Andrea Carmantini
Phonetic Error Analysis of Raw Waveform Acoustic Models with Parametric and Non-Parametric CNNs
Jun 02, 2024
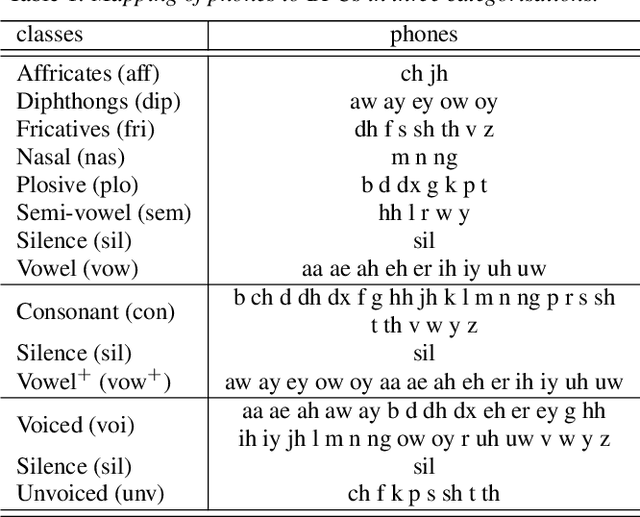
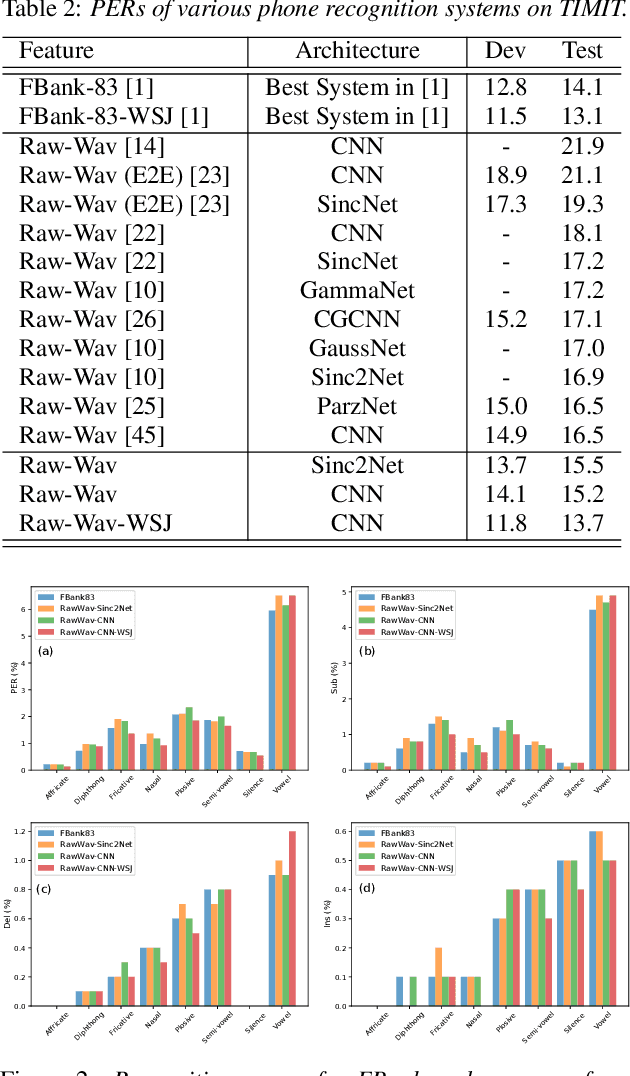

Abstract:In this paper, we analyse the error patterns of the raw waveform acoustic models in TIMIT's phone recognition task. Our analysis goes beyond the conventional phone error rate (PER) metric. We categorise the phones into three groups: {affricate, diphthong, fricative, nasal, plosive, semi-vowel, vowel, silence}, {consonant, vowel+, silence}, and {voiced, unvoiced, silence} and, compute the PER for each broad phonetic class in each category. We also construct a confusion matrix for each category using the substitution errors and compare the confusion patterns with those of the Filterbank and Wav2vec 2.0 systems. Our raw waveform acoustic models consists of parametric (Sinc2Net) or non-parametric CNNs and Bidirectional LSTMs, achieving down to 13.7%/15.2% PERs on TIMIT Dev/Test sets, outperforming reported PERs for raw waveform models in the literature. We also investigate the impact of transfer learning from WSJ on the phonetic error patterns and confusion matrices. It reduces the PER to 11.8%/13.7% on the Dev/Test sets.
The Edinburgh International Accents of English Corpus: Towards the Democratization of English ASR
Mar 31, 2023Abstract:English is the most widely spoken language in the world, used daily by millions of people as a first or second language in many different contexts. As a result, there are many varieties of English. Although the great many advances in English automatic speech recognition (ASR) over the past decades, results are usually reported based on test datasets which fail to represent the diversity of English as spoken today around the globe. We present the first release of The Edinburgh International Accents of English Corpus (EdAcc). This dataset attempts to better represent the wide diversity of English, encompassing almost 40 hours of dyadic video call conversations between friends. Unlike other datasets, EdAcc includes a wide range of first and second-language varieties of English and a linguistic background profile of each speaker. Results on latest public, and commercial models show that EdAcc highlights shortcomings of current English ASR models. The best performing model, trained on 680 thousand hours of transcribed data, obtains an average of 19.7% word error rate (WER) -- in contrast to the 2.7% WER obtained when evaluated on US English clean read speech. Across all models, we observe a drop in performance on Indian, Jamaican, and Nigerian English speakers. Recordings, linguistic backgrounds, data statement, and evaluation scripts are released on our website (https://groups.inf.ed.ac.uk/edacc/) under CC-BY-SA license.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge