Anant V. Nori
TransforMAP: Transformer for Memory Access Prediction
May 29, 2022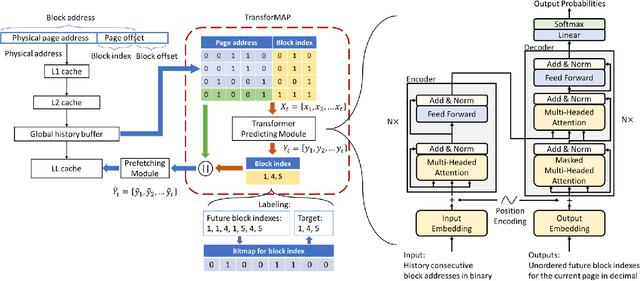
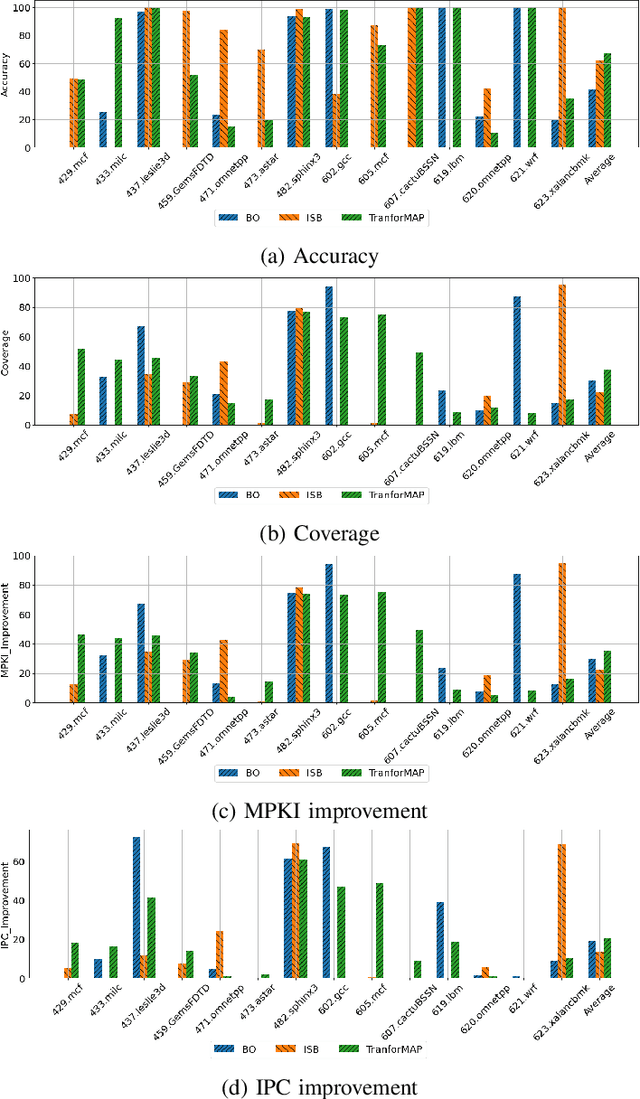
Abstract:Data Prefetching is a technique that can hide memory latency by fetching data before it is needed by a program. Prefetching relies on accurate memory access prediction, to which task machine learning based methods are increasingly applied. Unlike previous approaches that learn from deltas or offsets and perform one access prediction, we develop TransforMAP, based on the powerful Transformer model, that can learn from the whole address space and perform multiple cache line predictions. We propose to use the binary of memory addresses as model input, which avoids information loss and saves a token table in hardware. We design a block index bitmap to collect unordered future page offsets under the current page address as learning labels. As a result, our model can learn temporal patterns as well as spatial patterns within a page. In a practical implementation, this approach has the potential to hide prediction latency because it prefetches multiple cache lines likely to be used in a long horizon. We show that our approach achieves 35.67% MPKI improvement and 20.55% IPC improvement in simulation, higher than state-of-the-art Best-Offset prefetcher and ISB prefetcher.
Fine-Grained Address Segmentation for Attention-Based Variable-Degree Prefetching
May 01, 2022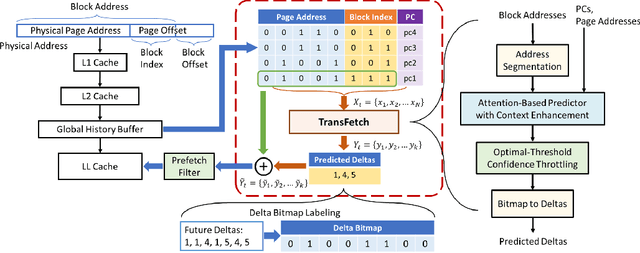
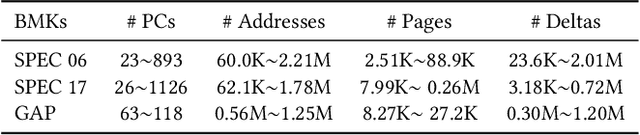
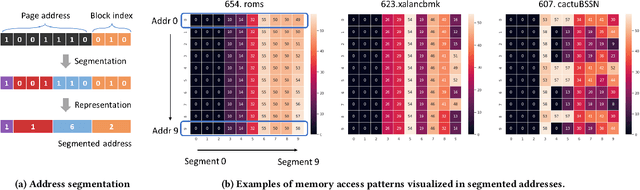
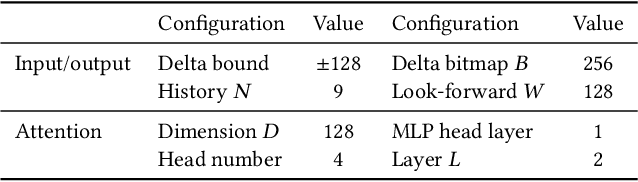
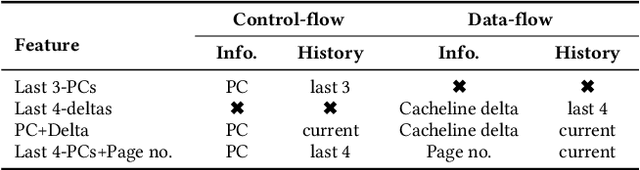
Abstract:Machine learning algorithms have shown potential to improve prefetching performance by accurately predicting future memory accesses. Existing approaches are based on the modeling of text prediction, considering prefetching as a classification problem for sequence prediction. However, the vast and sparse memory address space leads to large vocabulary, which makes this modeling impractical. The number and order of outputs for multiple cache line prefetching are also fundamentally different from text prediction. We propose TransFetch, a novel way to model prefetching. To reduce vocabulary size, we use fine-grained address segmentation as input. To predict unordered sets of future addresses, we use delta bitmaps for multiple outputs. We apply an attention-based network to learn the mapping between input and output. Prediction experiments demonstrate that address segmentation achieves 26% - 36% higher F1-score than delta inputs and 15% - 24% higher F1-score than page & offset inputs for SPEC 2006, SPEC 2017, and GAP benchmarks. Simulation results show that TransFetch achieves 38.75% IPC improvement compared with no prefetching, outperforming the best-performing rule-based prefetcher BOP by 10.44%, and ML-based prefetcher Voyager by 6.64%.
Pythia: A Customizable Hardware Prefetching Framework Using Online Reinforcement Learning
Oct 19, 2021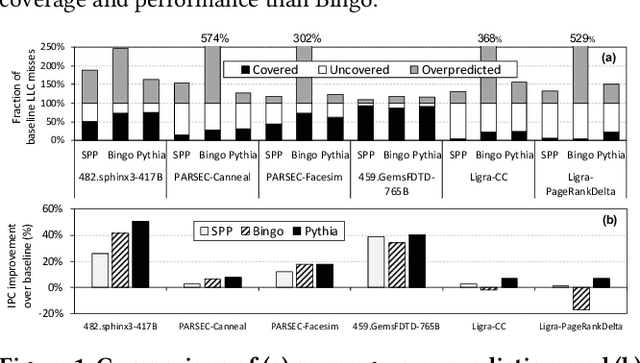
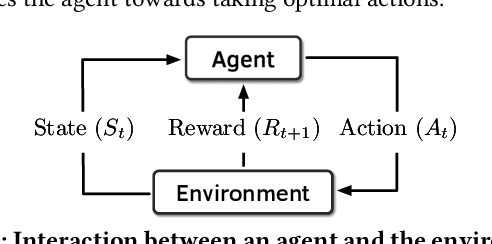
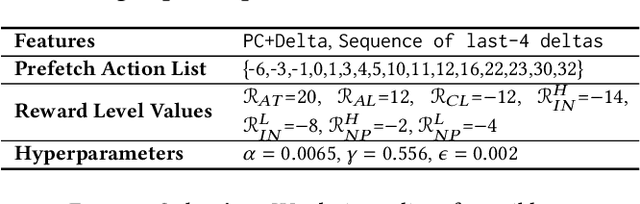
Abstract:Past research has proposed numerous hardware prefetching techniques, most of which rely on exploiting one specific type of program context information (e.g., program counter, cacheline address) to predict future memory accesses. These techniques either completely neglect a prefetcher's undesirable effects (e.g., memory bandwidth usage) on the overall system, or incorporate system-level feedback as an afterthought to a system-unaware prefetch algorithm. We show that prior prefetchers often lose their performance benefit over a wide range of workloads and system configurations due to their inherent inability to take multiple different types of program context and system-level feedback information into account while prefetching. In this paper, we make a case for designing a holistic prefetch algorithm that learns to prefetch using multiple different types of program context and system-level feedback information inherent to its design. To this end, we propose Pythia, which formulates the prefetcher as a reinforcement learning agent. For every demand request, Pythia observes multiple different types of program context information to make a prefetch decision. For every prefetch decision, Pythia receives a numerical reward that evaluates prefetch quality under the current memory bandwidth usage. Pythia uses this reward to reinforce the correlation between program context information and prefetch decision to generate highly accurate, timely, and system-aware prefetch requests in the future. Our extensive evaluations using simulation and hardware synthesis show that Pythia outperforms multiple state-of-the-art prefetchers over a wide range of workloads and system configurations, while incurring only 1.03% area overhead over a desktop-class processor and no software changes in workloads. The source code of Pythia can be freely downloaded from https://github.com/CMU-SAFARI/Pythia.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge