Bahador Saket
Georgia Tech
Towards Leveraging Large Language Models for Automated Medical Q&A Evaluation
Sep 03, 2024



Abstract:This paper explores the potential of using Large Language Models (LLMs) to automate the evaluation of responses in medical Question and Answer (Q\&A) systems, a crucial form of Natural Language Processing. Traditionally, human evaluation has been indispensable for assessing the quality of these responses. However, manual evaluation by medical professionals is time-consuming and costly. Our study examines whether LLMs can reliably replicate human evaluations by using questions derived from patient data, thereby saving valuable time for medical experts. While the findings suggest promising results, further research is needed to address more specific or complex questions that were beyond the scope of this initial investigation.
Visual Analytics for Automated Model Discovery
Oct 02, 2018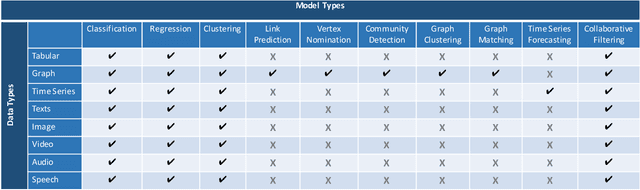
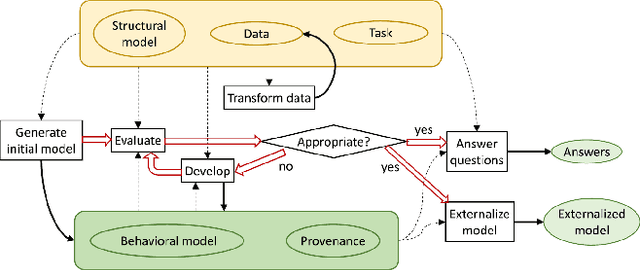
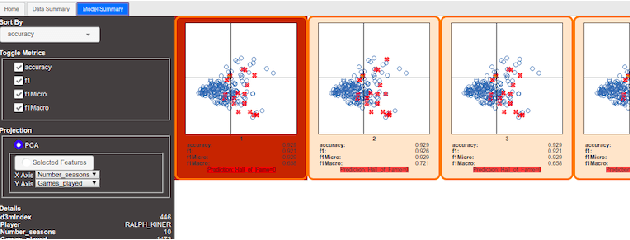
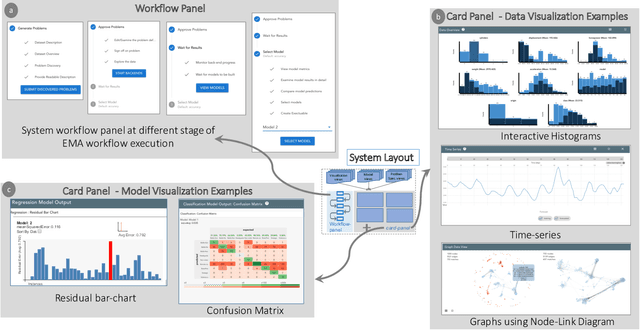
Abstract:A recent advancement in the machine learning community is the development of automated machine learning (autoML) systems, such as autoWeka or Google's Cloud AutoML, which automate the model selection and tuning process. However, while autoML tools give users access to arbitrarily complex models, they typically return those models with little context or explanation. Visual analytics can be helpful in giving a user of autoML insight into their data, and a more complete understanding of the models discovered by autoML, including differences between multiple models. In this work, we describe how visual analytics for automated model discovery differs from traditional visual analytics for machine learning. First, we propose an architecture based on an extension of existing visual analytics frameworks. Then we describe a prototype system Snowcat, developed according to the presented framework and architecture, that aids users in generating models for a diverse set of data and modeling tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge