Amit K. Chakraborty
Turning mechanistic models into forecasters by using machine learning
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:The equations of complex dynamical systems may not be identified by expert knowledge, especially if the underlying mechanisms are unknown. Data-driven discovery methods address this challenge by inferring governing equations from time-series data using a library of functions constructed from the measured variables. However, these methods typically assume time-invariant coefficients, which limits their ability to capture evolving system dynamics. To overcome this limitation, we allow some of the parameters to vary over time, learn their temporal evolution directly from data, and infer a system of equations that incorporates both constant and time-varying parameters. We then transform this framework into a forecasting model by predicting the time-varying parameters and substituting these predictions into the learned equations. The model is validated using datasets for Susceptible-Infected-Recovered, Consumer--Resource, greenhouse gas concentration, and Cyanobacteria cell count. By dynamically adapting to temporal shifts, our proposed model achieved a mean absolute error below 3\% for learning a time series and below 6\% for forecasting up to a month ahead. We additionally compare forecasting performance against CNN-LSTM and Gradient Boosting Machine (GBM), and show that our model outperforms these methods across most datasets. Our findings demonstrate that integrating time-varying parameters into data-driven discovery of differential equations improves both modeling accuracy and forecasting performance.
Deep Learning for Disease Outbreak Prediction: A Robust Early Warning Signal for Transcritical Bifurcations
Jan 14, 2025



Abstract:Early Warning Signals (EWSs) are vital for implementing preventive measures before a disease turns into a pandemic. While new diseases exhibit unique behaviors, they often share fundamental characteristics from a dynamical systems perspective. Moreover, measurements during disease outbreaks are often corrupted by different noise sources, posing challenges for Time Series Classification (TSC) tasks. In this study, we address the problem of having a robust EWS for disease outbreak prediction using a best-performing deep learning model in the domain of TSC. We employed two simulated datasets to train the model: one representing generated dynamical systems with randomly selected polynomial terms to model new disease behaviors, and another simulating noise-induced disease dynamics to account for noisy measurements. The model's performance was analyzed using both simulated data from different disease models and real-world data, including influenza and COVID-19. Results demonstrate that the proposed model outperforms previous models, effectively providing EWSs of impending outbreaks across various scenarios. This study bridges advancements in deep learning with the ability to provide robust early warning signals in noisy environments, making it highly applicable to real-world crises involving emerging disease outbreaks.
Methane projections from Canada's oil sands tailings using scientific deep learning reveal significant underestimation
Nov 11, 2024


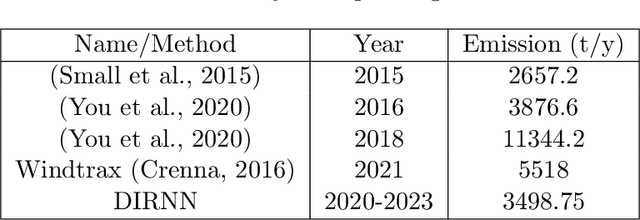
Abstract:Bitumen extraction for the production of synthetic crude oil in Canada's Athabasca Oil Sands industry has recently come under spotlight for being a significant source of greenhouse gas emission. A major cause of concern is methane, a greenhouse gas produced by the anaerobic biodegradation of hydrocarbons in oil sands residues, or tailings, stored in settle basins commonly known as oil sands tailing ponds. In order to determine the methane emitting potential of these tailing ponds and have future methane projections, we use real-time weather data, mechanistic models developed from laboratory controlled experiments, and industrial reports to train a physics constrained machine learning model. Our trained model can successfully identify the directions of active ponds and estimate their emission levels, which are generally hard to obtain due to data sampling restrictions. We found that each active oil sands tailing pond could emit between 950 to 1500 tonnes of methane per year, whose environmental impact is equivalent to carbon dioxide emissions from at least 6000 gasoline powered vehicles. Although abandoned ponds are often presumed to have insignificant emissions, our findings indicate that these ponds could become active over time and potentially emit up to 1000 tonnes of methane each year. Taking an average over all datasets that was used in model training, we estimate that emissions around major oil sands regions would need to be reduced by approximately 12% over a year, to reduce the average methane concentrations to 2005 levels.
Early detection of disease outbreaks and non-outbreaks using incidence data
Apr 13, 2024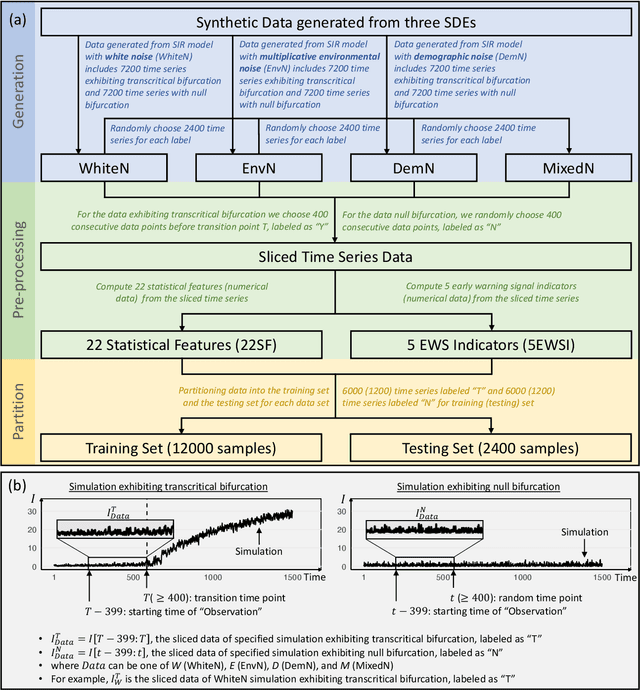
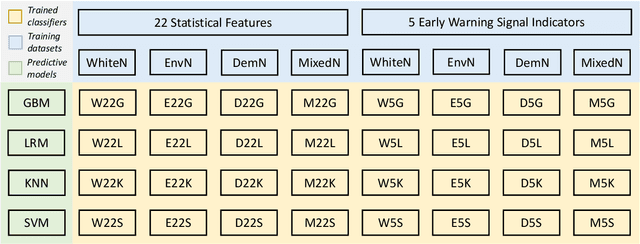
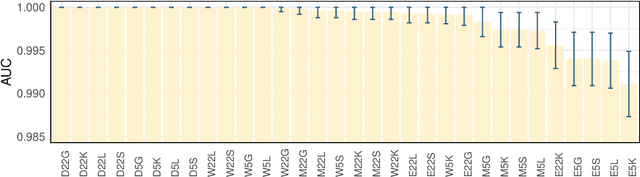
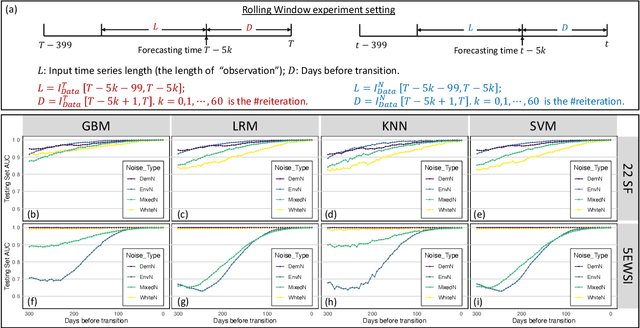
Abstract:Forecasting the occurrence and absence of novel disease outbreaks is essential for disease management. Here, we develop a general model, with no real-world training data, that accurately forecasts outbreaks and non-outbreaks. We propose a novel framework, using a feature-based time series classification method to forecast outbreaks and non-outbreaks. We tested our methods on synthetic data from a Susceptible-Infected-Recovered model for slowly changing, noisy disease dynamics. Outbreak sequences give a transcritical bifurcation within a specified future time window, whereas non-outbreak (null bifurcation) sequences do not. We identified incipient differences in time series of infectives leading to future outbreaks and non-outbreaks. These differences are reflected in 22 statistical features and 5 early warning signal indicators. Classifier performance, given by the area under the receiver-operating curve, ranged from 0.99 for large expanding windows of training data to 0.7 for small rolling windows. Real-world performances of classifiers were tested on two empirical datasets, COVID-19 data from Singapore and SARS data from Hong Kong, with two classifiers exhibiting high accuracy. In summary, we showed that there are statistical features that distinguish outbreak and non-outbreak sequences long before outbreaks occur. We could detect these differences in synthetic and real-world data sets, well before potential outbreaks occur.
An early warning indicator trained on stochastic disease-spreading models with different noises
Mar 24, 2024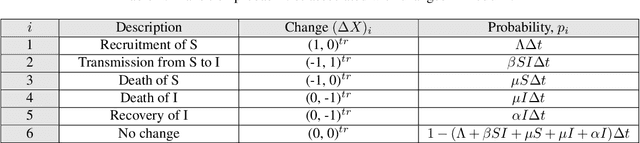
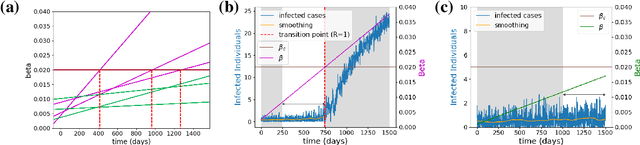
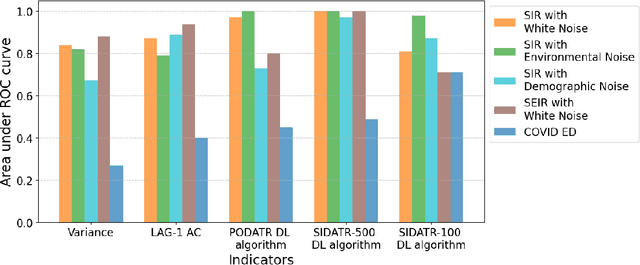
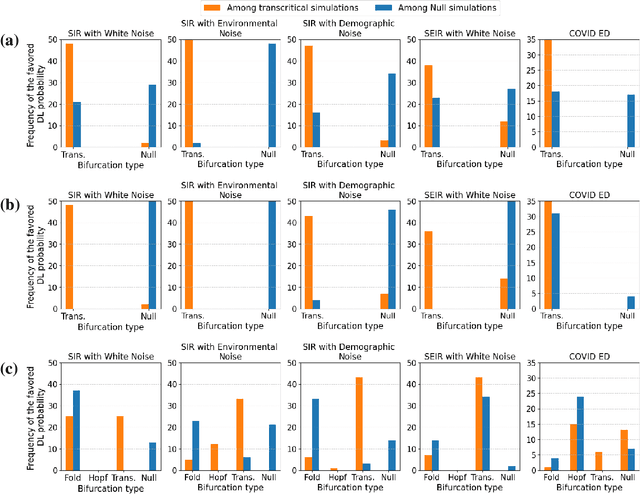
Abstract:The timely detection of disease outbreaks through reliable early warning signals (EWSs) is indispensable for effective public health mitigation strategies. Nevertheless, the intricate dynamics of real-world disease spread, often influenced by diverse sources of noise and limited data in the early stages of outbreaks, pose a significant challenge in developing reliable EWSs, as the performance of existing indicators varies with extrinsic and intrinsic noises. Here, we address the challenge of modeling disease when the measurements are corrupted by additive white noise, multiplicative environmental noise, and demographic noise into a standard epidemic mathematical model. To navigate the complexities introduced by these noise sources, we employ a deep learning algorithm that provides EWS in infectious disease outbreak by training on noise-induced disease-spreading models. The indicator's effectiveness is demonstrated through its application to real-world COVID-19 cases in Edmonton and simulated time series derived from diverse disease spread models affected by noise. Notably, the indicator captures an impending transition in a time series of disease outbreaks and outperforms existing indicators. This study contributes to advancing early warning capabilities by addressing the intricate dynamics inherent in real-world disease spread, presenting a promising avenue for enhancing public health preparedness and response efforts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge