Anwei Li
Weighted Concordance Index Loss-based Multimodal Survival Modeling for Radiation Encephalopathy Assessment in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Radiotherapy
Jun 23, 2022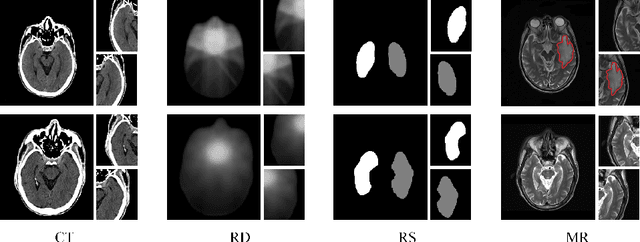
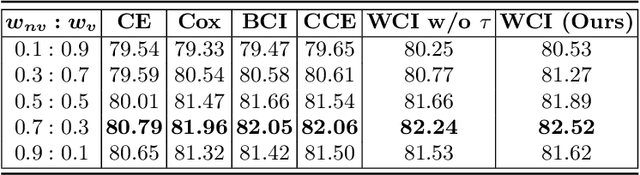
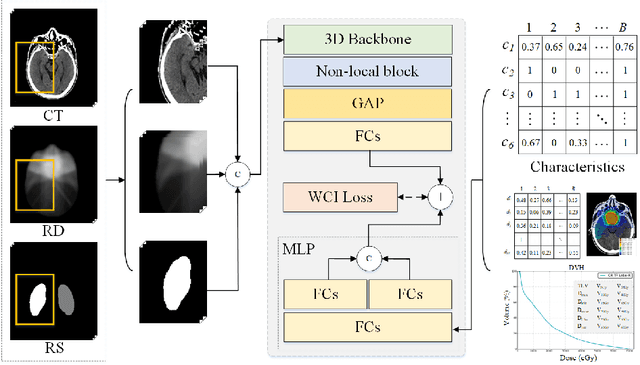
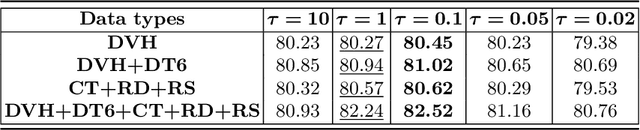
Abstract:Radiation encephalopathy (REP) is the most common complication for nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) radiotherapy. It is highly desirable to assist clinicians in optimizing the NPC radiotherapy regimen to reduce radiotherapy-induced temporal lobe injury (RTLI) according to the probability of REP onset. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first exploration of predicting radiotherapy-induced REP by jointly exploiting image and non-image data in NPC radiotherapy regimen. We cast REP prediction as a survival analysis task and evaluate the predictive accuracy in terms of the concordance index (CI). We design a deep multimodal survival network (MSN) with two feature extractors to learn discriminative features from multimodal data. One feature extractor imposes feature selection on non-image data, and the other learns visual features from images. Because the priorly balanced CI (BCI) loss function directly maximizing the CI is sensitive to uneven sampling per batch. Hence, we propose a novel weighted CI (WCI) loss function to leverage all REP samples effectively by assigning their different weights with a dual average operation. We further introduce a temperature hyper-parameter for our WCI to sharpen the risk difference of sample pairs to help model convergence. We extensively evaluate our WCI on a private dataset to demonstrate its favourability against its counterparts. The experimental results also show multimodal data of NPC radiotherapy can bring more gains for REP risk prediction.
Siamese Encoder-based Spatial-Temporal Mixer for Growth Trend Prediction of Lung Nodules on CT Scans
Jun 07, 2022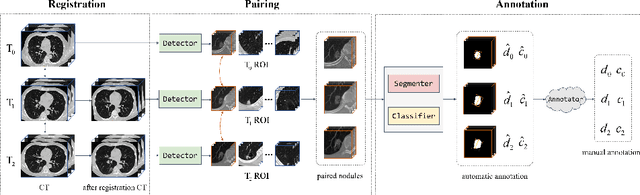
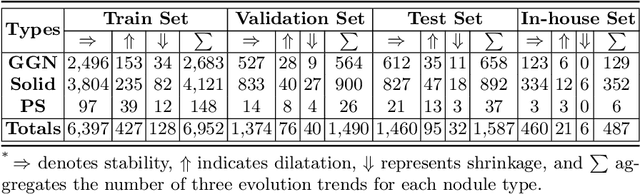
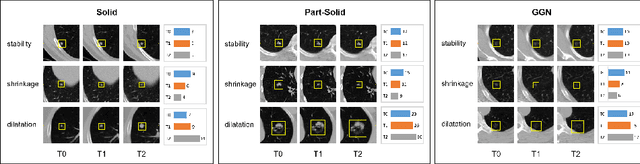
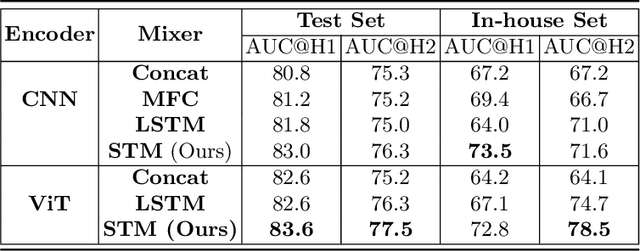
Abstract:In the management of lung nodules, we are desirable to predict nodule evolution in terms of its diameter variation on Computed Tomography (CT) scans and then provide a follow-up recommendation according to the predicted result of the growing trend of the nodule. In order to improve the performance of growth trend prediction for lung nodules, it is vital to compare the changes of the same nodule in consecutive CT scans. Motivated by this, we screened out 4,666 subjects with more than two consecutive CT scans from the National Lung Screening Trial (NLST) dataset to organize a temporal dataset called NLSTt. In specific, we first detect and pair regions of interest (ROIs) covering the same nodule based on registered CT scans. After that, we predict the texture category and diameter size of the nodules through models. Last, we annotate the evolution class of each nodule according to its changes in diameter. Based on the built NLSTt dataset, we propose a siamese encoder to simultaneously exploit the discriminative features of 3D ROIs detected from consecutive CT scans. Then we novelly design a spatial-temporal mixer (STM) to leverage the interval changes of the same nodule in sequential 3D ROIs and capture spatial dependencies of nodule regions and the current 3D ROI. According to the clinical diagnosis routine, we employ hierarchical loss to pay more attention to growing nodules. The extensive experiments on our organized dataset demonstrate the advantage of our proposed method. We also conduct experiments on an in-house dataset to evaluate the clinical utility of our method by comparing it against skilled clinicians.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge