An Lao
Frequency Spectrum is More Effective for Multimodal Representation and Fusion: A Multimodal Spectrum Rumor Detector
Dec 18, 2023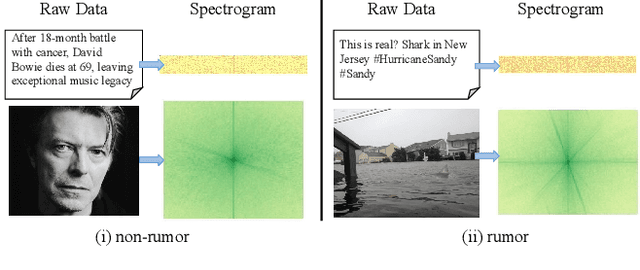
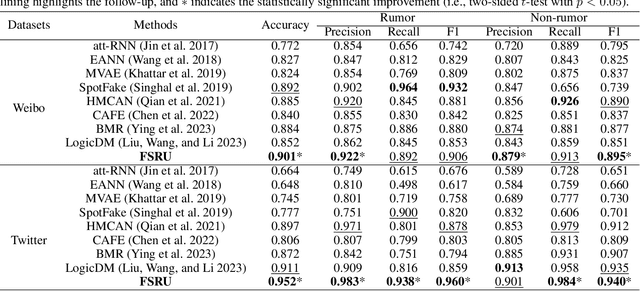
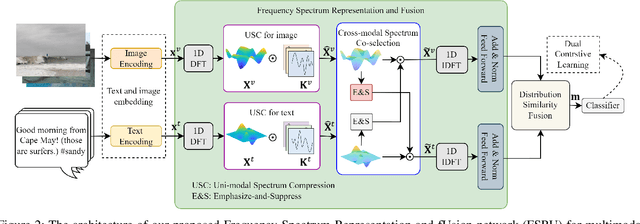
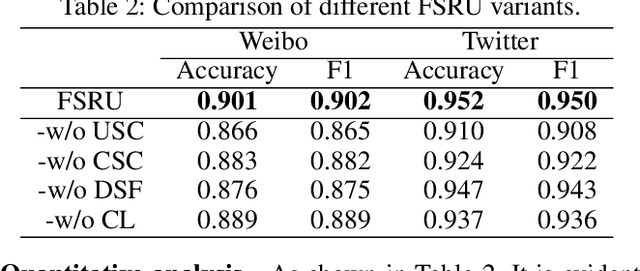
Abstract:Multimodal content, such as mixing text with images, presents significant challenges to rumor detection in social media. Existing multimodal rumor detection has focused on mixing tokens among spatial and sequential locations for unimodal representation or fusing clues of rumor veracity across modalities. However, they suffer from less discriminative unimodal representation and are vulnerable to intricate location dependencies in the time-consuming fusion of spatial and sequential tokens. This work makes the first attempt at multimodal rumor detection in the frequency domain, which efficiently transforms spatial features into the frequency spectrum and obtains highly discriminative spectrum features for multimodal representation and fusion. A novel Frequency Spectrum Representation and fUsion network (FSRU) with dual contrastive learning reveals the frequency spectrum is more effective for multimodal representation and fusion, extracting the informative components for rumor detection. FSRU involves three novel mechanisms: utilizing the Fourier transform to convert features in the spatial domain to the frequency domain, the unimodal spectrum compression, and the cross-modal spectrum co-selection module in the frequency domain. Substantial experiments show that FSRU achieves satisfactory multimodal rumor detection performance.
Rumor Detection with Hierarchical Representation on Bipartite Adhoc Event Trees
Apr 27, 2023



Abstract:The rapid growth of social media has caused tremendous effects on information propagation, raising extreme challenges in detecting rumors. Existing rumor detection methods typically exploit the reposting propagation of a rumor candidate for detection by regarding all reposts to a rumor candidate as a temporal sequence and learning semantics representations of the repost sequence. However, extracting informative support from the topological structure of propagation and the influence of reposting authors for debunking rumors is crucial, which generally has not been well addressed by existing methods. In this paper, we organize a claim post in circulation as an adhoc event tree, extract event elements, and convert it to bipartite adhoc event trees in terms of both posts and authors, i.e., author tree and post tree. Accordingly, we propose a novel rumor detection model with hierarchical representation on the bipartite adhoc event trees called BAET. Specifically, we introduce word embedding and feature encoder for the author and post tree, respectively, and design a root-aware attention module to perform node representation. Then we adopt the tree-like RNN model to capture the structural correlations and propose a tree-aware attention module to learn tree representation for the author tree and post tree, respectively. Extensive experimental results on two public Twitter datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of BAET in exploring and exploiting the rumor propagation structure and the superior detection performance of BAET over state-of-the-art baseline methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge