Binbin Zhu
Delay-Aware Task Offloading for Heterogeneous VLC-RF-based Vehicular Fog Computing
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Vehicular fog computing (VFC) is a promising paradigm for reducing the computation burden of vehicles, thus supporting delay-sensitive services in next-generation transportation networks. However, traditional VFC schemes rely on radio frequency (RF) communications, which limits their adaptability for dense vehicular environments. In this paper, a heterogeneous visible light communication (VLC)-RF architecture is designed for VFC systems to facilitate efficient task offloading. Specifically, computing tasks are dynamically partitioned and offloaded to idle vehicles via both VLC and RF links, thereby fully exploiting the interference resilience of VLC and the coverage advantage of RF. To minimize the average task processing delay (TPD), an optimization problem of task offloading and computing resource allocation is formulated, and then solved by the developed residual-based majorization-minimization (RBMM) algorithm. Simulation results confirm that the heterogeneous VLC-RF architecture with the proposed algorithm achieves a 15% average TPD reduction compared to VFC systems relying solely on VLC or RF.
Brachial Plexus Nerve Trunk Segmentation Using Deep Learning: A Comparative Study with Doctors' Manual Segmentation
May 17, 2022
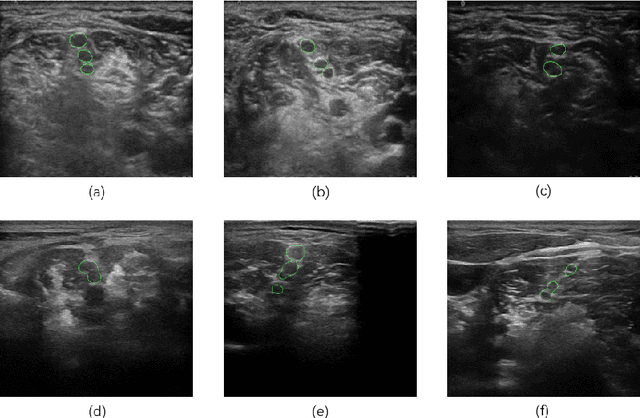
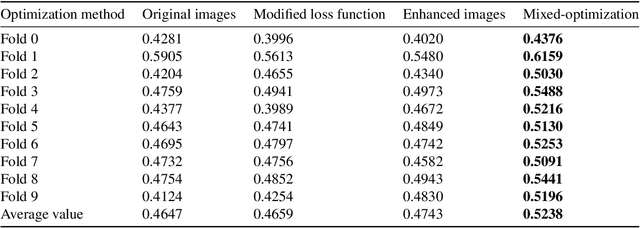
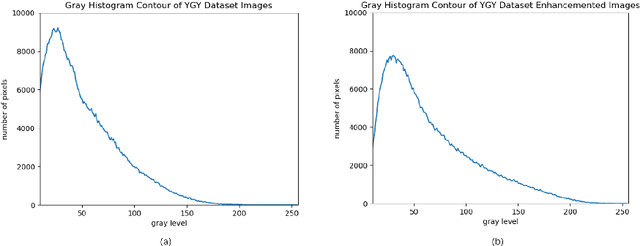
Abstract:Ultrasound-guided nerve block anesthesia (UGNB) is a high-tech visual nerve block anesthesia method that can observe the target nerve and its surrounding structures, the puncture needle's advancement, and local anesthetics spread in real-time. The key in UGNB is nerve identification. With the help of deep learning methods, the automatic identification or segmentation of nerves can be realized, assisting doctors in completing nerve block anesthesia accurately and efficiently. Here, we establish a public dataset containing 320 ultrasound images of brachial plexus (BP). Three experienced doctors jointly produce the BP segmentation ground truth and label brachial plexus trunks. We design a brachial plexus segmentation system (BPSegSys) based on deep learning. BPSegSys achieves experienced-doctor-level nerve identification performance in various experiments. We evaluate BPSegSys' performance in terms of intersection-over-union (IoU), a commonly used performance measure for segmentation experiments. Considering three dataset groups in our established public dataset, the IoU of BPSegSys are 0.5238, 0.4715, and 0.5029, respectively, which exceed the IoU 0.5205, 0.4704, and 0.4979 of experienced doctors. In addition, we show that BPSegSys can help doctors identify brachial plexus trunks more accurately, with IoU improvement up to 27%, which has significant clinical application value.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge