Arpit Prajapati
3DCoMPaT200: Language-Grounded Compositional Understanding of Parts and Materials of 3D Shapes
Jan 12, 2025



Abstract:Understanding objects in 3D at the part level is essential for humans and robots to navigate and interact with the environment. Current datasets for part-level 3D object understanding encompass a limited range of categories. For instance, the ShapeNet-Part and PartNet datasets only include 16, and 24 object categories respectively. The 3DCoMPaT dataset, specifically designed for compositional understanding of parts and materials, contains only 42 object categories. To foster richer and fine-grained part-level 3D understanding, we introduce 3DCoMPaT200, a large-scale dataset tailored for compositional understanding of object parts and materials, with 200 object categories with $\approx$5 times larger object vocabulary compared to 3DCoMPaT and $\approx$ 4 times larger part categories. Concretely, 3DCoMPaT200 significantly expands upon 3DCoMPaT, featuring 1,031 fine-grained part categories and 293 distinct material classes for compositional application to 3D object parts. Additionally, to address the complexities of compositional 3D modeling, we propose a novel task of Compositional Part Shape Retrieval using ULIP to provide a strong 3D foundational model for 3D Compositional Understanding. This method evaluates the model shape retrieval performance given one, three, or six parts described in text format. These results show that the model's performance improves with an increasing number of style compositions, highlighting the critical role of the compositional dataset. Such results underscore the dataset's effectiveness in enhancing models' capability to understand complex 3D shapes from a compositional perspective. Code and Data can be found at http://github.com/3DCoMPaT200/3DCoMPaT200
3DCoMPaT$^{++}$: An improved Large-scale 3D Vision Dataset for Compositional Recognition
Oct 27, 2023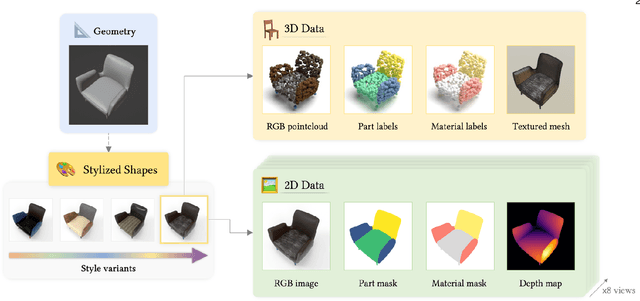
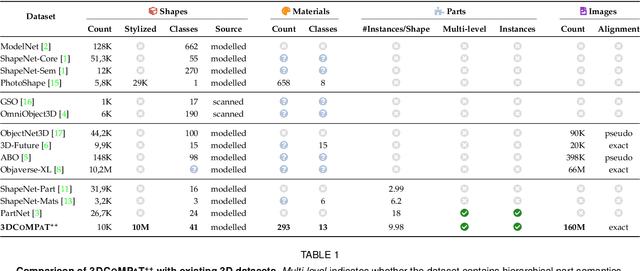
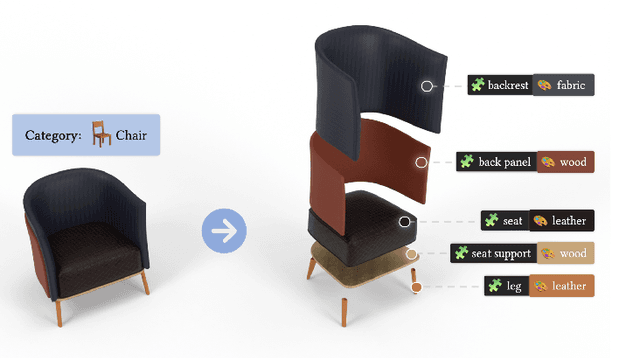
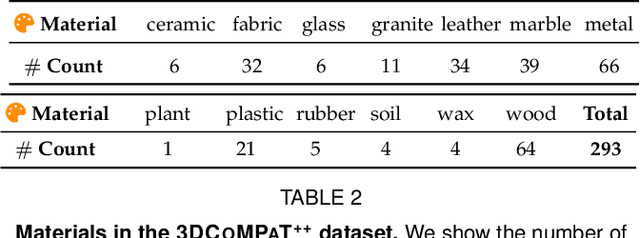
Abstract:In this work, we present 3DCoMPaT$^{++}$, a multimodal 2D/3D dataset with 160 million rendered views of more than 10 million stylized 3D shapes carefully annotated at the part-instance level, alongside matching RGB point clouds, 3D textured meshes, depth maps, and segmentation masks. 3DCoMPaT$^{++}$ covers 41 shape categories, 275 fine-grained part categories, and 293 fine-grained material classes that can be compositionally applied to parts of 3D objects. We render a subset of one million stylized shapes from four equally spaced views as well as four randomized views, leading to a total of 160 million renderings. Parts are segmented at the instance level, with coarse-grained and fine-grained semantic levels. We introduce a new task, called Grounded CoMPaT Recognition (GCR), to collectively recognize and ground compositions of materials on parts of 3D objects. Additionally, we report the outcomes of a data challenge organized at CVPR2023, showcasing the winning method's utilization of a modified PointNet$^{++}$ model trained on 6D inputs, and exploring alternative techniques for GCR enhancement. We hope our work will help ease future research on compositional 3D Vision.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge