Ammar Battah
Generative AI and Large Language Models for Cyber Security: All Insights You Need
May 21, 2024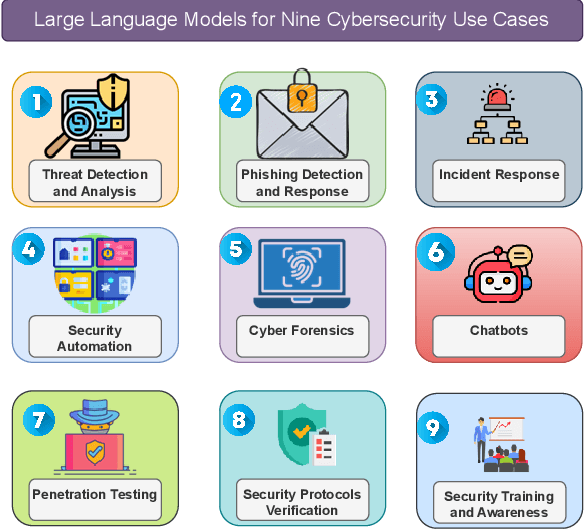
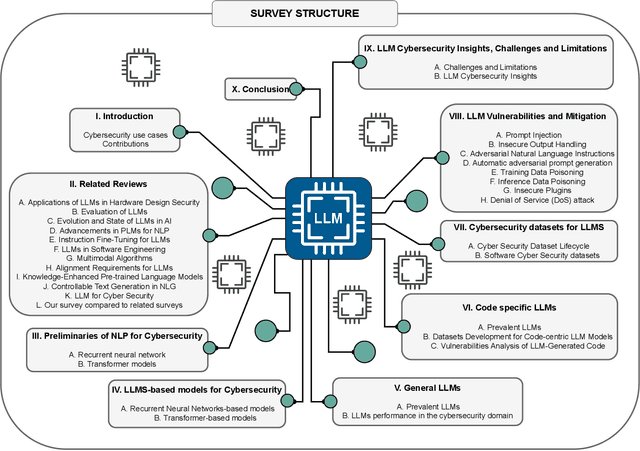
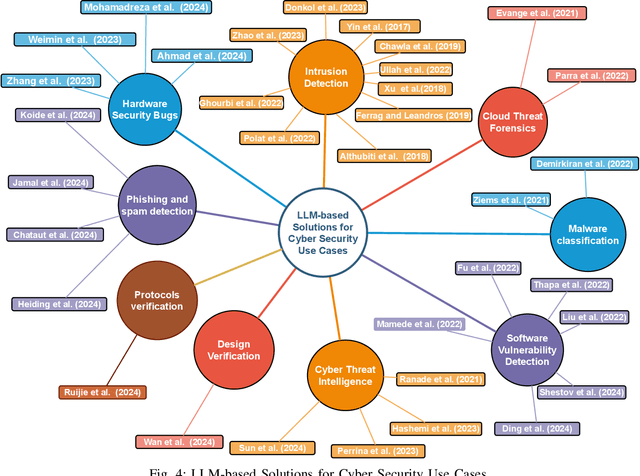
Abstract:This paper provides a comprehensive review of the future of cybersecurity through Generative AI and Large Language Models (LLMs). We explore LLM applications across various domains, including hardware design security, intrusion detection, software engineering, design verification, cyber threat intelligence, malware detection, and phishing detection. We present an overview of LLM evolution and its current state, focusing on advancements in models such as GPT-4, GPT-3.5, Mixtral-8x7B, BERT, Falcon2, and LLaMA. Our analysis extends to LLM vulnerabilities, such as prompt injection, insecure output handling, data poisoning, DDoS attacks, and adversarial instructions. We delve into mitigation strategies to protect these models, providing a comprehensive look at potential attack scenarios and prevention techniques. Furthermore, we evaluate the performance of 42 LLM models in cybersecurity knowledge and hardware security, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses. We thoroughly evaluate cybersecurity datasets for LLM training and testing, covering the lifecycle from data creation to usage and identifying gaps for future research. In addition, we review new strategies for leveraging LLMs, including techniques like Half-Quadratic Quantization (HQQ), Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (RLHF), Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), Quantized Low-Rank Adapters (QLoRA), and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). These insights aim to enhance real-time cybersecurity defenses and improve the sophistication of LLM applications in threat detection and response. Our paper provides a foundational understanding and strategic direction for integrating LLMs into future cybersecurity frameworks, emphasizing innovation and robust model deployment to safeguard against evolving cyber threats.
SecureFalcon: The Next Cyber Reasoning System for Cyber Security
Jul 13, 2023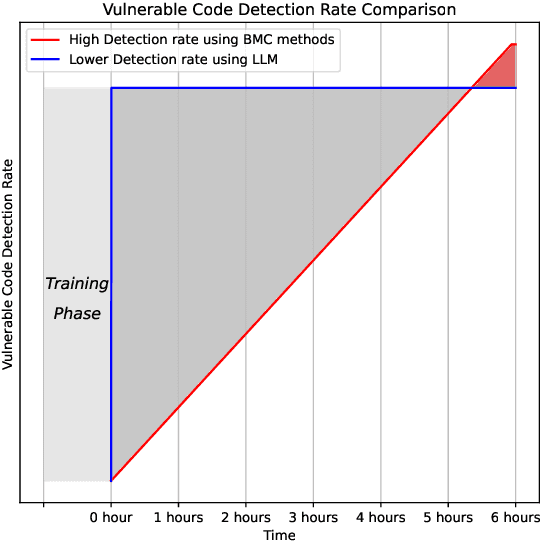
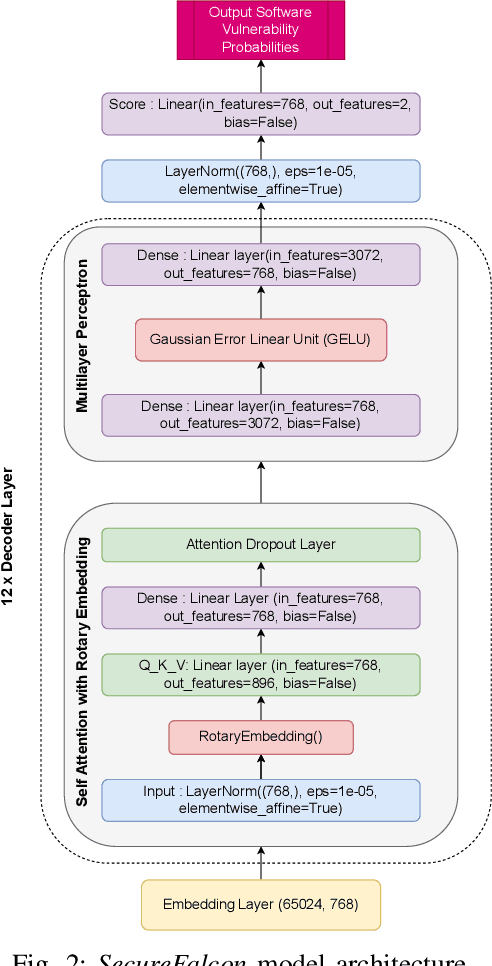
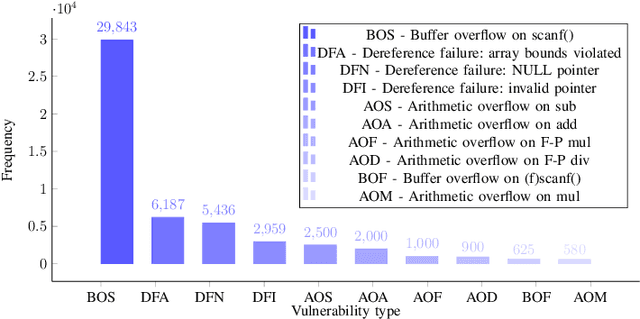
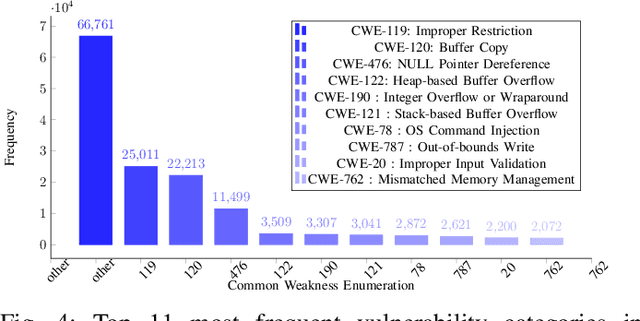
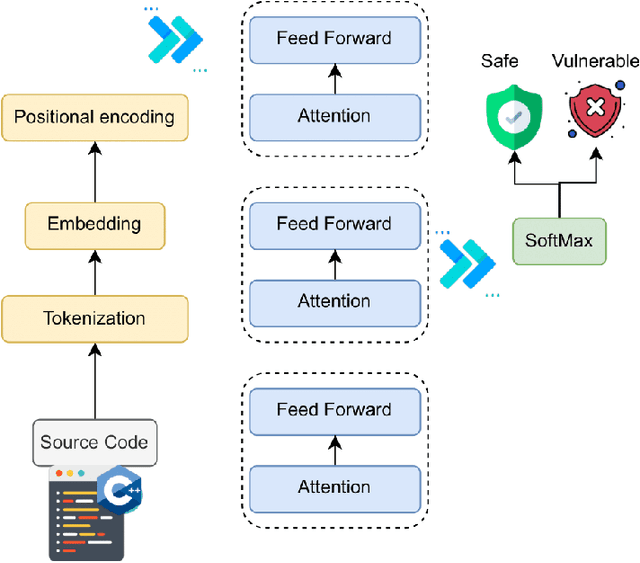
Abstract:Software vulnerabilities leading to various detriments such as crashes, data loss, and security breaches, significantly hinder the quality, affecting the market adoption of software applications and systems. Although traditional methods such as automated software testing, fault localization, and repair have been intensively studied, static analysis tools are most commonly used and have an inherent false positives rate, posing a solid challenge to developer productivity. Large Language Models (LLMs) offer a promising solution to these persistent issues. Among these, FalconLLM has shown substantial potential in identifying intricate patterns and complex vulnerabilities, hence crucial in software vulnerability detection. In this paper, for the first time, FalconLLM is being fine-tuned for cybersecurity applications, thus introducing SecureFalcon, an innovative model architecture built upon FalconLLM. SecureFalcon is trained to differentiate between vulnerable and non-vulnerable C code samples. We build a new training dataset, FormAI, constructed thanks to Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) and formal verification to evaluate its performance. SecureFalcon achieved an impressive 94% accuracy rate in detecting software vulnerabilities, emphasizing its significant potential to redefine software vulnerability detection methods in cybersecurity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge