Amy Karlson
Simultaneous Gesture Classification and Localization with an Automatic Gesture Annotation Model
Jan 20, 2024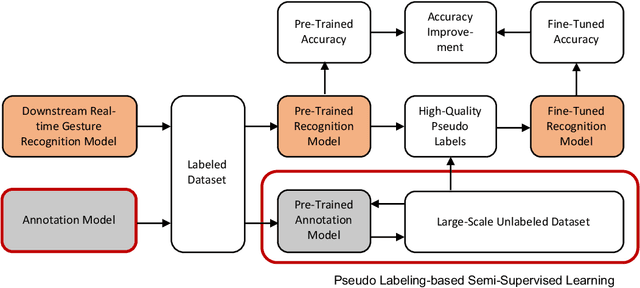
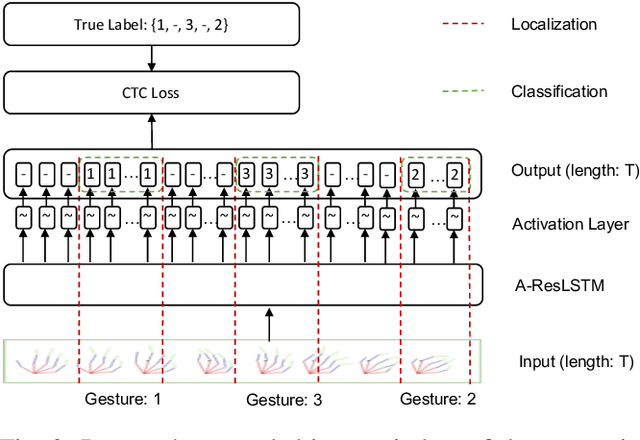
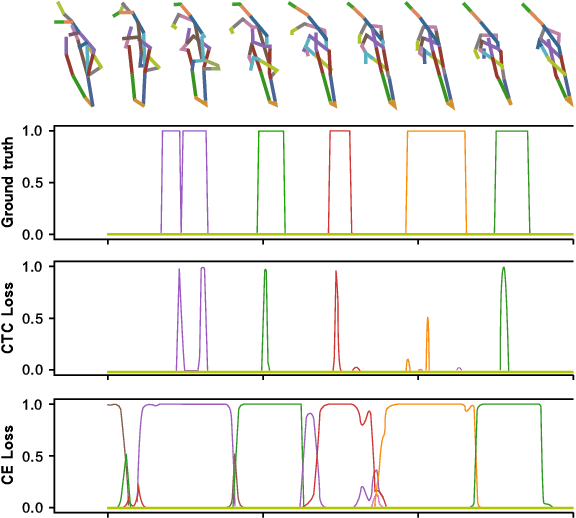
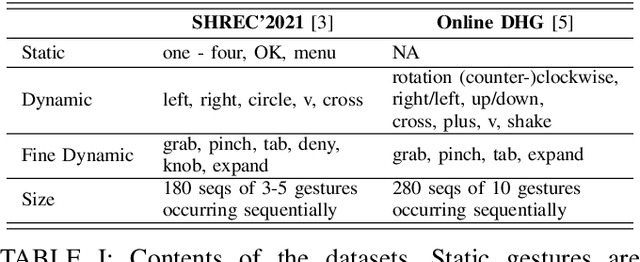
Abstract:Training a real-time gesture recognition model heavily relies on annotated data. However, manual data annotation is costly and demands substantial human effort. In order to address this challenge, we propose a novel annotation model that can automatically annotate gesture classes and identify their temporal ranges. Our ablation study demonstrates that our annotation model design surpasses the baseline in terms of both gesture classification accuracy (3-4\% improvement) and localization accuracy (71-75\% improvement). We believe that this annotation model has immense potential to improve the training of downstream gesture recognition models using unlabeled datasets.
Towards Open-World Gesture Recognition
Jan 20, 2024



Abstract:Static machine learning methods in gesture recognition assume that training and test data come from the same underlying distribution. However, in real-world applications involving gesture recognition on wrist-worn devices, data distribution may change over time. We formulate this problem of adapting recognition models to new tasks, where new data patterns emerge, as open-world gesture recognition (OWGR). We propose leveraging continual learning to make machine learning models adaptive to new tasks without degrading performance on previously learned tasks. However, the exploration of parameters for questions around when and how to train and deploy recognition models requires time-consuming user studies and is sometimes impractical. To address this challenge, we propose a design engineering approach that enables offline analysis on a collected large-scale dataset with various parameters and compares different continual learning methods. Finally, design guidelines are provided to enhance the development of an open-world wrist-worn gesture recognition process.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge