Barry Drake
WellFactor: Patient Profiling using Integrative Embedding of Healthcare Data
Dec 21, 2023



Abstract:In the rapidly evolving healthcare industry, platforms now have access to not only traditional medical records, but also diverse data sets encompassing various patient interactions, such as those from healthcare web portals. To address this rich diversity of data, we introduce WellFactor: a method that derives patient profiles by integrating information from these sources. Central to our approach is the utilization of constrained low-rank approximation. WellFactor is optimized to handle the sparsity that is often inherent in healthcare data. Moreover, by incorporating task-specific label information, our method refines the embedding results, offering a more informed perspective on patients. One important feature of WellFactor is its ability to compute embeddings for new, previously unobserved patient data instantaneously, eliminating the need to revisit the entire data set or recomputing the embedding. Comprehensive evaluations on real-world healthcare data demonstrate WellFactor's effectiveness. It produces better results compared to other existing methods in classification performance, yields meaningful clustering of patients, and delivers consistent results in patient similarity searches and predictions.
Patient Clustering via Integrated Profiling of Clinical and Digital Data
Aug 22, 2023


Abstract:We introduce a novel profile-based patient clustering model designed for clinical data in healthcare. By utilizing a method grounded on constrained low-rank approximation, our model takes advantage of patients' clinical data and digital interaction data, including browsing and search, to construct patient profiles. As a result of the method, nonnegative embedding vectors are generated, serving as a low-dimensional representation of the patients. Our model was assessed using real-world patient data from a healthcare web portal, with a comprehensive evaluation approach which considered clustering and recommendation capabilities. In comparison to other baselines, our approach demonstrated superior performance in terms of clustering coherence and recommendation accuracy.
PSI Draft Specification
May 02, 2022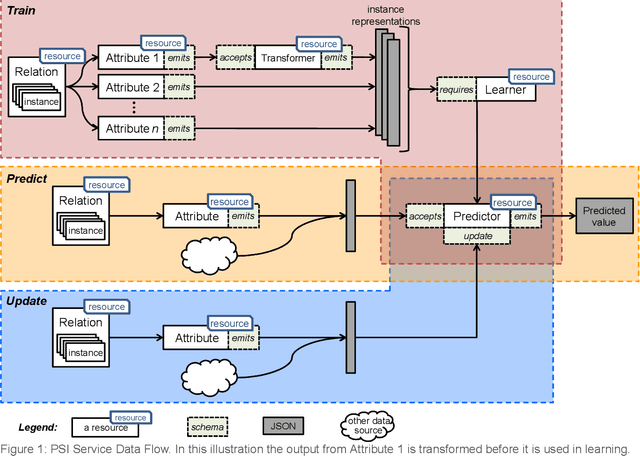
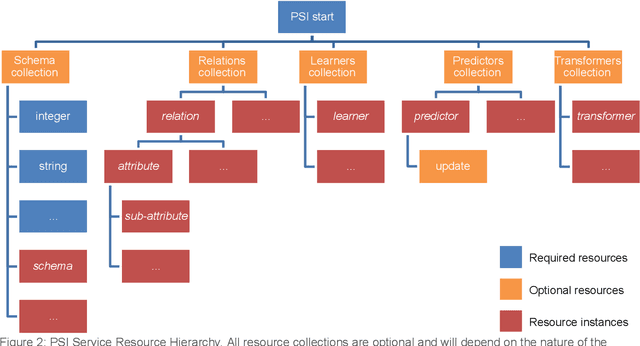
Abstract:This document presents the draft specification for delivering machine learning services over HTTP, developed as part of the Protocols and Structures for Inference project, which concluded in 2013. It presents the motivation for providing machine learning as a service, followed by a description of the essential and optional components of such a service.
Hybrid Clustering based on Content and Connection Structure using Joint Nonnegative Matrix Factorization
Mar 28, 2017


Abstract:We present a hybrid method for latent information discovery on the data sets containing both text content and connection structure based on constrained low rank approximation. The new method jointly optimizes the Nonnegative Matrix Factorization (NMF) objective function for text clustering and the Symmetric NMF (SymNMF) objective function for graph clustering. We propose an effective algorithm for the joint NMF objective function, based on a block coordinate descent (BCD) framework. The proposed hybrid method discovers content associations via latent connections found using SymNMF. The method can also be applied with a natural conversion of the problem when a hypergraph formulation is used or the content is associated with hypergraph edges. Experimental results show that by simultaneously utilizing both content and connection structure, our hybrid method produces higher quality clustering results compared to the other NMF clustering methods that uses content alone (standard NMF) or connection structure alone (SymNMF). We also present some interesting applications to several types of real world data such as citation recommendations of papers. The hybrid method proposed in this paper can also be applied to general data expressed with both feature space vectors and pairwise similarities and can be extended to the case with multiple feature spaces or multiple similarity measures.
Fast Clustering and Topic Modeling Based on Rank-2 Nonnegative Matrix Factorization
Oct 02, 2015

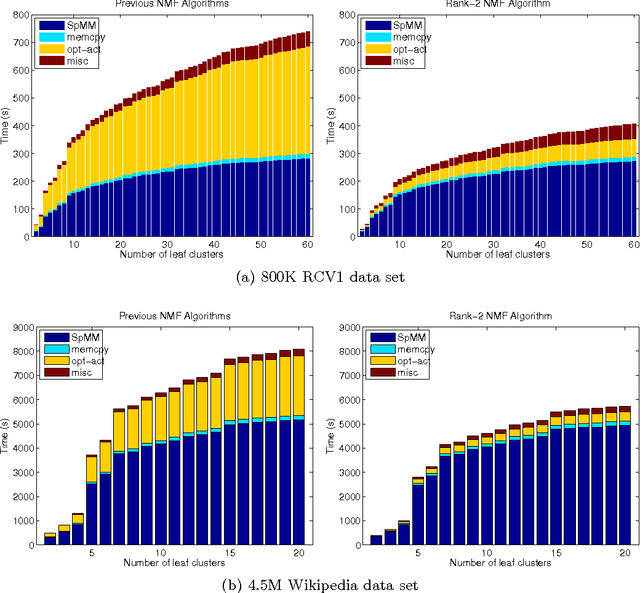
Abstract:The importance of unsupervised clustering and topic modeling is well recognized with ever-increasing volumes of text data. In this paper, we propose a fast method for hierarchical clustering and topic modeling called HierNMF2. Our method is based on fast Rank-2 nonnegative matrix factorization (NMF) that performs binary clustering and an efficient node splitting rule. Further utilizing the final leaf nodes generated in HierNMF2 and the idea of nonnegative least squares fitting, we propose a new clustering/topic modeling method called FlatNMF2 that recovers a flat clustering/topic modeling result in a very simple yet significantly more effective way than any other existing methods. We implement highly optimized open source software in C++ for both HierNMF2 and FlatNMF2 for hierarchical and partitional clustering/topic modeling of document data sets. Substantial experimental tests are presented that illustrate significant improvements both in computational time as well as quality of solutions. We compare our methods to other clustering methods including K-means, standard NMF, and CLUTO, and also topic modeling methods including latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) and recently proposed algorithms for NMF with separability constraints. Overall, we present efficient tools for analyzing large-scale data sets, and techniques that can be generalized to many other data analytics problem domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge