Andrew W. Palmer
The Autonomous Siemens Tram
Feb 08, 2021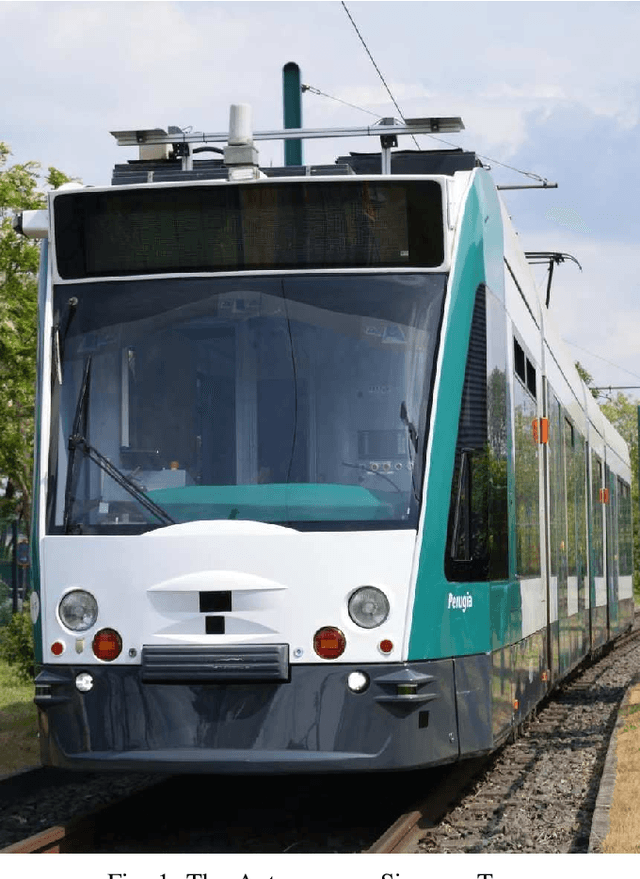

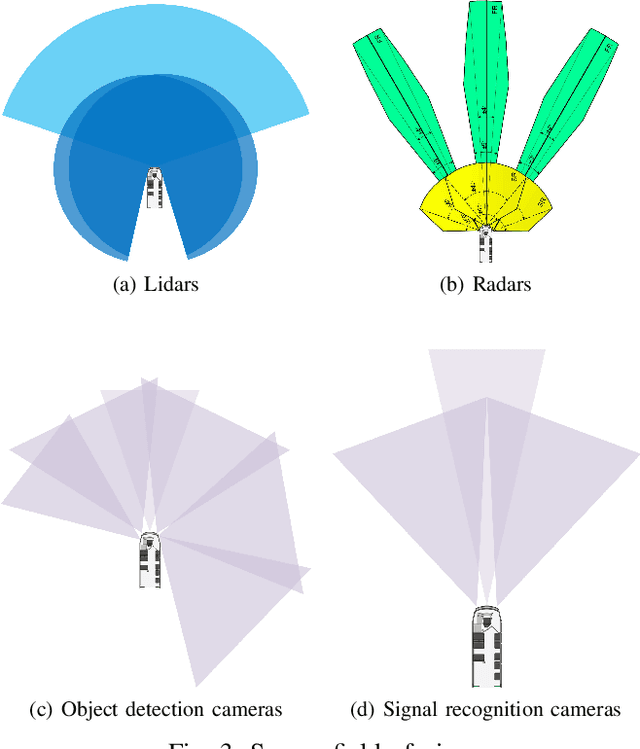
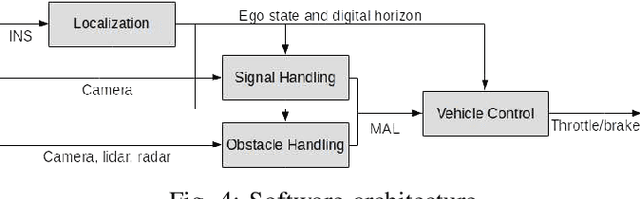
Abstract:This paper presents the Autonomous Siemens Tram that was publicly demonstrated in Potsdam, Germany during the InnoTrans 2018 exhibition. The system was built on a Siemens Combino tram and used a multi-modal sensor suite to localize the vehicle, and to detect and respond to traffic signals and obstacles. An overview of the hardware and the developed localization, signal handling, and obstacle handling components is presented, along with a summary of their performance.
* 6 pages, presented at the 2020 International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC)
Experimental Comparison of Visual-Aided Odometry Methods for Rail Vehicles
Apr 01, 2019



Abstract:Today, rail vehicle localization is based on infrastructure-side Balises (beacons) together with on-board odometry to determine whether a rail segment is occupied. Such a coarse locking leads to a sub-optimal usage of the rail networks. New railway standards propose the use of moving blocks centered around the rail vehicles to increase the capacity of the network. However, this approach requires accurate and robust position and velocity estimation of all vehicles. In this work, we investigate the applicability, challenges and limitations of current visual and visual-inertial motion estimation frameworks for rail applications. An evaluation against RTK-GPS ground truth is performed on multiple datasets recorded in industrial, sub-urban, and forest environments. Our results show that stereo visual-inertial odometry has a great potential to provide a precise motion estimation because of its complementing sensor modalities and shows superior performance in challenging situations compared to other frameworks.
Robust Odometry using Sensor Consensus Analysis
Mar 06, 2018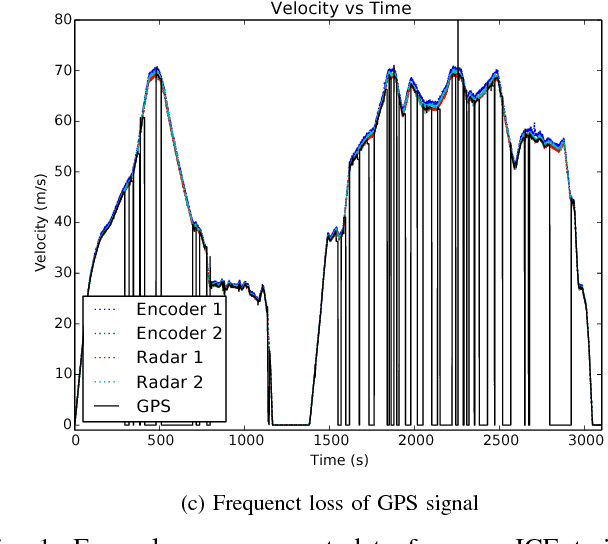
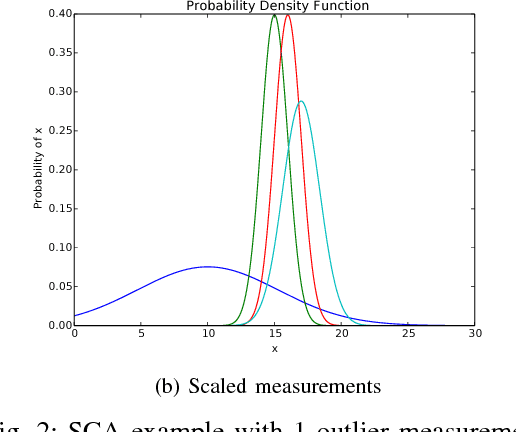

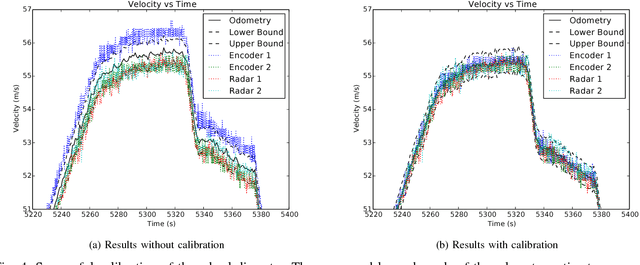
Abstract:Odometry forms an important component of many manned and autonomous systems. In the rail industry in particular, having precise and robust odometry is crucial for the correct operation of the Automatic Train Protection systems that ensure the safety of high-speed trains in operation around the world. Two problems commonly encountered in such odometry systems are miscalibration of the wheel encoders and slippage of the wheels under acceleration and braking, resulting in incorrect velocity estimates. This paper introduces an odometry system that addresses these problems. It comprises of an Extended Kalman Filter that tracks the calibration of the wheel encoders as state variables, and a measurement pre-processing stage called Sensor Consensus Analysis (SCA) that scales the uncertainty of a measurement based on how consistent it is with the measurements of the other sensors. SCA uses the statistical z-test to determine when an individual measurement is inconsistent with the other measurements, and scales the uncertainty until the z-test passes. This system is demonstrated on data from German Intercity-Express high-speed trains and it is shown to successfully deal with errors due to miscalibration and wheel slip.
Modelling resource contention in multi-robot task allocation problems with uncertain timing
Feb 08, 2017


Abstract:This paper proposes an analytical framework for modelling resource contention in multi-robot systems, where the travel times and task durations are uncertain. It uses several approximation methods to quickly and accurately calculate the probability distributions describing the times at which the tasks start and finish. Specific contributions include a method for calculating the probability of a set of independent normally distributed random events occurring in a given order, an upper bound on that probability, and a method for calculating the most likely and $n$-th most likely orders of occurrence for a set of independent normally distributed random events that have equal standard deviations. The complete framework is shown to be much faster than a Monte Carlo approach for the same accuracy in two multi-robot task allocation problems. This is a general framework that is agnostic to the optimisation method and objective function used, and is applicable to a wide range of robotics and non-robotics problems.
Weekly maintenance scheduling using exact and genetic methods
Oct 17, 2016



Abstract:The weekly maintenance schedule specifies when maintenance activities should be performed on the equipment, taking into account the availability of workers and maintenance bays, and other operational constraints. The current approach to generating this schedule is labour intensive and requires coordination between the maintenance schedulers and operations staff to minimise its impact on the operation of the mine. This paper presents methods for automatically generating this schedule from the list of maintenance tasks to be performed, the availability roster of the maintenance staff, and time windows in which each piece of equipment is available for maintenance. Both Mixed-Integer Linear Programming (MILP) and genetic algorithms are evaluated, with the genetic algorithm shown to significantly outperform the MILP. Two fitness functions for the genetic algorithm are also examined, with a linear fitness function outperforming an inverse fitness function by up to 5% for the same calculation time. The genetic algorithm approach is computationally fast, allowing the schedule to be rapidly recalculated in response to unexpected delays and breakdowns.
Methods for Stochastic Collection and Replenishment (SCAR) optimisation for persistent autonomy
Jun 30, 2016



Abstract:Consideration of resources such as fuel, battery charge, and storage space, is a crucial requirement for the successful persistent operation of autonomous systems. The Stochastic Collection and Replenishment (SCAR) scenario is motivated by mining and agricultural scenarios where a dedicated replenishment agent transports a resource between a centralised replenishment point to agents using the resource in the field. The agents in the field typically operate within fixed areas (for example, benches in mining applications, and fields or orchards in agricultural scenarios), and the motion of the replenishment agent may be restricted by a road network. Existing research has typically approached the problem of scheduling the actions of the dedicated replenishment agent from a short-term and deterministic angle. This paper introduces a method of incorporating uncertainty in the schedule optimisation through a novel prediction framework, and a branch and bound optimisation method which uses the prediction framework to minimise the downtime of the agents. The prediction framework makes use of several Gaussian approximations to quickly calculate the risk-weighted cost of a schedule. The anytime nature of the branch and bound method is exploited within an MPC-like framework to outperform existing optimisation methods while providing reasonable calculation times in large scenarios.
* Revision 1
Applying Gaussian distributed constraints to Gaussian distributed variables
Apr 20, 2016



Abstract:This paper develops an analytical method of truncating inequality constrained Gaussian distributed variables where the constraints are themselves described by Gaussian distributions. Existing truncation methods either assume hard constraints, or use numerical methods to handle uncertain constraints. The proposed approach introduces moment-based Gaussian approximations of the truncated distribution. This method can be applied to numerous problems, with the motivating problem being Kalman filtering with uncertain constraints. In a simulation example, the developed method is shown to outperform unconstrained Kalman filtering by over 40% and hard-constrained Kalman filtering by over 17%.
Stochastic Collection and Replenishment (SCAR) Optimisation for Persistent Autonomy
Mar 07, 2016



Abstract:Robots have a finite supply of resources such as fuel, battery charge, and storage space. The aim of the Stochastic Collection and Replenishment (SCAR) scenario is to use dedicated agents to refuel, recharge, or otherwise replenish robots in the field to facilitate persistent autonomy. This paper explores the optimisation of the SCAR scenario with a single replenishment agent, using several different objective functions. The problem is framed as a combinatorial optimisation problem, and A* is used to find the optimal schedule. Through a computational study, a ratio objective function is shown to have superior performance compared with a total weighted tardiness objective function, with a greater performance advantage present when using shorter schedule lengths. The importance of incorporating uncertainty in the objective function used in the optimisation process is also highlighted, in particular for scenarios in which the replenishment agent is under- or fully-utilised.
Stochastic Collection and Replenishment : Objective Functions
Mar 07, 2016



Abstract:This paper introduces two objective functions for computing the expected cost in the Stochastic Collection and Replenishment (SCAR) scenario. In the SCAR scenario, multiple user agents have a limited supply of a resource that they either use or collect, depending on the scenario. To enable persistent autonomy, dedicated replenishment agents travel to the user agents and replenish or collect their supply of the resource, thus allowing them to operate indefinitely in the field. Of the two objective functions, one uses a Monte Carlo method, while the other uses a significantly faster analytical method. Approximations to multiplication, division and inversion of Gaussian distributed variables are used to facilitate propagation of probability distributions in the analytical method when Gaussian distributed parameters are used. The analytical objective function is shown to have greater than 99% comparison accuracy when compared with the Monte Carlo objective function while achieving speed gains of several orders of magnitude.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge