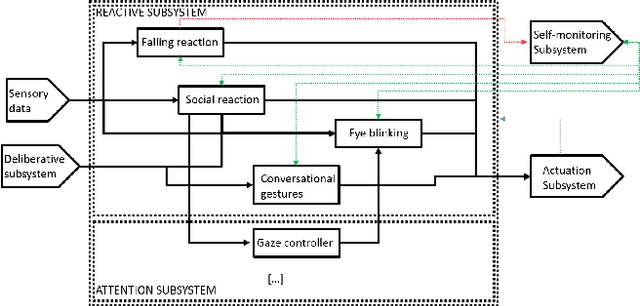
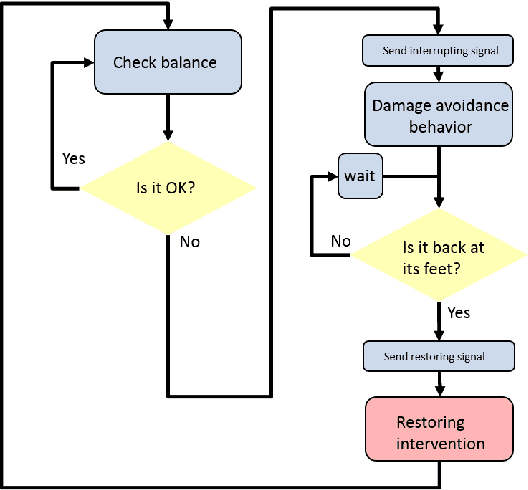
Abstract:There is a lack of autonomy on traditional Robot-Assisted Therapy systems interacting with children with autism. To overcome this limitation a supervised autonomous robot controller is being built. In this paper we present a multilayer reactive system within such controller. The goal of this Reactive system is to allow the robot to appropriately react to the child's behavior creating the illusion of being alive.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge