Ashutosh Kumar Singh
MAIDS: Malicious Agent Identification-based Data Security Model for Cloud Environments
Dec 19, 2024Abstract:With the vigorous development of cloud computing, most organizations have shifted their data and applications to the cloud environment for storage, computation, and sharing purposes. During storage and data sharing across the participating entities, a malicious agent may gain access to outsourced data from the cloud environment. A malicious agent is an entity that deliberately breaches the data. This information accessed might be misused or revealed to unauthorized parties. Therefore, data protection and prediction of malicious agents have become a demanding task that needs to be addressed appropriately. To deal with this crucial and challenging issue, this paper presents a Malicious Agent Identification-based Data Security (MAIDS) Model which utilizes XGBoost machine learning classification algorithm for securing data allocation and communication among different participating entities in the cloud system. The proposed model explores and computes intended multiple security parameters associated with online data communication or transactions. Correspondingly, a security-focused knowledge database is produced for developing the XGBoost Classifier-based Malicious Agent Prediction (XC-MAP) unit. Unlike the existing approaches, which only identify malicious agents after data leaks, MAIDS proactively identifies malicious agents by examining their eligibility for respective data access. In this way, the model provides a comprehensive solution to safeguard crucial data from both intentional and non-intentional breaches, by granting data to authorized agents only by evaluating the agents behavior and predicting the malicious agent before granting data.
* 28 pages, 10 figures
A Global Medical Data Security and Privacy Preserving Standards Identification Framework for Electronic Healthcare Consumers
Oct 04, 2024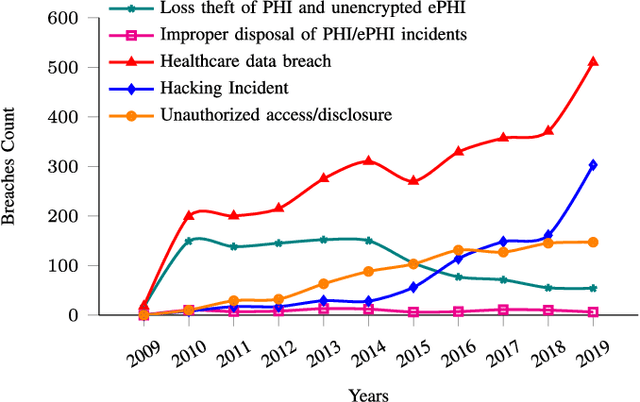
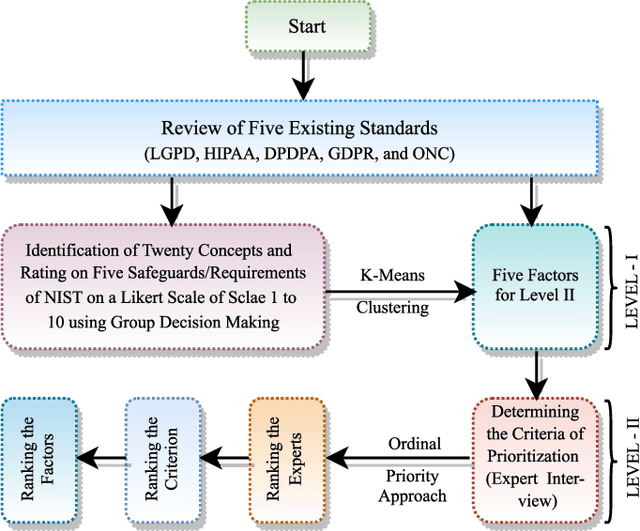
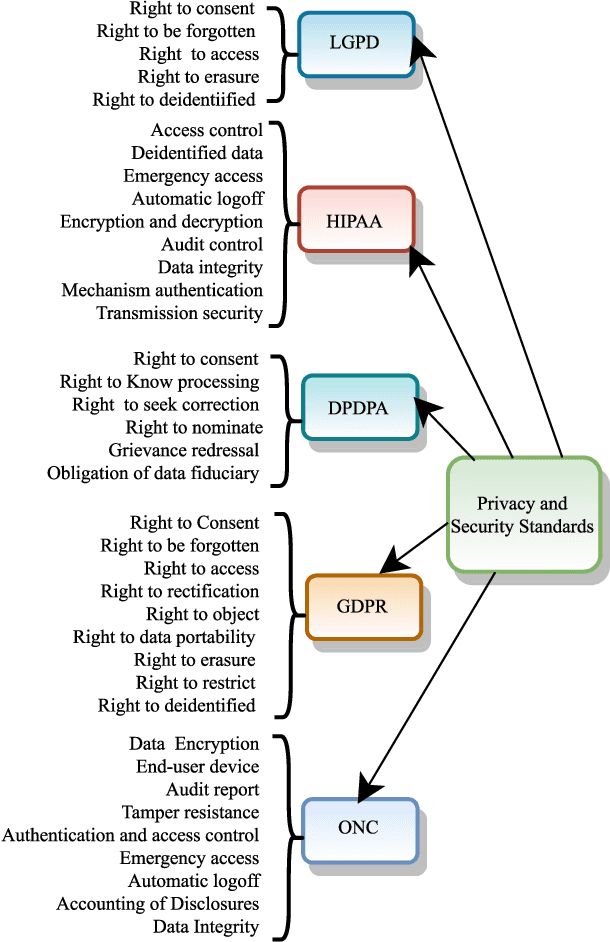
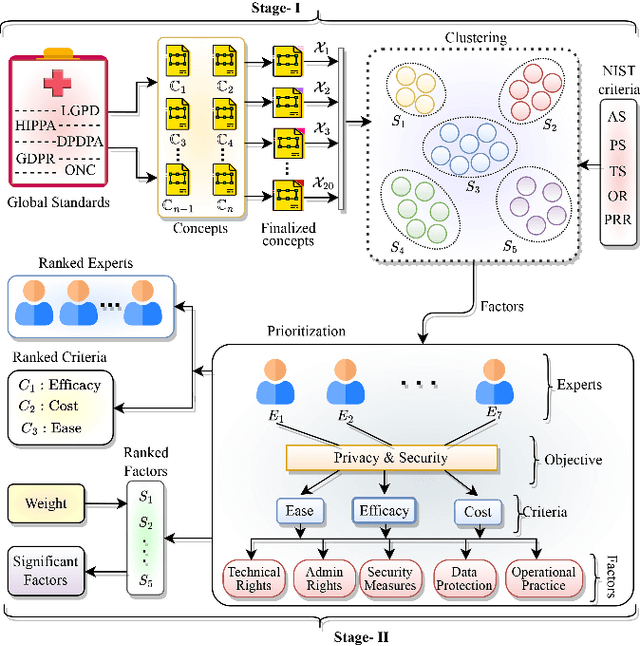
Abstract:Electronic Health Records (EHR) are crucial for the success of digital healthcare, with a focus on putting consumers at the center of this transformation. However, the digitalization of healthcare records brings along security and privacy risks for personal data. The major concern is that different countries have varying standards for the security and privacy of medical data. This paper proposed a novel and comprehensive framework to standardize these rules globally, bringing them together on a common platform. To support this proposal, the study reviews existing literature to understand the research interest in this issue. It also examines six key laws and standards related to security and privacy, identifying twenty concepts. The proposed framework utilized K-means clustering to categorize these concepts and identify five key factors. Finally, an Ordinal Priority Approach is applied to determine the preferred implementation of these factors in the context of EHRs. The proposed study provides a descriptive then prescriptive framework for the implementation of privacy and security in the context of electronic health records. Therefore, the findings of the proposed framework are useful for professionals and policymakers in improving the security and privacy associated with EHRs.
A smart resource management mechanism with trust access control for cloud computing environment
Dec 10, 2022Abstract:The core of the computer business now offers subscription-based on-demand services with the help of cloud computing. We may now share resources among multiple users by using virtualization, which creates a virtual instance of a computer system running in an abstracted hardware layer. It provides infinite computing capabilities through its massive cloud datacenters, in contrast to early distributed computing models, and has been incredibly popular in recent years because to its continually growing infrastructure, user base, and hosted data volume. This article suggests a conceptual framework for a workload management paradigm in cloud settings that is both safe and performance-efficient. A resource management unit is used in this paradigm for energy and performing virtual machine allocation with efficiency, assuring the safe execution of users' applications, and protecting against data breaches brought on by unauthorised virtual machine access real-time. A secure virtual machine management unit controls the resource management unit and is created to produce data on unlawful access or intercommunication. Additionally, a workload analyzer unit works simultaneously to estimate resource consumption data to help the resource management unit be more effective during virtual machine allocation. The suggested model functions differently to effectively serve the same objective, including data encryption and decryption prior to transfer, usage of trust access mechanism to prevent unauthorised access to virtual machines, which creates extra computational cost overhead.
A Privacy-Preserving Outsourced Data Model in Cloud Environment
Nov 24, 2022Abstract:Nowadays, more and more machine learning applications, such as medical diagnosis, online fraud detection, email spam filtering, etc., services are provided by cloud computing. The cloud service provider collects the data from the various owners to train or classify the machine learning system in the cloud environment. However, multiple data owners may not entirely rely on the cloud platform that a third party engages. Therefore, data security and privacy problems are among the critical hindrances to using machine learning tools, particularly with multiple data owners. In addition, unauthorized entities can detect the statistical input data and infer the machine learning model parameters. Therefore, a privacy-preserving model is proposed, which protects the privacy of the data without compromising machine learning efficiency. In order to protect the data of data owners, the epsilon-differential privacy is used, and fog nodes are used to address the problem of the lower bandwidth and latency in this proposed scheme. The noise is produced by the epsilon-differential mechanism, which is then added to the data. Moreover, the noise is injected at the data owner site to protect the owners data. Fog nodes collect the noise-added data from the data owners, then shift it to the cloud platform for storage, computation, and performing the classification tasks purposes.
PCA-RF: An Efficient Parkinson's Disease Prediction Model based on Random Forest Classification
Mar 21, 2022



Abstract:In this modern era of overpopulation disease prediction is a crucial step in diagnosing various diseases at an early stage. With the advancement of various machine learning algorithms, the prediction has become quite easy. However, the complex and the selection of an optimal machine learning technique for the given dataset greatly affects the accuracy of the model. A large amount of datasets exists globally but there is no effective use of it due to its unstructured format. Hence, a lot of different techniques are available to extract something useful for the real world to implement. Therefore, accuracy becomes a major metric in evaluating the model. In this paper, a disease prediction approach is proposed that implements a random forest classifier on Parkinson's disease. We compared the accuracy of this model with the Principal Component Analysis (PCA) applied Artificial Neural Network (ANN) model and captured a visible difference. The model secured a significant accuracy of up to 90%.
MLRM: A Multiple Linear Regression based Model for Average Temperature Prediction of A Day
Mar 11, 2022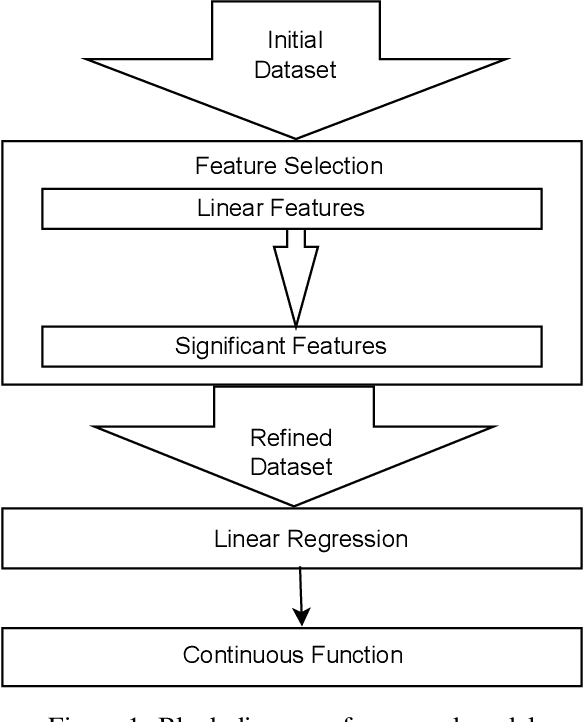
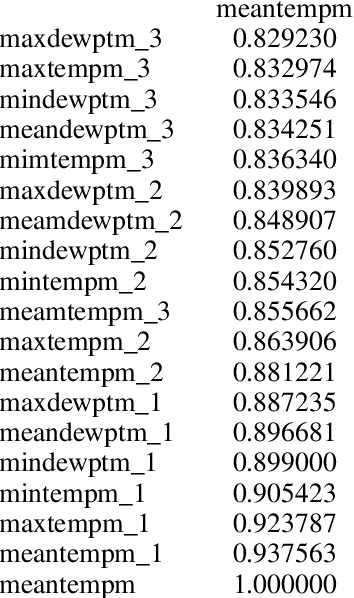
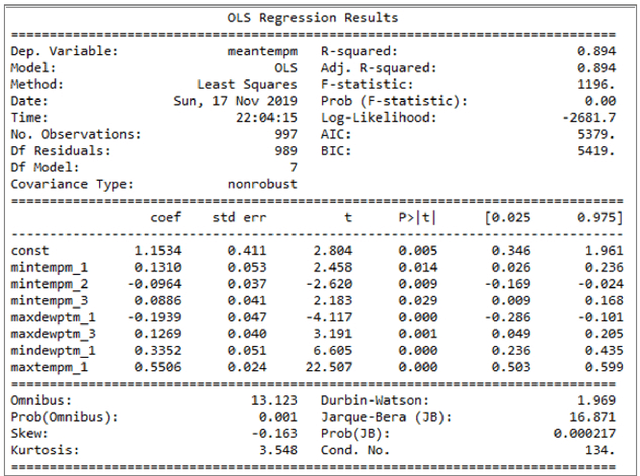
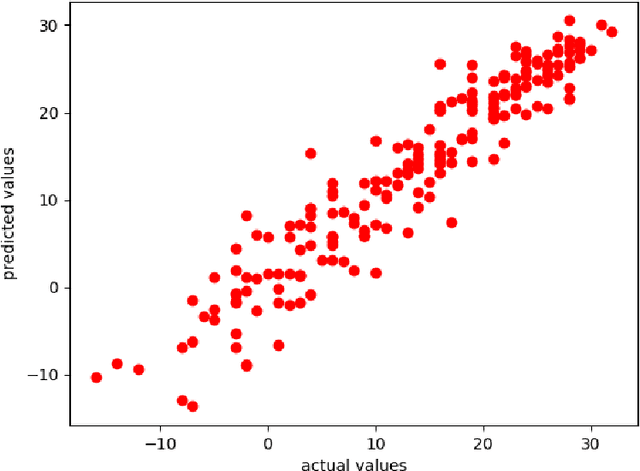
Abstract:Weather is a phenomenon that affects everything and everyone around us on a daily basis. Weather prediction has been an important point of study for decades as researchers have tried to predict the weather and climatic changes using traditional meteorological techniques. With the advent of modern technologies and computing power, we can do so with the help of machine learning techniques. We aim to predict the weather of an area using past meteorological data and features using the Multiple Linear Regression Model. The performance of the model is evaluated and a conclusion is drawn. The model is successfully able to predict the average temperature of a day with an error of 2.8 degrees Celsius.
HiSA-SMFM: Historical and Sentiment Analysis based Stock Market Forecasting Model
Mar 10, 2022



Abstract:One of the pillars to build a country's economy is the stock market. Over the years, people are investing in stock markets to earn as much profit as possible from the amount of money that they possess. Hence, it is vital to have a prediction model which can accurately predict future stock prices. With the help of machine learning, it is not an impossible task as the various machine learning techniques if modeled properly may be able to provide the best prediction values. This would enable the investors to decide whether to buy, sell or hold the share. The aim of this paper is to predict the future of the financial stocks of a company with improved accuracy. In this paper, we have proposed the use of historical as well as sentiment data to efficiently predict stock prices by applying LSTM. It has been found by analyzing the existing research in the area of sentiment analysis that there is a strong correlation between the movement of stock prices and the publication of news articles. Therefore, in this paper, we have integrated these factors to predict the stock prices more accurately.
A study on Machine Learning Approaches for Player Performance and Match Results Prediction
Aug 23, 2021Abstract:Cricket is unarguably one of the most popular sports in the world. Predicting the outcome of a cricket match has become a fundamental problem as we are advancing in the field of machine learning. Multiple researchers have tried to predict the outcome of a cricket match or a tournament, or to predict the performance of players during a match, or to predict the players who should be selected as per their current performance, form, morale, etc. using machine learning and artificial intelligence techniques keeping in mind extensive detailing, features, and parameters. We discuss some of these techniques along with a brief comparison among these techniques.
Credit Card Fraud Detection using Machine Learning: A Study
Aug 23, 2021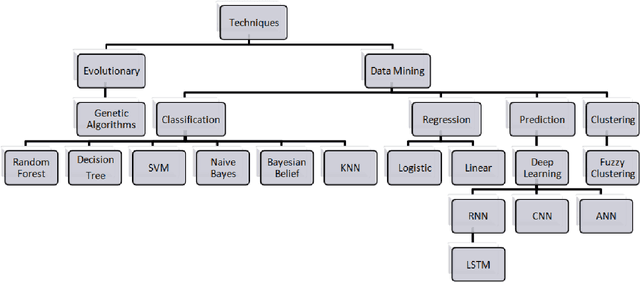
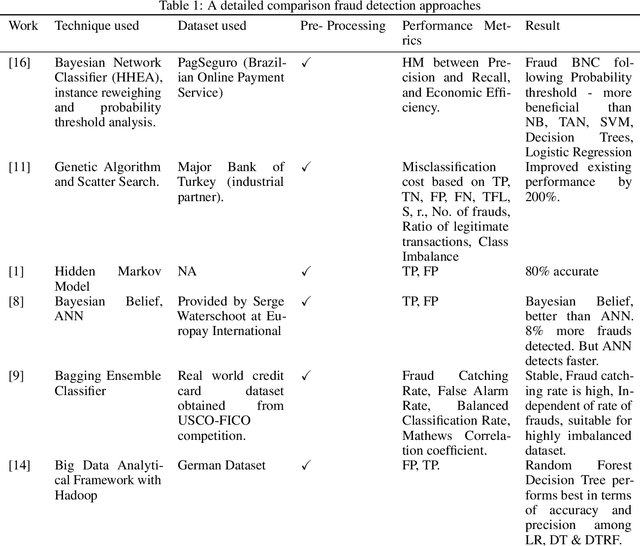
Abstract:As the world is rapidly moving towards digitization and money transactions are becoming cashless, the use of credit cards has rapidly increased. The fraud activities associated with it have also been increasing which leads to a huge loss to the financial institutions. Therefore, we need to analyze and detect the fraudulent transaction from the non-fraudulent ones. In this paper, we present a comprehensive review of various methods used to detect credit card fraud. These methodologies include Hidden Markov Model, Decision Trees, Logistic Regression, Support Vector Machines (SVM), Genetic algorithm, Neural Networks, Random Forests, Bayesian Belief Network. A comprehensive analysis of various techniques is presented. We conclude the paper with the pros and cons of the same as stated in the respective papers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge