Bach Phan Tat
MultiMed-ST: Large-scale Many-to-many Multilingual Medical Speech Translation
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:Multilingual speech translation (ST) in the medical domain enhances patient care by enabling efficient communication across language barriers, alleviating specialized workforce shortages, and facilitating improved diagnosis and treatment, particularly during pandemics. In this work, we present the first systematic study on medical ST, to our best knowledge, by releasing MultiMed-ST, a large-scale ST dataset for the medical domain, spanning all translation directions in five languages: Vietnamese, English, German, French, Traditional Chinese and Simplified Chinese, together with the models. With 290,000 samples, our dataset is the largest medical machine translation (MT) dataset and the largest many-to-many multilingual ST among all domains. Secondly, we present the most extensive analysis study in ST research to date, including: empirical baselines, bilingual-multilingual comparative study, end-to-end vs. cascaded comparative study, task-specific vs. multi-task sequence-to-sequence (seq2seq) comparative study, code-switch analysis, and quantitative-qualitative error analysis. All code, data, and models are available online: https://github.com/leduckhai/MultiMed-ST.
MultiMed: Multilingual Medical Speech Recognition via Attention Encoder Decoder
Sep 21, 2024



Abstract:Multilingual automatic speech recognition (ASR) in the medical domain serves as a foundational task for various downstream applications such as speech translation, spoken language understanding, and voice-activated assistants. This technology enhances patient care by enabling efficient communication across language barriers, alleviating specialized workforce shortages, and facilitating improved diagnosis and treatment, particularly during pandemics. In this work, we introduce MultiMed, a collection of small-to-large end-to-end ASR models for the medical domain, spanning five languages: Vietnamese, English, German, French, and Mandarin Chinese, together with the corresponding real-world ASR dataset. To our best knowledge, MultiMed stands as the largest and the first multilingual medical ASR dataset, in terms of total duration, number of speakers, diversity of diseases, recording conditions, speaker roles, unique medical terms, accents, and ICD-10 codes. Secondly, we establish the empirical baselines, present the first reproducible study of multilinguality in medical ASR, conduct a layer-wise ablation study for end-to-end ASR training, and provide the first linguistic analysis for multilingual medical ASR. All code, data, and models are available online https://github.com/leduckhai/MultiMed/tree/master/MultiMed
Sentiment Reasoning for Healthcare
Jul 24, 2024
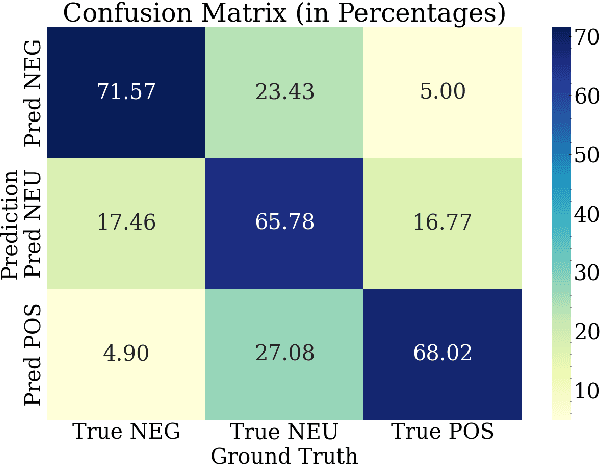


Abstract:Transparency in AI decision-making is crucial in healthcare due to the severe consequences of errors, and this is important for building trust among AI and users in sentiment analysis task. Incorporating reasoning capabilities helps Large Language Models (LLMs) understand human emotions within broader contexts, handle nuanced and ambiguous language, and infer underlying sentiments that may not be explicitly stated. In this work, we introduce a new task - Sentiment Reasoning - for both speech and text modalities, along with our proposed multimodal multitask framework and dataset. Our study showed that rationale-augmented training enhances model performance in sentiment classification across both human transcript and ASR settings. Also, we found that the generated rationales typically exhibit different vocabularies compared to human-generated rationales, but maintain similar semantics. All code, data (English-translated and Vietnamese) and models are published online: https://github.com/leduckhai/MultiMed
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge