Vinaytosh Mishra
A Global Cybersecurity Standardization Framework for Healthcare Informatics
Oct 06, 2024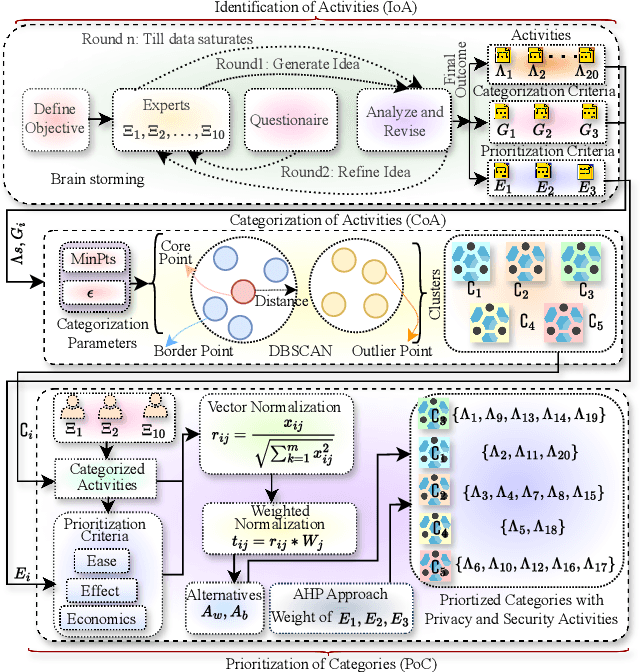
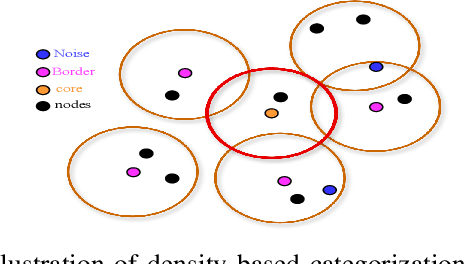
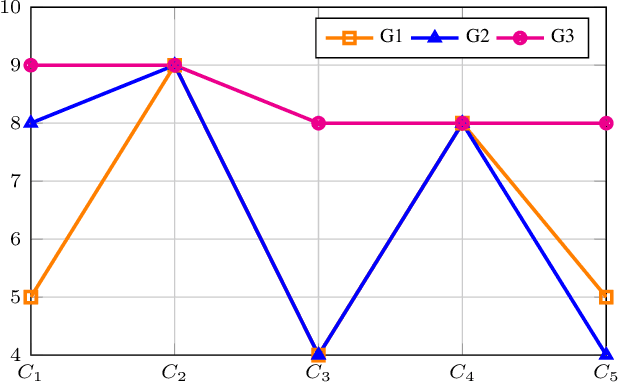
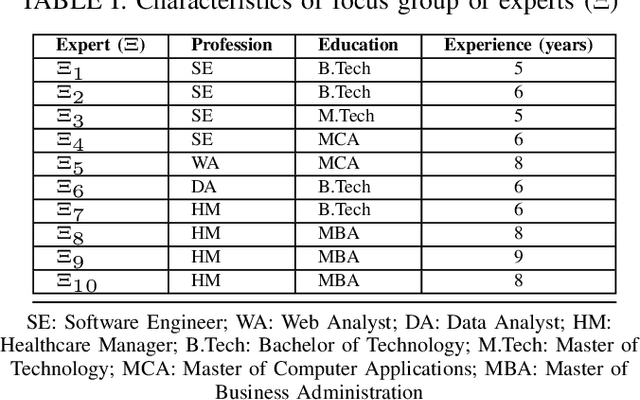
Abstract:Healthcare has witnessed an increased digitalization in the post-COVID world. Technologies such as the medical internet of things and wearable devices are generating a plethora of data available on the cloud anytime from anywhere. This data can be analyzed using advanced artificial intelligence techniques for diagnosis, prognosis, or even treatment of disease. This advancement comes with a major risk to protecting and securing protected health information (PHI). The prevailing regulations for preserving PHI are neither comprehensive nor easy to implement. The study first identifies twenty activities crucial for privacy and security, then categorizes them into five homogeneous categories namely: $\complement_1$ (Policy and Compliance Management), $\complement_2$ (Employee Training and Awareness), $\complement_3$ (Data Protection and Privacy Control), $\complement_4$ (Monitoring and Response), and $\complement_5$ (Technology and Infrastructure Security) and prioritizes these categories to provide a framework for the implementation of privacy and security in a wise manner. The framework utilized the Delphi Method to identify activities, criteria for categorization, and prioritization. Categorization is based on the Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (DBSCAN), and prioritization is performed using a Technique for Order of Preference by Similarity to the Ideal Solution (TOPSIS). The outcomes conclude that $\complement_3$ activities should be given first preference in implementation and followed by $\complement_1$ and $\complement_2$ activities. Finally, $\complement_4$ and $\complement_5$ should be implemented. The prioritized view of identified clustered healthcare activities related to security and privacy, are useful for healthcare policymakers and healthcare informatics professionals.
A Global Medical Data Security and Privacy Preserving Standards Identification Framework for Electronic Healthcare Consumers
Oct 04, 2024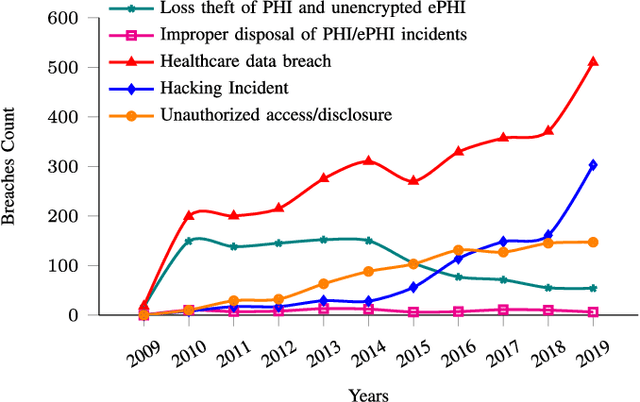
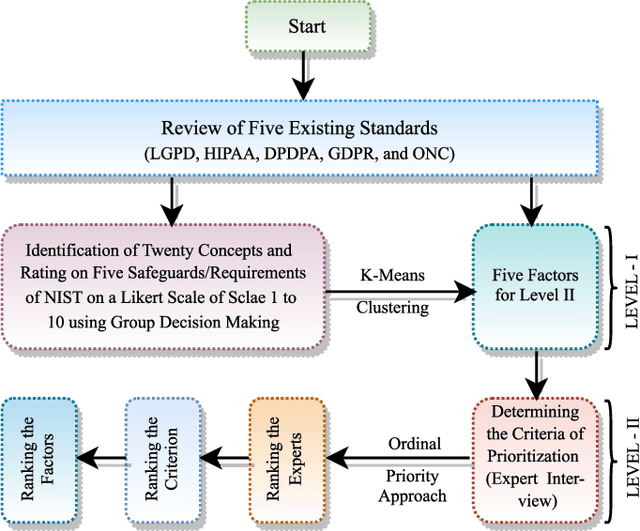
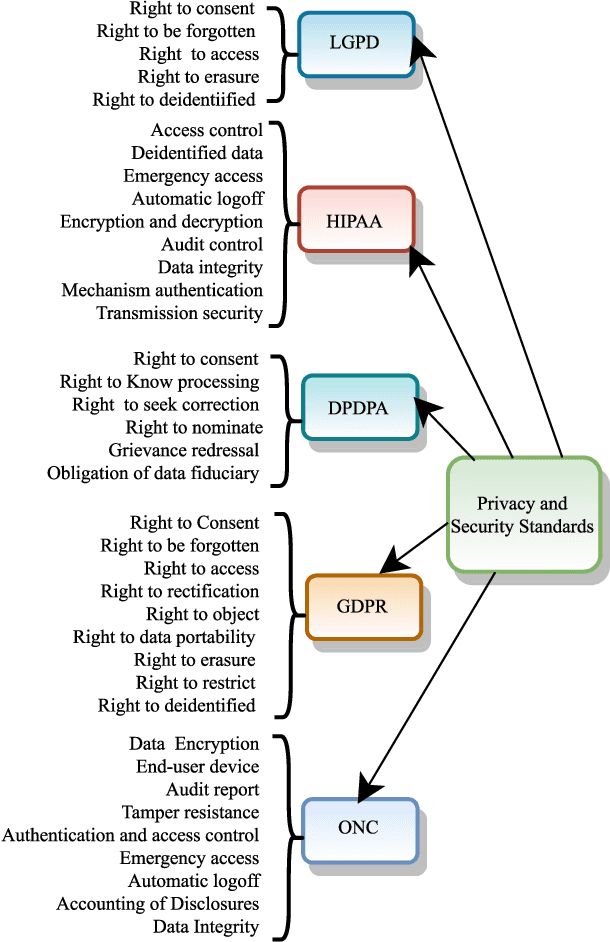
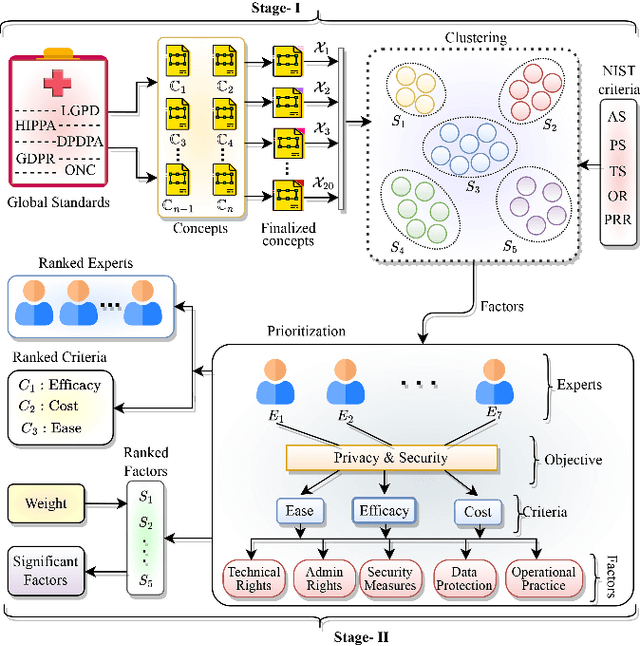
Abstract:Electronic Health Records (EHR) are crucial for the success of digital healthcare, with a focus on putting consumers at the center of this transformation. However, the digitalization of healthcare records brings along security and privacy risks for personal data. The major concern is that different countries have varying standards for the security and privacy of medical data. This paper proposed a novel and comprehensive framework to standardize these rules globally, bringing them together on a common platform. To support this proposal, the study reviews existing literature to understand the research interest in this issue. It also examines six key laws and standards related to security and privacy, identifying twenty concepts. The proposed framework utilized K-means clustering to categorize these concepts and identify five key factors. Finally, an Ordinal Priority Approach is applied to determine the preferred implementation of these factors in the context of EHRs. The proposed study provides a descriptive then prescriptive framework for the implementation of privacy and security in the context of electronic health records. Therefore, the findings of the proposed framework are useful for professionals and policymakers in improving the security and privacy associated with EHRs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge