Asif Raza
Embracing Language Inclusivity and Diversity in CLIP through Continual Language Learning
Jan 30, 2024
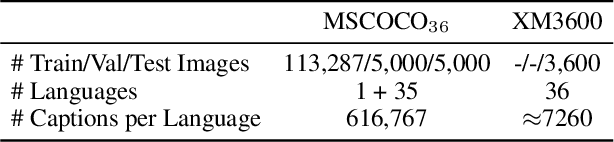
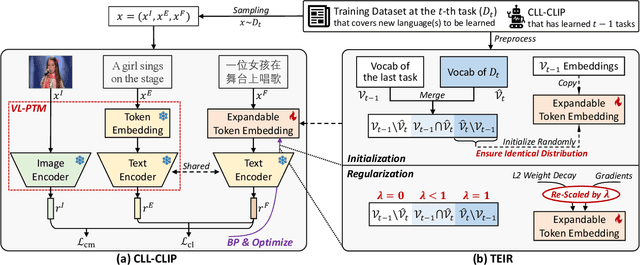
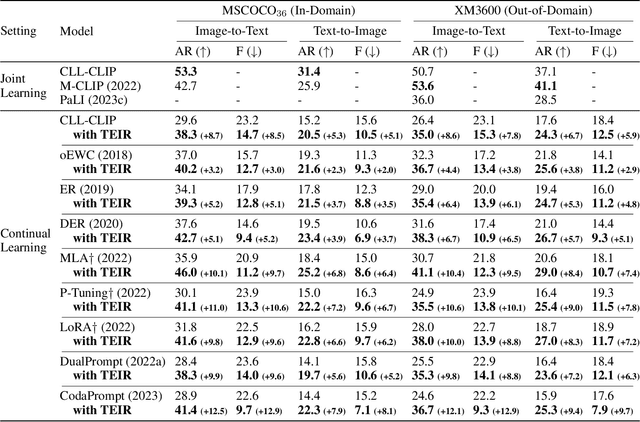
Abstract:While vision-language pre-trained models (VL-PTMs) have advanced multimodal research in recent years, their mastery in a few languages like English restricts their applicability in broader communities. To this end, there is an increasing interest in developing multilingual VL models via a joint-learning setup, which, however, could be unrealistic due to expensive costs and data availability. In this work, we propose to extend VL-PTMs' language capacity by continual language learning (CLL), where a model needs to update its linguistic knowledge incrementally without suffering from catastrophic forgetting (CF). We begin our study by introducing a model dubbed CLL-CLIP, which builds upon CLIP, a prevailing VL-PTM that has acquired image-English text alignment. Specifically, CLL-CLIP contains an expandable token embedding layer to handle linguistic differences. It solely trains token embeddings to improve memory stability and is optimized under cross-modal and cross-lingual objectives to learn the alignment between images and multilingual texts. To alleviate CF raised by covariate shift and lexical overlap, we further propose a novel approach that ensures the identical distribution of all token embeddings during initialization and regularizes token embedding learning during training. We construct a CLL benchmark covering 36 languages based on MSCOCO and XM3600 datasets and then evaluate multilingual image-text retrieval performance. Extensive experiments verify the effectiveness of CLL-CLIP and show that our approach can boost CLL-CLIP, e.g., by 6.7% in text-to-image average Recall@1 on XM3600, and improve various state-of-the-art methods consistently. Our code and data are available at \url{https://github.com/yangbang18/CLFM}.
Customizing General-Purpose Foundation Models for Medical Report Generation
Jun 09, 2023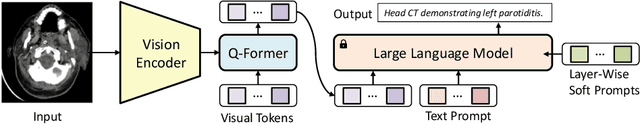
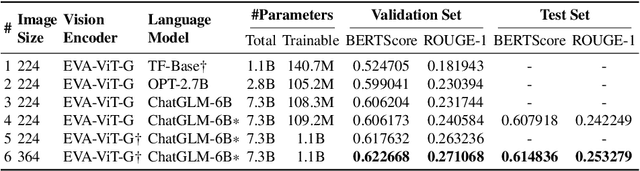

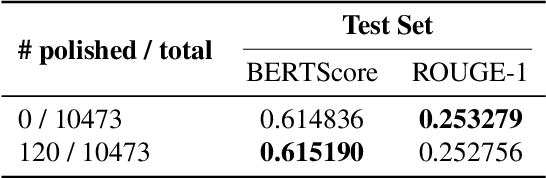
Abstract:Medical caption prediction which can be regarded as a task of medical report generation (MRG), requires the automatic generation of coherent and accurate captions for the given medical images. However, the scarcity of labelled medical image-report pairs presents great challenges in the development of deep and large-scale neural networks capable of harnessing the potential artificial general intelligence power like large language models (LLMs). In this work, we propose customizing off-the-shelf general-purpose large-scale pre-trained models, i.e., foundation models (FMs), in computer vision and natural language processing with a specific focus on medical report generation. Specifically, following BLIP-2, a state-of-the-art vision-language pre-training approach, we introduce our encoder-decoder-based MRG model. This model utilizes a lightweight query Transformer to connect two FMs: the giant vision Transformer EVA-ViT-g and a bilingual LLM trained to align with human intentions (referred to as ChatGLM-6B). Furthermore, we conduct ablative experiments on the trainable components of the model to identify the crucial factors for effective transfer learning. Our findings demonstrate that unfreezing EVA-ViT-g to learn medical image representations, followed by parameter-efficient training of ChatGLM-6B to capture the writing styles of medical reports, is essential for achieving optimal results. Our best attempt (PCLmed Team) achieved the 4th and the 2nd, respectively, out of 13 participating teams, based on the BERTScore and ROUGE-1 metrics, in the ImageCLEFmedical Caption 2023 Caption Prediction Task competition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge