Barath Raj Kandur Raja
COPS: A Compact On-device Pipeline for real-time Smishing detection
Feb 06, 2024Abstract:Smartphones have become indispensable in our daily lives and can do almost everything, from communication to online shopping. However, with the increased usage, cybercrime aimed at mobile devices is rocketing. Smishing attacks, in particular, have observed a significant upsurge in recent years. This problem is further exacerbated by the perpetrator creating new deceptive websites daily, with an average life cycle of under 15 hours. This renders the standard practice of keeping a database of malicious URLs ineffective. To this end, we propose a novel on-device pipeline: COPS that intelligently identifies features of fraudulent messages and URLs to alert the user in real-time. COPS is a lightweight pipeline with a detection module based on the Disentangled Variational Autoencoder of size 3.46MB for smishing and URL phishing detection, and we benchmark it on open datasets. We achieve an accuracy of 98.15% and 99.5%, respectively, for both tasks, with a false negative and false positive rate of a mere 0.037 and 0.015, outperforming previous works with the added advantage of ensuring real-time alerts on resource-constrained devices.
TrICy: Trigger-guided Data-to-text Generation with Intent aware Attention-Copy
Jan 25, 2024



Abstract:Data-to-text (D2T) generation is a crucial task in many natural language understanding (NLU) applications and forms the foundation of task-oriented dialog systems. In the context of conversational AI solutions that can work directly with local data on the user's device, architectures utilizing large pre-trained language models (PLMs) are impractical for on-device deployment due to a high memory footprint. To this end, we propose TrICy, a novel lightweight framework for an enhanced D2T task that generates text sequences based on the intent in context and may further be guided by user-provided triggers. We leverage an attention-copy mechanism to predict out-of-vocabulary (OOV) words accurately. Performance analyses on E2E NLG dataset (BLEU: 66.43%, ROUGE-L: 70.14%), WebNLG dataset (BLEU: Seen 64.08%, Unseen 52.35%), and our Custom dataset related to text messaging applications, showcase our architecture's effectiveness. Moreover, we show that by leveraging an optional trigger input, data-to-text generation quality increases significantly and achieves the new SOTA score of 69.29% BLEU for E2E NLG. Furthermore, our analyses show that TrICy achieves at least 24% and 3% improvement in BLEU and METEOR respectively over LLMs like GPT-3, ChatGPT, and Llama 2. We also demonstrate that in some scenarios, performance improvement due to triggers is observed even when they are absent in training.
PrivPAS: A real time Privacy-Preserving AI System and applied ethics
Feb 08, 2022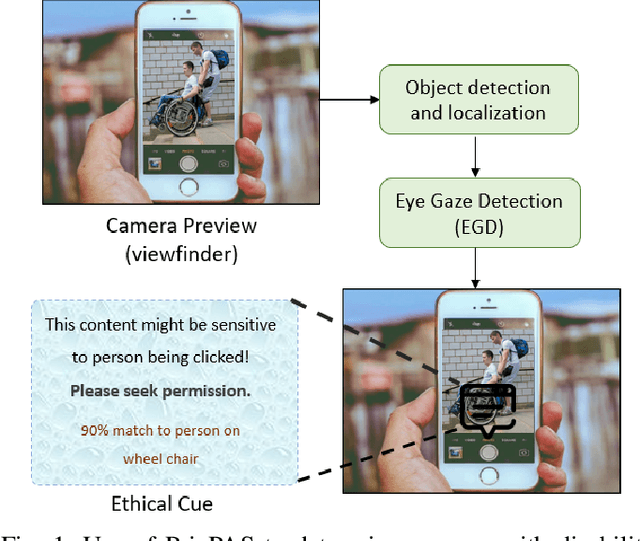

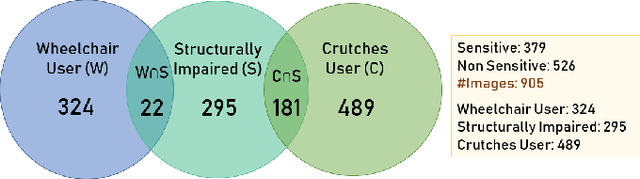
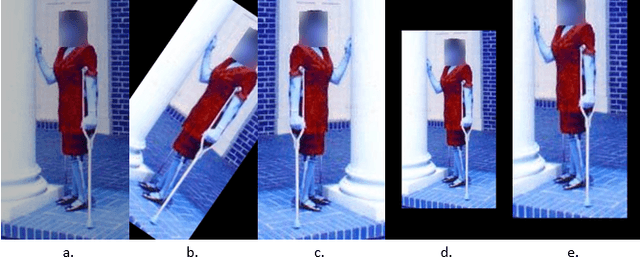
Abstract:With 3.78 billion social media users worldwide in 2021 (48% of the human population), almost 3 billion images are shared daily. At the same time, a consistent evolution of smartphone cameras has led to a photography explosion with 85% of all new pictures being captured using smartphones. However, lately, there has been an increased discussion of privacy concerns when a person being photographed is unaware of the picture being taken or has reservations about the same being shared. These privacy violations are amplified for people with disabilities, who may find it challenging to raise dissent even if they are aware. Such unauthorized image captures may also be misused to gain sympathy by third-party organizations, leading to a privacy breach. Privacy for people with disabilities has so far received comparatively less attention from the AI community. This motivates us to work towards a solution to generate privacy-conscious cues for raising awareness in smartphone users of any sensitivity in their viewfinder content. To this end, we introduce PrivPAS (A real time Privacy-Preserving AI System) a novel framework to identify sensitive content. Additionally, we curate and annotate a dataset to identify and localize accessibility markers and classify whether an image is sensitive to a featured subject with a disability. We demonstrate that the proposed lightweight architecture, with a memory footprint of a mere 8.49MB, achieves a high mAP of 89.52% on resource-constrained devices. Furthermore, our pipeline, trained on face anonymized data, achieves an F1-score of 73.1%.
edATLAS: An Efficient Disambiguation Algorithm for Texting in Languages with Abugida Scripts
Jan 05, 2021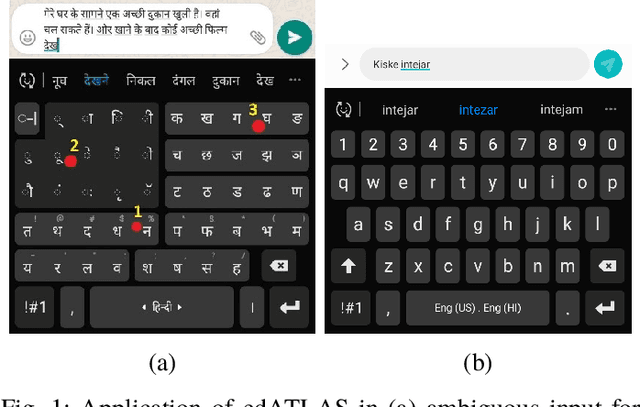
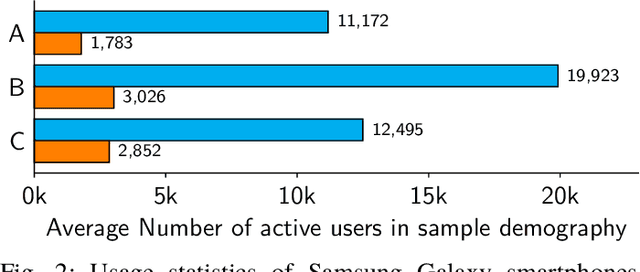
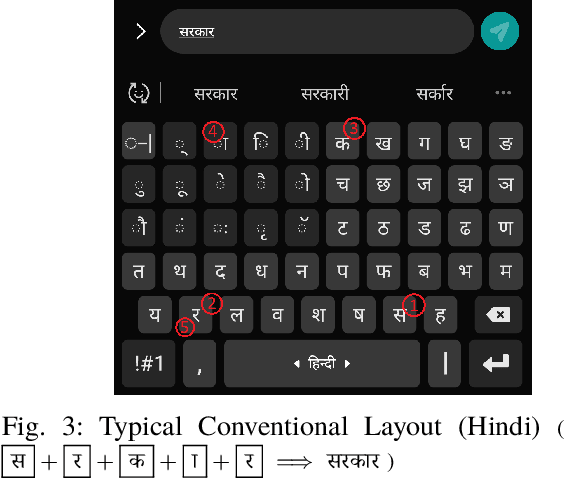
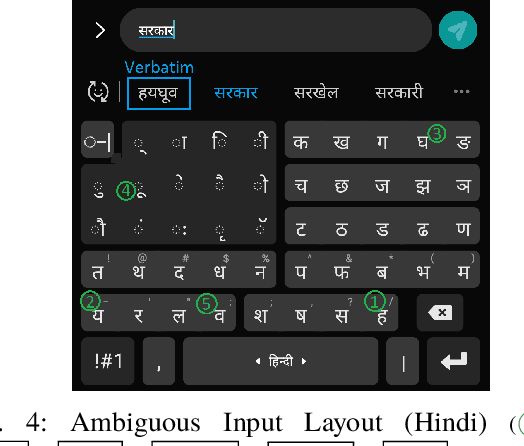
Abstract:Abugida refers to a phonogram writing system where each syllable is represented using a single consonant or typographic ligature, along with a default vowel or optional diacritic(s) to denote other vowels. However, texting in these languages has some unique challenges in spite of the advent of devices with soft keyboard supporting custom key layouts. The number of characters in these languages is large enough to require characters to be spread over multiple views in the layout. Having to switch between views many times to type a single word hinders the natural thought process. This prevents popular usage of native keyboard layouts. On the other hand, supporting romanized scripts (native words transcribed using Latin characters) with language model based suggestions is also set back by the lack of uniform romanization rules. To this end, we propose a disambiguation algorithm and showcase its usefulness in two novel mutually non-exclusive input methods for languages natively using the abugida writing system: (a) disambiguation of ambiguous input for abugida scripts, and (b) disambiguation of word variants in romanized scripts. We benchmark these approaches using public datasets, and show an improvement in typing speed by 19.49%, 25.13%, and 14.89%, in Hindi, Bengali, and Thai, respectively, using Ambiguous Input, owing to the human ease of locating keys combined with the efficiency of our inference method. Our Word Variant Disambiguation (WDA) maps valid variants of romanized words, previously treated as Out-of-Vocab, to a vocabulary of 100k words with high accuracy, leading to an increase in Error Correction F1 score by 10.03% and Next Word Prediction (NWP) by 62.50% on average.
LiteMuL: A Lightweight On-Device Sequence Tagger using Multi-task Learning
Dec 15, 2020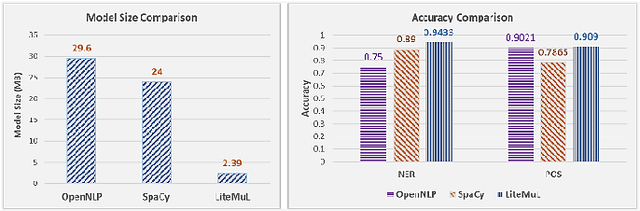
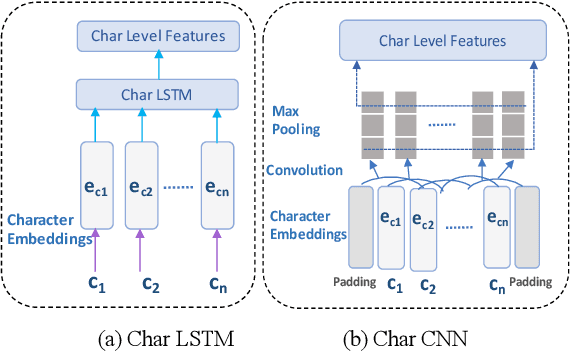
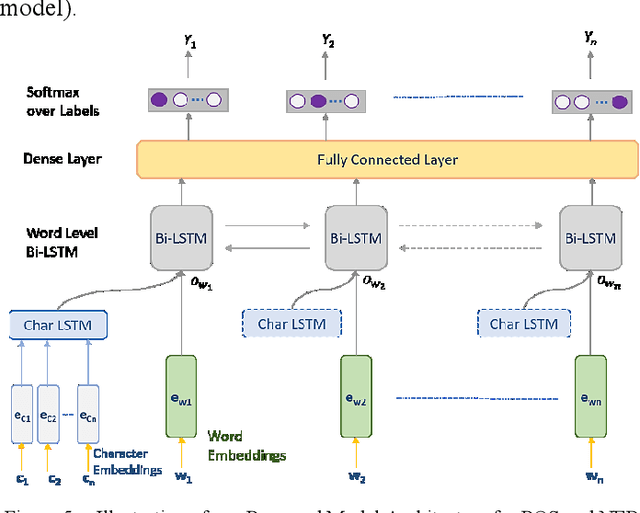
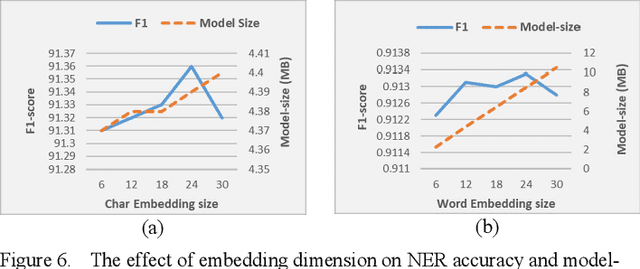
Abstract:Named entity detection and Parts-of-speech tagging are the key tasks for many NLP applications. Although the current state of the art methods achieved near perfection for long, formal, structured text there are hindrances in deploying these models on memory-constrained devices such as mobile phones. Furthermore, the performance of these models is degraded when they encounter short, informal, and casual conversations. To overcome these difficulties, we present LiteMuL - a lightweight on-device sequence tagger that can efficiently process the user conversations using a Multi-Task Learning (MTL) approach. To the best of our knowledge, the proposed model is the first on-device MTL neural model for sequence tagging. Our LiteMuL model is about 2.39 MB in size and achieved an accuracy of 0.9433 (for NER), 0.9090 (for POS) on the CoNLL 2003 dataset. The proposed LiteMuL not only outperforms the current state of the art results but also surpasses the results of our proposed on-device task-specific models, with accuracy gains of up to 11% and model-size reduction by 50%-56%. Our model is competitive with other MTL approaches for NER and POS tasks while outshines them with a low memory footprint. We also evaluated our model on custom-curated user conversations and observed impressive results.
EmpLite: A Lightweight Sequence Labeling Model for Emphasis Selection of Short Texts
Dec 15, 2020
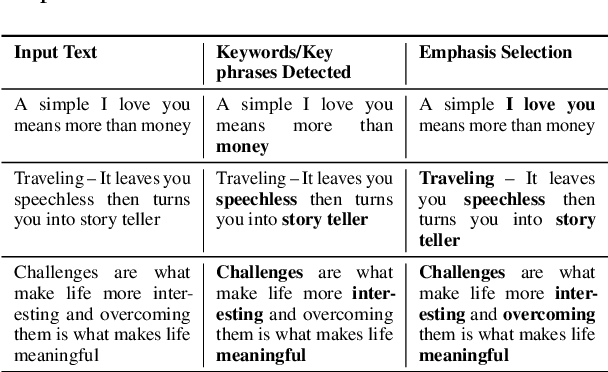
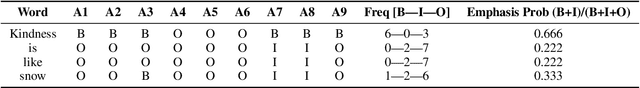
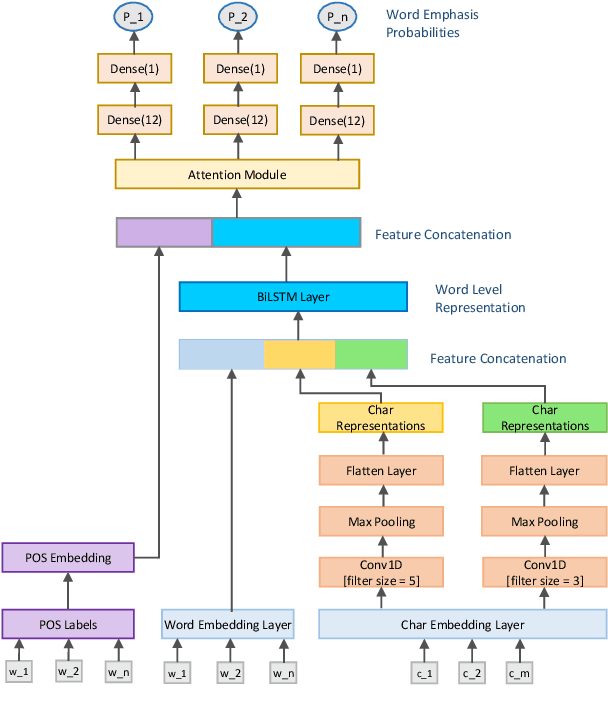
Abstract:Word emphasis in textual content aims at conveying the desired intention by changing the size, color, typeface, style (bold, italic, etc.), and other typographical features. The emphasized words are extremely helpful in drawing the readers' attention to specific information that the authors wish to emphasize. However, performing such emphasis using a soft keyboard for social media interactions is time-consuming and has an associated learning curve. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to automate the emphasis word detection on short written texts. To the best of our knowledge, this work presents the first lightweight deep learning approach for smartphone deployment of emphasis selection. Experimental results show that our approach achieves comparable accuracy at a much lower model size than existing models. Our best lightweight model has a memory footprint of 2.82 MB with a matching score of 0.716 on SemEval-2020 public benchmark dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge