Bingling Li
RetinaGS: Scalable Training for Dense Scene Rendering with Billion-Scale 3D Gaussians
Jun 17, 2024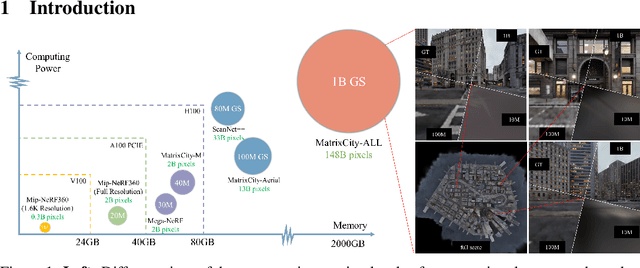
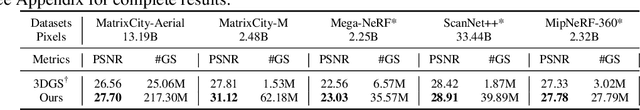

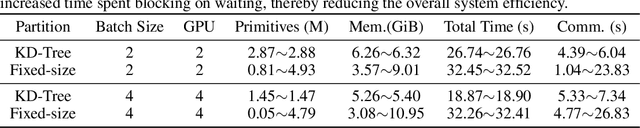
Abstract:In this work, we explore the possibility of training high-parameter 3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS) models on large-scale, high-resolution datasets. We design a general model parallel training method for 3DGS, named RetinaGS, which uses a proper rendering equation and can be applied to any scene and arbitrary distribution of Gaussian primitives. It enables us to explore the scaling behavior of 3DGS in terms of primitive numbers and training resolutions that were difficult to explore before and surpass previous state-of-the-art reconstruction quality. We observe a clear positive trend of increasing visual quality when increasing primitive numbers with our method. We also demonstrate the first attempt at training a 3DGS model with more than one billion primitives on the full MatrixCity dataset that attains a promising visual quality.
EPNet++: Cascade Bi-directional Fusion for Multi-Modal 3D Object Detection
Jan 12, 2022



Abstract:Recently, fusing the LiDAR point cloud and camera image to improve the performance and robustness of 3D object detection has received more and more attention, as these two modalities naturally possess strong complementarity. In this paper, we propose EPNet++ for multi-modal 3D object detection by introducing a novel Cascade Bi-directional Fusion~(CB-Fusion) module and a Multi-Modal Consistency~(MC) loss. More concretely, the proposed CB-Fusion module boosts the plentiful semantic information of point features with the image features in a cascade bi-directional interaction fusion manner, leading to more comprehensive and discriminative feature representations. The MC loss explicitly guarantees the consistency between predicted scores from two modalities to obtain more comprehensive and reliable confidence scores. The experiment results on the KITTI, JRDB and SUN-RGBD datasets demonstrate the superiority of EPNet++ over the state-of-the-art methods. Besides, we emphasize a critical but easily overlooked problem, which is to explore the performance and robustness of a 3D detector in a sparser scene. Extensive experiments present that EPNet++ outperforms the existing SOTA methods with remarkable margins in highly sparse point cloud cases, which might be an available direction to reduce the expensive cost of LiDAR sensors. Code will be released in the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge