Banafsheh Rekabdar
LLM-Enhanced Reinforcement Learning for Time Series Anomaly Detection
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Detecting anomalies in time series data is crucial for finance, healthcare, sensor networks, and industrial monitoring applications. However, time series anomaly detection often suffers from sparse labels, complex temporal patterns, and costly expert annotation. We propose a unified framework that integrates Large Language Model (LLM)-based potential functions for reward shaping with Reinforcement Learning (RL), Variational Autoencoder (VAE)-enhanced dynamic reward scaling, and active learning with label propagation. An LSTM-based RL agent leverages LLM-derived semantic rewards to guide exploration, while VAE reconstruction errors add unsupervised anomaly signals. Active learning selects the most uncertain samples, and label propagation efficiently expands labeled data. Evaluations on Yahoo-A1 and SMD benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art detection accuracy under limited labeling budgets and operates effectively in data-constrained settings. This study highlights the promise of combining LLMs with RL and advanced unsupervised techniques for robust, scalable anomaly detection in real-world applications.
Hierarchical Vector-Quantized Latents for Perceptual Low-Resolution Video Compression
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:The exponential growth of video traffic has placed increasing demands on bandwidth and storage infrastructure, particularly for content delivery networks (CDNs) and edge devices. While traditional video codecs like H.264 and HEVC achieve high compression ratios, they are designed primarily for pixel-domain reconstruction and lack native support for machine learning-centric latent representations, limiting their integration into deep learning pipelines. In this work, we present a Multi-Scale Vector Quantized Variational Autoencoder (MS-VQ-VAE) designed to generate compact, high-fidelity latent representations of low-resolution video, suitable for efficient storage, transmission, and client-side decoding. Our architecture extends the VQ-VAE-2 framework to a spatiotemporal setting, introducing a two-level hierarchical latent structure built with 3D residual convolutions. The model is lightweight (approximately 18.5M parameters) and optimized for 64x64 resolution video clips, making it appropriate for deployment on edge devices with constrained compute and memory resources. To improve perceptual reconstruction quality, we incorporate a perceptual loss derived from a pre-trained VGG16 network. Trained on the UCF101 dataset using 2-second video clips (32 frames at 16 FPS), on the test set we achieve 25.96 dB PSNR and 0.8375 SSIM. On validation, our model improves over the single-scale baseline by 1.41 dB PSNR and 0.0248 SSIM. The proposed framework is well-suited for scalable video compression in bandwidth-sensitive scenarios, including real-time streaming, mobile video analytics, and CDN-level storage optimization.
Dynamic Reward Scaling for Multivariate Time Series Anomaly Detection: A VAE-Enhanced Reinforcement Learning Approach
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:Detecting anomalies in multivariate time series is essential for monitoring complex industrial systems, where high dimensionality, limited labeled data, and subtle dependencies between sensors cause significant challenges. This paper presents a deep reinforcement learning framework that combines a Variational Autoencoder (VAE), an LSTM-based Deep Q-Network (DQN), dynamic reward shaping, and an active learning module to address these issues in a unified learning framework. The main contribution is the implementation of Dynamic Reward Scaling for Multivariate Time Series Anomaly Detection (DRSMT), which demonstrates how each component enhances the detection process. The VAE captures compact latent representations and reduces noise. The DQN enables adaptive, sequential anomaly classification, and the dynamic reward shaping balances exploration and exploitation during training by adjusting the importance of reconstruction and classification signals. In addition, active learning identifies the most uncertain samples for labeling, reducing the need for extensive manual supervision. Experiments on two multivariate benchmarks, namely Server Machine Dataset (SMD) and Water Distribution Testbed (WADI), show that the proposed method outperforms existing baselines in F1-score and AU-PR. These results highlight the effectiveness of combining generative modeling, reinforcement learning, and selective supervision for accurate and scalable anomaly detection in real-world multivariate systems.
Dynamic and Adaptive Feature Generation with LLM
Jun 04, 2024



Abstract:The representation of feature space is a crucial environment where data points get vectorized and embedded for upcoming modeling. Thus the efficacy of machine learning (ML) algorithms is closely related to the quality of feature engineering. As one of the most important techniques, feature generation transforms raw data into an optimized feature space conducive to model training and further refines the space. Despite the advancements in automated feature engineering and feature generation, current methodologies often suffer from three fundamental issues: lack of explainability, limited applicability, and inflexible strategy. These shortcomings frequently hinder and limit the deployment of ML models across varied scenarios. Our research introduces a novel approach adopting large language models (LLMs) and feature-generating prompts to address these challenges. We propose a dynamic and adaptive feature generation method that enhances the interpretability of the feature generation process. Our approach broadens the applicability across various data types and tasks and draws advantages over strategic flexibility. A broad range of experiments showcases that our approach is significantly superior to existing methods.
A Survey of AI Music Generation Tools and Models
Aug 24, 2023Abstract:In this work, we provide a comprehensive survey of AI music generation tools, including both research projects and commercialized applications. To conduct our analysis, we classified music generation approaches into three categories: parameter-based, text-based, and visual-based classes. Our survey highlights the diverse possibilities and functional features of these tools, which cater to a wide range of users, from regular listeners to professional musicians. We observed that each tool has its own set of advantages and limitations. As a result, we have compiled a comprehensive list of these factors that should be considered during the tool selection process. Moreover, our survey offers critical insights into the underlying mechanisms and challenges of AI music generation.
Predictive Probability Path Planning Model For Dynamic Environments
Jul 29, 2020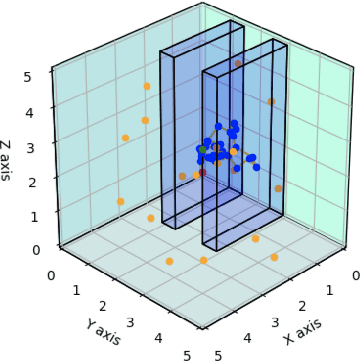
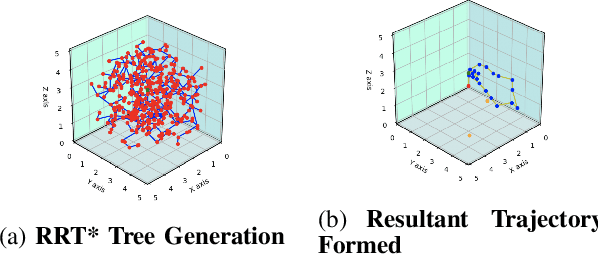
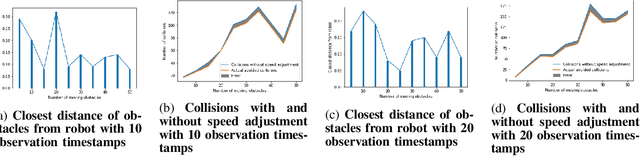
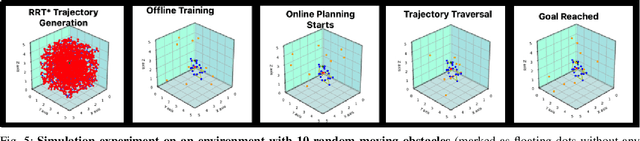
Abstract:Path planning in dynamic environments is essential to high-risk applications such as unmanned aerial vehicles, self-driving cars, and autonomous underwater vehicles. In this paper, we generate collision-free trajectories for a robot within any given environment with temporal and spatial uncertainties caused due to randomly moving obstacles. We use two Poisson distributions to model the movements of obstacles across the generated trajectory of a robot in both space and time to determine the probability of collision with an obstacle. Measures are taken to avoid an obstacle by intelligently manipulating the speed of the robot at space-time intervals where a larger number of obstacles intersect the trajectory of the robot. Our method potentially reduces the use of computationally expensive collision detection libraries. Based on our experiments, there has been a significant improvement over existing methods in terms of safety, accuracy, execution time and computational cost. Our results show a high level of accuracy between the predicted and actual number of collisions with moving obstacles.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge