Amanjit Kainth
Differentiable Greedy Networks
Oct 30, 2018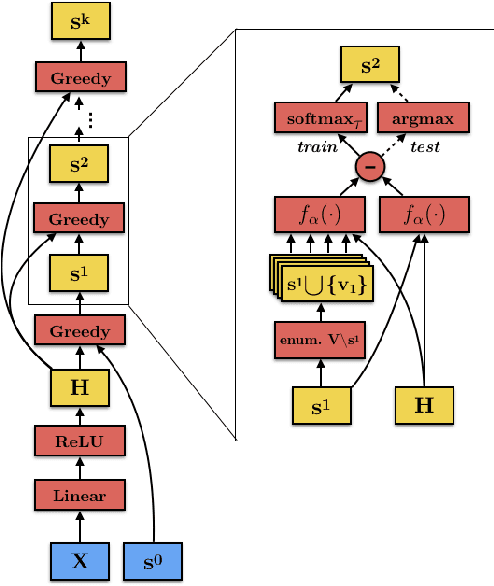
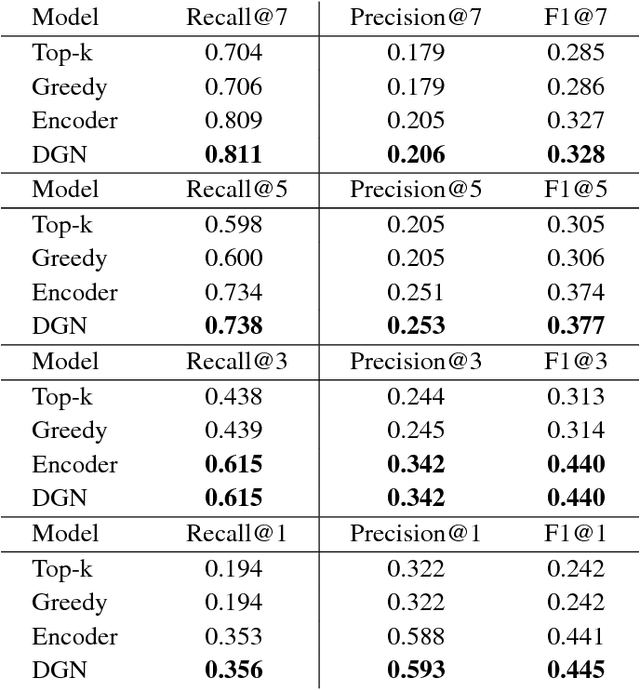
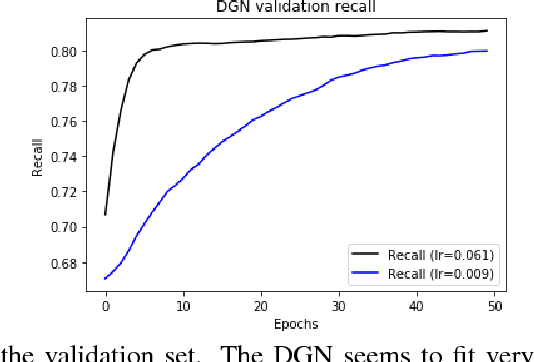
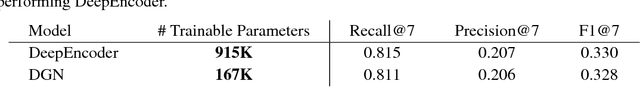
Abstract:Optimal selection of a subset of items from a given set is a hard problem that requires combinatorial optimization. In this paper, we propose a subset selection algorithm that is trainable with gradient-based methods yet achieves near-optimal performance via submodular optimization. We focus on the task of identifying a relevant set of sentences for claim verification in the context of the FEVER task. Conventional methods for this task look at sentences on their individual merit and thus do not optimize the informativeness of sentences as a set. We show that our proposed method which builds on the idea of unfolding a greedy algorithm into a computational graph allows both interpretability and gradient-based training. The proposed differentiable greedy network (DGN) outperforms discrete optimization algorithms as well as other baseline methods in terms of precision and recall.
Direct optimization of F-measure for retrieval-based personal question answering
Sep 28, 2018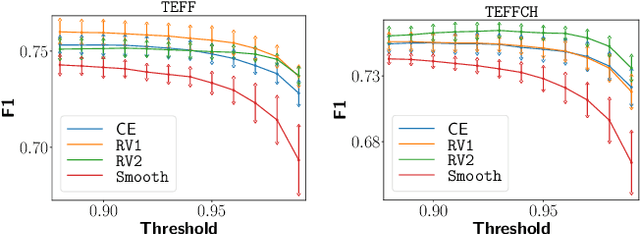
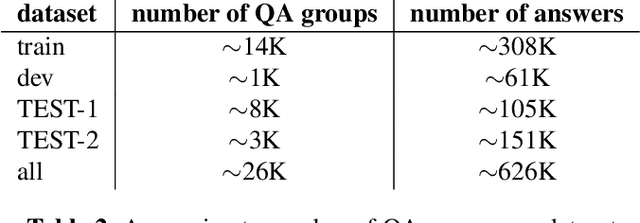
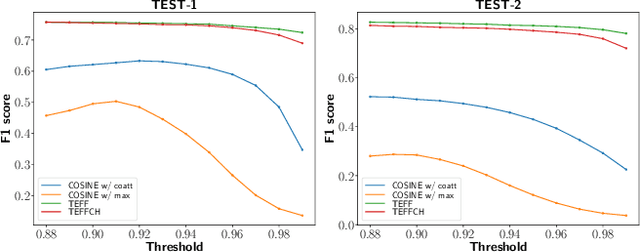
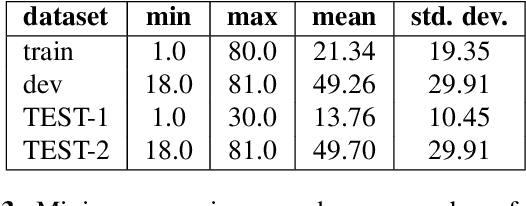
Abstract:Recent advances in spoken language technologies and the introduction of many customer facing products, have given rise to a wide customer reliance on smart personal assistants for many of their daily tasks. In this paper, we present a system to reduce users' cognitive load by extending personal assistants with long-term personal memory where users can store and retrieve by voice, arbitrary pieces of information. The problem is framed as a neural retrieval based question answering system where answers are selected from previously stored user memories. We propose to directly optimize the end-to-end retrieval performance, measured by the F1-score, using reinforcement learning, leading to better performance on our experimental test set(s).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge