Armstrong Foundjem
Jack
Multi-Agent Framework for Threat Mitigation and Resilience in AI-Based Systems
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Machine learning (ML) underpins foundation models in finance, healthcare, and critical infrastructure, making them targets for data poisoning, model extraction, prompt injection, automated jailbreaking, and preference-guided black-box attacks that exploit model comparisons. Larger models can be more vulnerable to introspection-driven jailbreaks and cross-modal manipulation. Traditional cybersecurity lacks ML-specific threat modeling for foundation, multimodal, and RAG systems. Objective: Characterize ML security risks by identifying dominant TTPs, vulnerabilities, and targeted lifecycle stages. Methods: We extract 93 threats from MITRE ATLAS (26), AI Incident Database (12), and literature (55), and analyze 854 GitHub/Python repositories. A multi-agent RAG system (ChatGPT-4o, temp 0.4) mines 300+ articles to build an ontology-driven threat graph linking TTPs, vulnerabilities, and stages. Results: We identify unreported threats including commercial LLM API model stealing, parameter memorization leakage, and preference-guided text-only jailbreaks. Dominant TTPs include MASTERKEY-style jailbreaking, federated poisoning, diffusion backdoors, and preference optimization leakage, mainly impacting pre-training and inference. Graph analysis reveals dense vulnerability clusters in libraries with poor patch propagation. Conclusion: Adaptive, ML-specific security frameworks, combining dependency hygiene, threat intelligence, and monitoring, are essential to mitigate supply-chain and inference risks across the ML lifecycle.
AI Benchmark Democratization and Carpentry
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Benchmarks are a cornerstone of modern machine learning, enabling reproducibility, comparison, and scientific progress. However, AI benchmarks are increasingly complex, requiring dynamic, AI-focused workflows. Rapid evolution in model architectures, scale, datasets, and deployment contexts makes evaluation a moving target. Large language models often memorize static benchmarks, causing a gap between benchmark results and real-world performance. Beyond traditional static benchmarks, continuous adaptive benchmarking frameworks are needed to align scientific assessment with deployment risks. This calls for skills and education in AI Benchmark Carpentry. From our experience with MLCommons, educational initiatives, and programs like the DOE's Trillion Parameter Consortium, key barriers include high resource demands, limited access to specialized hardware, lack of benchmark design expertise, and uncertainty in relating results to application domains. Current benchmarks often emphasize peak performance on top-tier hardware, offering limited guidance for diverse, real-world scenarios. Benchmarking must become dynamic, incorporating evolving models, updated data, and heterogeneous platforms while maintaining transparency, reproducibility, and interpretability. Democratization requires both technical innovation and systematic education across levels, building sustained expertise in benchmark design and use. Benchmarks should support application-relevant comparisons, enabling informed, context-sensitive decisions. Dynamic, inclusive benchmarking will ensure evaluation keeps pace with AI evolution and supports responsible, reproducible, and accessible AI deployment. Community efforts can provide a foundation for AI Benchmark Carpentry.
Risk Management for Mitigating Benchmark Failure Modes: BenchRisk
Oct 24, 2025Abstract:Large language model (LLM) benchmarks inform LLM use decisions (e.g., "is this LLM safe to deploy for my use case and context?"). However, benchmarks may be rendered unreliable by various failure modes that impact benchmark bias, variance, coverage, or people's capacity to understand benchmark evidence. Using the National Institute of Standards and Technology's risk management process as a foundation, this research iteratively analyzed 26 popular benchmarks, identifying 57 potential failure modes and 196 corresponding mitigation strategies. The mitigations reduce failure likelihood and/or severity, providing a frame for evaluating "benchmark risk," which is scored to provide a metaevaluation benchmark: BenchRisk. Higher scores indicate that benchmark users are less likely to reach an incorrect or unsupported conclusion about an LLM. All 26 scored benchmarks present significant risk within one or more of the five scored dimensions (comprehensiveness, intelligibility, consistency, correctness, and longevity), which points to important open research directions for the field of LLM benchmarking. The BenchRisk workflow allows for comparison between benchmarks; as an open-source tool, it also facilitates the identification and sharing of risks and their mitigations.
Deep Learning Model Reuse in the HuggingFace Community: Challenges, Benefit and Trends
Jan 24, 2024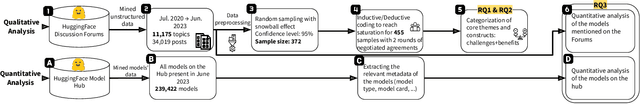

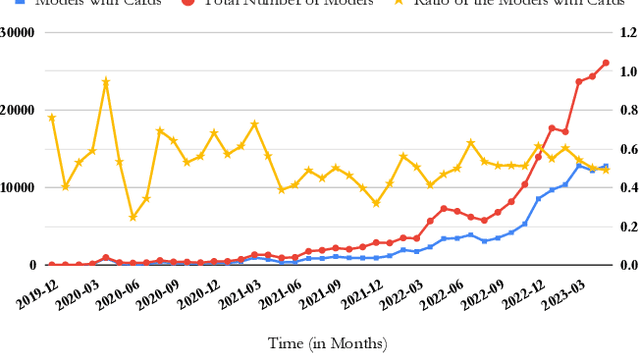
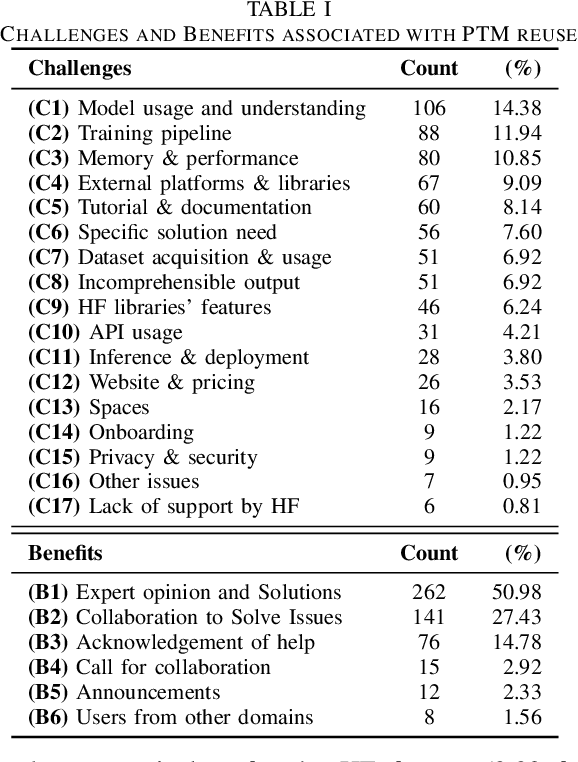
Abstract:The ubiquity of large-scale Pre-Trained Models (PTMs) is on the rise, sparking interest in model hubs, and dedicated platforms for hosting PTMs. Despite this trend, a comprehensive exploration of the challenges that users encounter and how the community leverages PTMs remains lacking. To address this gap, we conducted an extensive mixed-methods empirical study by focusing on discussion forums and the model hub of HuggingFace, the largest public model hub. Based on our qualitative analysis, we present a taxonomy of the challenges and benefits associated with PTM reuse within this community. We then conduct a quantitative study to track model-type trends and model documentation evolution over time. Our findings highlight prevalent challenges such as limited guidance for beginner users, struggles with model output comprehensibility in training or inference, and a lack of model understanding. We also identified interesting trends among models where some models maintain high upload rates despite a decline in topics related to them. Additionally, we found that despite the introduction of model documentation tools, its quantity has not increased over time, leading to difficulties in model comprehension and selection among users. Our study sheds light on new challenges in reusing PTMs that were not reported before and we provide recommendations for various stakeholders involved in PTM reuse.
Studying the Practices of Testing Machine Learning Software in the Wild
Dec 19, 2023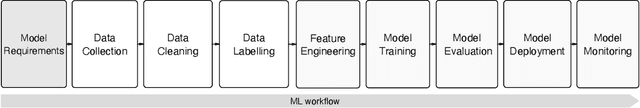
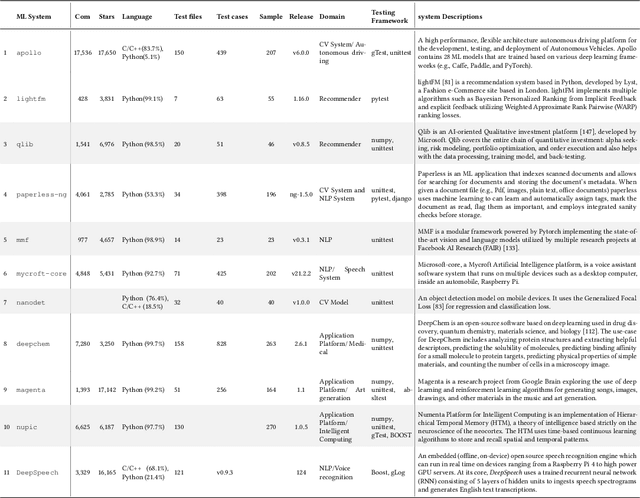
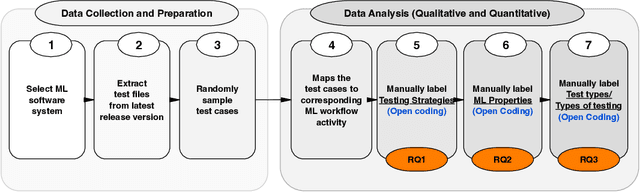
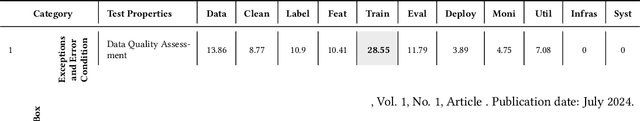
Abstract:Background: We are witnessing an increasing adoption of machine learning (ML), especially deep learning (DL) algorithms in many software systems, including safety-critical systems such as health care systems or autonomous driving vehicles. Ensuring the software quality of these systems is yet an open challenge for the research community, mainly due to the inductive nature of ML software systems. Traditionally, software systems were constructed deductively, by writing down the rules that govern the behavior of the system as program code. However, for ML software, these rules are inferred from training data. Few recent research advances in the quality assurance of ML systems have adapted different concepts from traditional software testing, such as mutation testing, to help improve the reliability of ML software systems. However, it is unclear if any of these proposed testing techniques from research are adopted in practice. There is little empirical evidence about the testing strategies of ML engineers. Aims: To fill this gap, we perform the first fine-grained empirical study on ML testing practices in the wild, to identify the ML properties being tested, the followed testing strategies, and their implementation throughout the ML workflow. Method: First, we systematically summarized the different testing strategies (e.g., Oracle Approximation), the tested ML properties (e.g., Correctness, Bias, and Fairness), and the testing methods (e.g., Unit test) from the literature. Then, we conducted a study to understand the practices of testing ML software. Results: In our findings: 1) we identified four (4) major categories of testing strategy including Grey-box, White-box, Black-box, and Heuristic-based techniques that are used by the ML engineers to find software bugs. 2) We identified 16 ML properties that are tested in the ML workflow.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge