Benchun Zhou
Scrape, Cut, Paste and Learn: Automated Dataset Generation Applied to Parcel Logistics
Oct 18, 2022
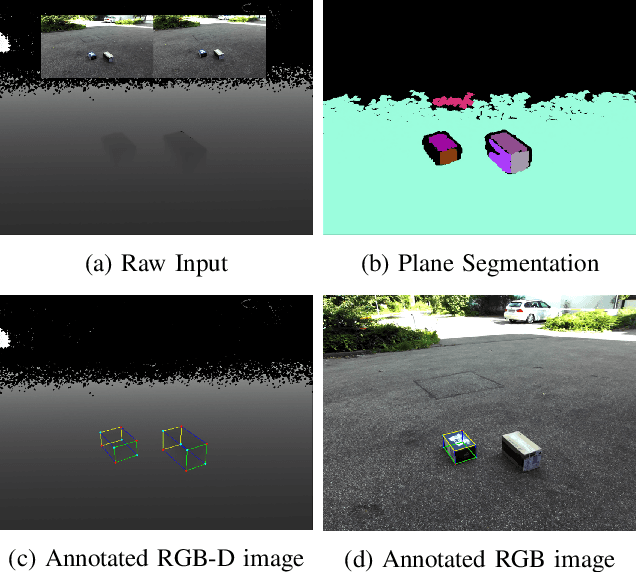


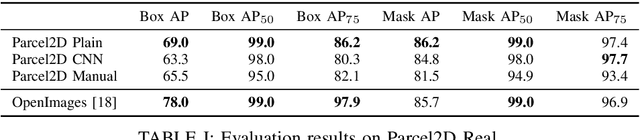
Abstract:State-of-the-art approaches in computer vision heavily rely on sufficiently large training datasets. For real-world applications, obtaining such a dataset is usually a tedious task. In this paper, we present a fully automated pipeline to generate a synthetic dataset for instance segmentation in four steps. In contrast to existing work, our pipeline covers every step from data acquisition to the final dataset. We first scrape images for the objects of interest from popular image search engines and since we rely only on text-based queries the resulting data comprises a wide variety of images. Hence, image selection is necessary as a second step. This approach of image scraping and selection relaxes the need for a real-world domain-specific dataset that must be either publicly available or created for this purpose. We employ an object-agnostic background removal model and compare three different methods for image selection: Object-agnostic pre-processing, manual image selection and CNN-based image selection. In the third step, we generate random arrangements of the object of interest and distractors on arbitrary backgrounds. Finally, the composition of the images is done by pasting the objects using four different blending methods. We present a case study for our dataset generation approach by considering parcel segmentation. For the evaluation we created a dataset of parcel photos that were annotated automatically. We find that (1) our dataset generation pipeline allows a successful transfer to real test images (Mask AP 86.2), (2) a very accurate image selection process - in contrast to human intuition - is not crucial and a broader category definition can help to bridge the domain gap, (3) the usage of blending methods is beneficial compared to simple copy-and-paste. We made our full code for scraping, image composition and training publicly available at https://a-nau.github.io/parcel2d.
Learning to Guide: Guidance Law Based on Deep Meta-learning and Model Predictive Path Integral Control
Apr 15, 2019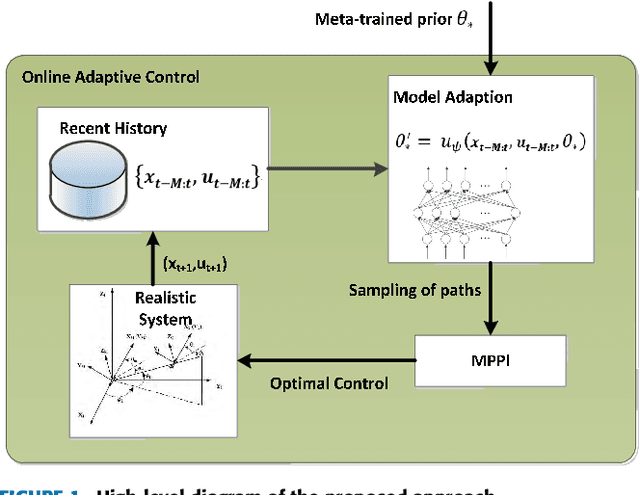
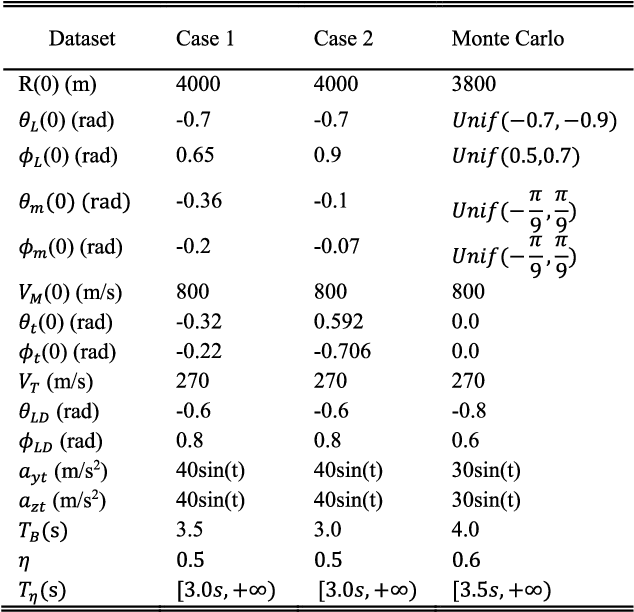
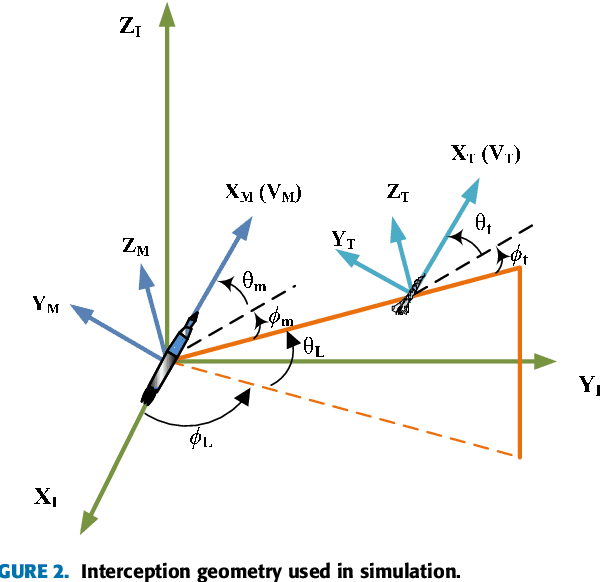
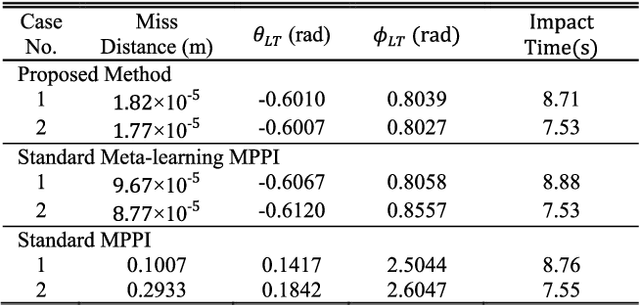
Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel guidance scheme based on model-based deep reinforcement learning (RL) technique. With model-based deep RL method, a deep neural network is trained as a predictive model of guidance dynamics which is incorporated into a model predictive path integral (MPPI) control framework. However the traditional MPPI framework assumes the actual environment similar to the training dataset for the deep neural network which is impractical in practice with different maneuvering of target, other perturbations and actuator failures. To address this problem, our method utilize meta-learning technique to make the deep neural dynamics model adapt to such changes online. With this approach we can alleviate the performance deterioration of standard MPPI control caused by the difference between actual environment and training data. Then, a novel guidance law for a varying velocity interceptor intercepting maneuvering target with desired terminal impact angle under actuator failure is constructed based on aforementioned techniques. Simulation and experiment results under different cases show the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed guidance law in achieving successful interceptions of maneuvering target.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge