Amardeep Kumar
LDKP: A Dataset for Identifying Keyphrases from Long Scientific Documents
Apr 01, 2022
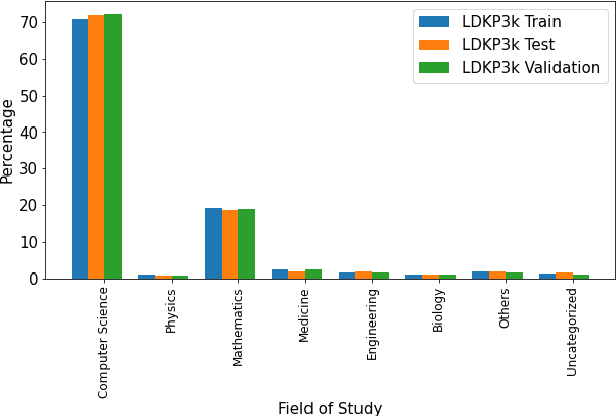
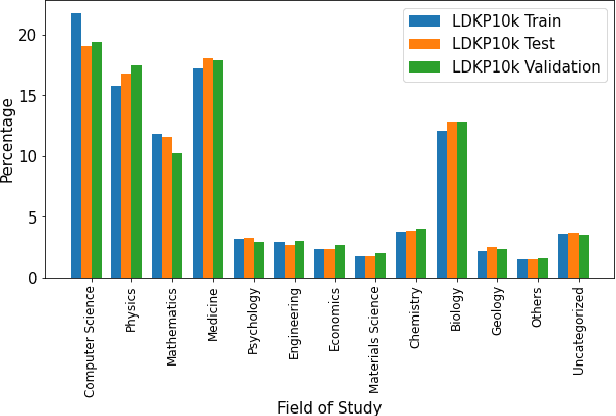

Abstract:Identifying keyphrases (KPs) from text documents is a fundamental task in natural language processing and information retrieval. Vast majority of the benchmark datasets for this task are from the scientific domain containing only the document title and abstract information. This limits keyphrase extraction (KPE) and keyphrase generation (KPG) algorithms to identify keyphrases from human-written summaries that are often very short (approx 8 sentences). This presents three challenges for real-world applications: human-written summaries are unavailable for most documents, the documents are almost always long, and a high percentage of KPs are directly found beyond the limited context of title and abstract. Therefore, we release two extensive corpora mapping KPs of ~1.3M and ~100K scientific articles with their fully extracted text and additional metadata including publication venue, year, author, field of study, and citations for facilitating research on this real-world problem.
GupShup: An Annotated Corpus for Abstractive Summarization of Open-Domain Code-Switched Conversations
Apr 17, 2021



Abstract:Code-switching is the communication phenomenon where speakers switch between different languages during a conversation. With the widespread adoption of conversational agents and chat platforms, code-switching has become an integral part of written conversations in many multi-lingual communities worldwide. This makes it essential to develop techniques for summarizing and understanding these conversations. Towards this objective, we introduce abstractive summarization of Hindi-English code-switched conversations and develop the first code-switched conversation summarization dataset - GupShup, which contains over 6,831 conversations in Hindi-English and their corresponding human-annotated summaries in English and Hindi-English. We present a detailed account of the entire data collection and annotation processes. We analyze the dataset using various code-switching statistics. We train state-of-the-art abstractive summarization models and report their performances using both automated metrics and human evaluation. Our results show that multi-lingual mBART and multi-view seq2seq models obtain the best performances on the new dataset
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge