Amna Elmustafa
SatBird: Bird Species Distribution Modeling with Remote Sensing and Citizen Science Data
Nov 02, 2023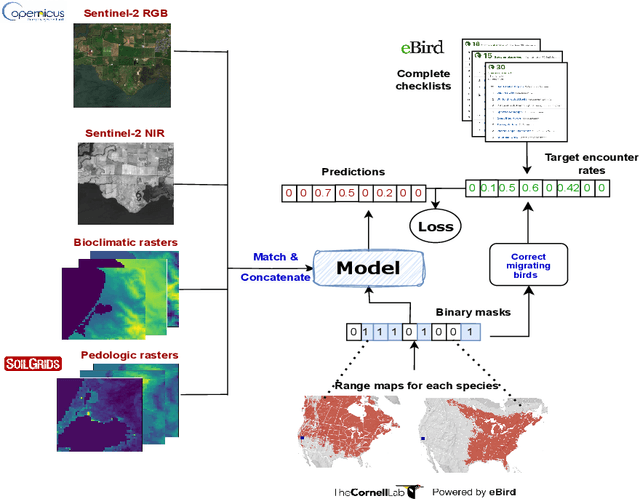
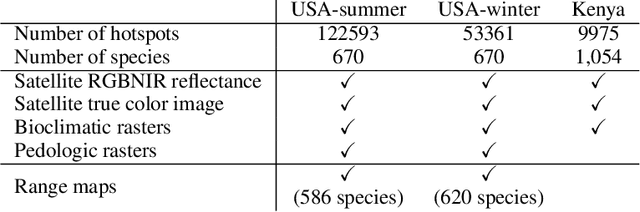
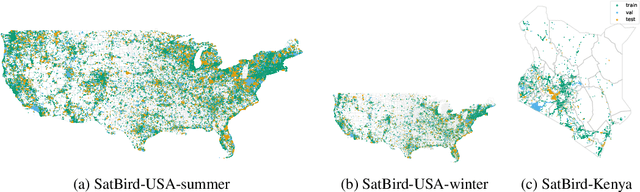
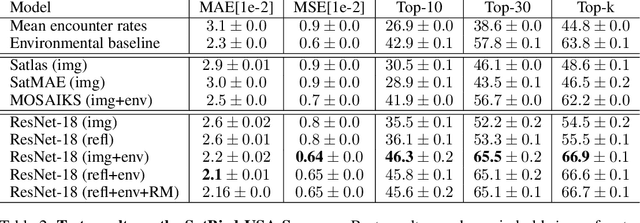
Abstract:Biodiversity is declining at an unprecedented rate, impacting ecosystem services necessary to ensure food, water, and human health and well-being. Understanding the distribution of species and their habitats is crucial for conservation policy planning. However, traditional methods in ecology for species distribution models (SDMs) generally focus either on narrow sets of species or narrow geographical areas and there remain significant knowledge gaps about the distribution of species. A major reason for this is the limited availability of data traditionally used, due to the prohibitive amount of effort and expertise required for traditional field monitoring. The wide availability of remote sensing data and the growing adoption of citizen science tools to collect species observations data at low cost offer an opportunity for improving biodiversity monitoring and enabling the modelling of complex ecosystems. We introduce a novel task for mapping bird species to their habitats by predicting species encounter rates from satellite images, and present SatBird, a satellite dataset of locations in the USA with labels derived from presence-absence observation data from the citizen science database eBird, considering summer (breeding) and winter seasons. We also provide a dataset in Kenya representing low-data regimes. We additionally provide environmental data and species range maps for each location. We benchmark a set of baselines on our dataset, including SOTA models for remote sensing tasks. SatBird opens up possibilities for scalably modelling properties of ecosystems worldwide.
HarvestNet: A Dataset for Detecting Smallholder Farming Activity Using Harvest Piles and Remote Sensing
Aug 23, 2023
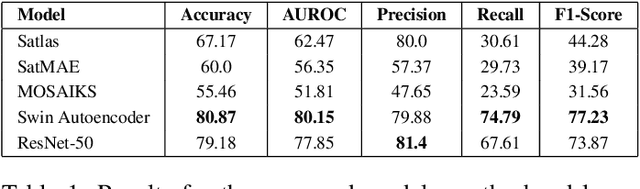

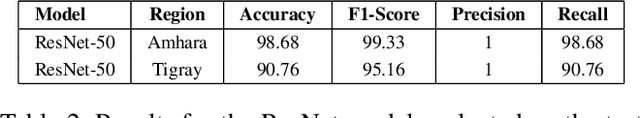
Abstract:Small farms contribute to a large share of the productive land in developing countries. In regions such as sub-Saharan Africa, where 80% of farms are small (under 2 ha in size), the task of mapping smallholder cropland is an important part of tracking sustainability measures such as crop productivity. However, the visually diverse and nuanced appearance of small farms has limited the effectiveness of traditional approaches to cropland mapping. Here we introduce a new approach based on the detection of harvest piles characteristic of many smallholder systems throughout the world. We present HarvestNet, a dataset for mapping the presence of farms in the Ethiopian regions of Tigray and Amhara during 2020-2023, collected using expert knowledge and satellite images, totaling 7k hand-labeled images and 2k ground collected labels. We also benchmark a set of baselines including SOTA models in remote sensing with our best models having around 80% classification performance on hand labelled data and 90%, 98% accuracy on ground truth data for Tigray, Amhara respectively. We also perform a visual comparison with a widely used pre-existing coverage map and show that our model detects an extra 56,621 hectares of cropland in Tigray. We conclude that remote sensing of harvest piles can contribute to more timely and accurate cropland assessments in food insecure region.
Bird Distribution Modelling using Remote Sensing and Citizen Science data
May 01, 2023


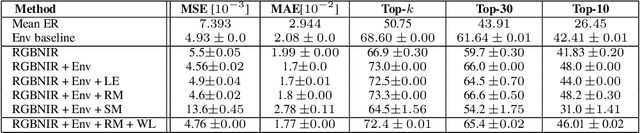
Abstract:Climate change is a major driver of biodiversity loss, changing the geographic range and abundance of many species. However, there remain significant knowledge gaps about the distribution of species, due principally to the amount of effort and expertise required for traditional field monitoring. We propose an approach leveraging computer vision to improve species distribution modelling, combining the wide availability of remote sensing data with sparse on-ground citizen science data. We introduce a novel task and dataset for mapping US bird species to their habitats by predicting species encounter rates from satellite images, along with baseline models which demonstrate the power of our approach. Our methods open up possibilities for scalably modelling ecosystems properties worldwide.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge