Ali Karimi
Introducing One Sided Margin Loss for Solving Classification Problems in Deep Networks
Jun 02, 2022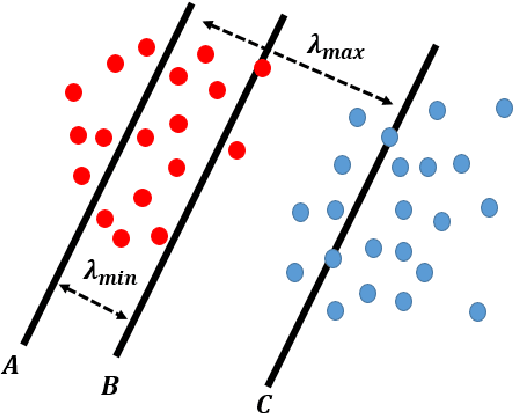
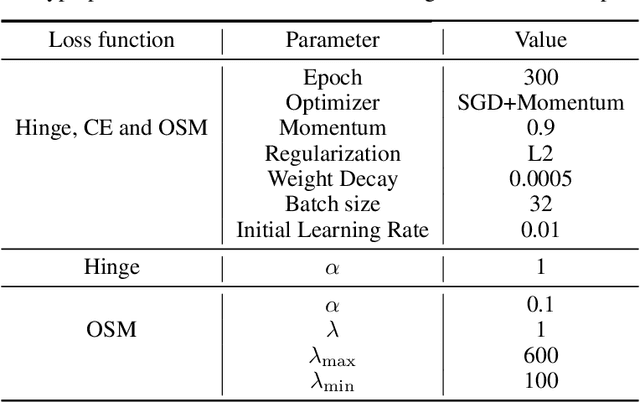

Abstract:This paper introduces a new loss function, OSM (One-Sided Margin), to solve maximum-margin classification problems effectively. Unlike the hinge loss, in OSM the margin is explicitly determined with corresponding hyperparameters and then the classification problem is solved. In experiments, we observe that using OSM loss leads to faster training speeds and better accuracies than binary and categorical cross-entropy in several commonly used deep models for classification and optical character recognition problems. OSM has consistently shown better classification accuracies over cross-entropy and hinge losses for small to large neural networks. it has also led to a more efficient training procedure. We achieved state-of-the-art accuracies for small networks on several benchmark datasets of CIFAR10(98.82\%), CIFAR100(91.56\%), Flowers(98.04\%), Stanford Cars(93.91\%) with considerable improvements over other loss functions. Moreover, the accuracies are rather better than cross-entropy and hinge loss for large networks. Therefore, we strongly believe that OSM is a powerful alternative to hinge and cross-entropy losses to train deep neural networks on classification tasks.
Learning Enhancement of CNNs via Separation Index Maximizing at the First Convolutional Layer
Jan 13, 2022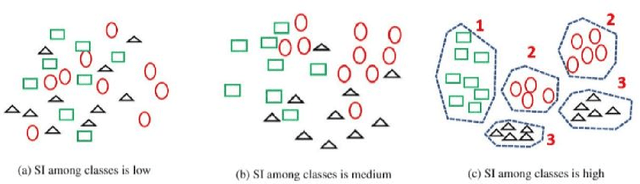
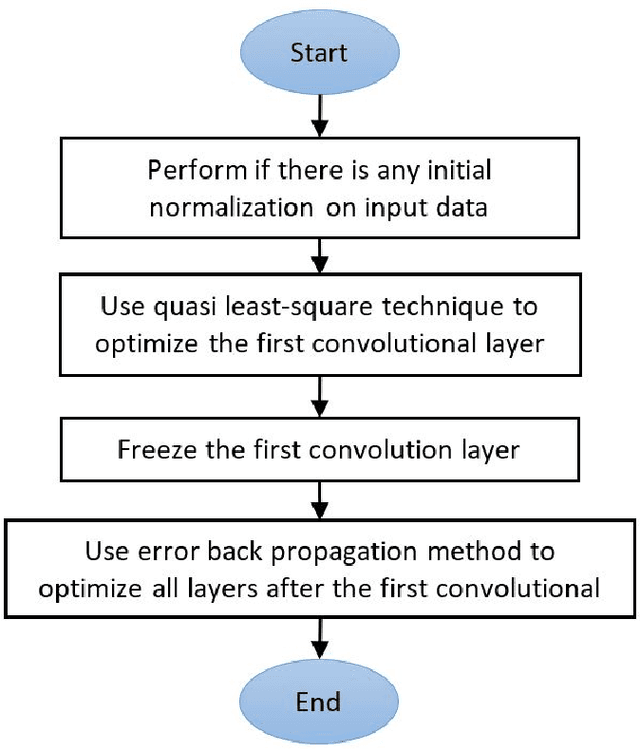

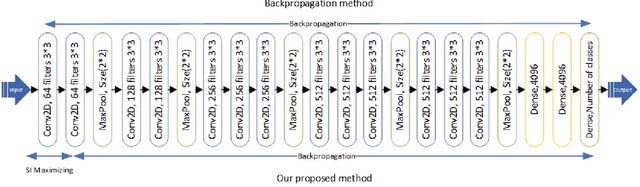
Abstract:In this paper, a straightforward enhancement learning algorithm based on Separation Index (SI) concept is proposed for Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). At first, the SI as a supervised complexity measure is explained its usage in better learning of CNNs for classification problems illustrate. Then, a learning strategy proposes through which the first layer of a CNN is optimized by maximizing the SI, and the further layers are trained through the backpropagation algorithm to learn further layers. In order to maximize the SI at the first layer, A variant of ranking loss is optimized by using the quasi least square error technique. Applying such a learning strategy to some known CNNs and datasets, its enhancement impact in almost all cases is demonstrated.
Soccer Event Detection Using Deep Learning
Feb 08, 2021


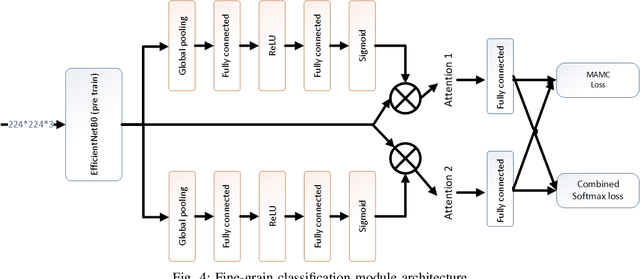
Abstract:Event detection is an important step in extracting knowledge from the video. In this paper, we propose a deep learning approach to detect events in a soccer match emphasizing the distinction between images of red and yellow cards and the correct detection of the images of selected events from other images. This method includes the following three modules: i) the variational autoencoder (VAE) module to differentiate between soccer images and others image, ii) the image classification module to classify the images of events, and iii) the fine-grain image classification module to classify the images of red and yellow cards. Additionally, a new dataset was introduced for soccer images classification that is employed to train the networks mentioned in the paper. In the final section, 10 UEFA Champions League matches are used to evaluate the networks' performance and precision in detecting the events. The experiments demonstrate that the proposed method achieves better performance than state-of-the-art methods.
EfficientNet-Absolute Zero for Continuous Speech Keyword Spotting
Dec 31, 2020
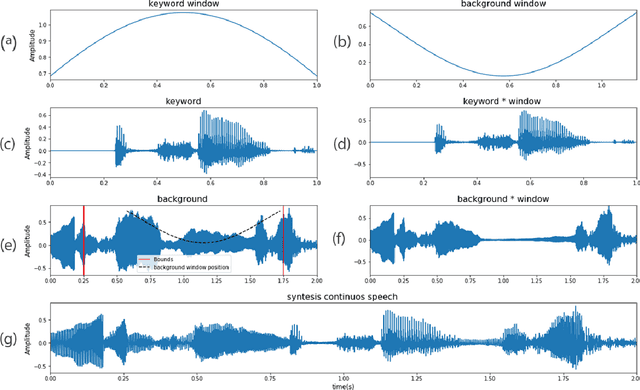
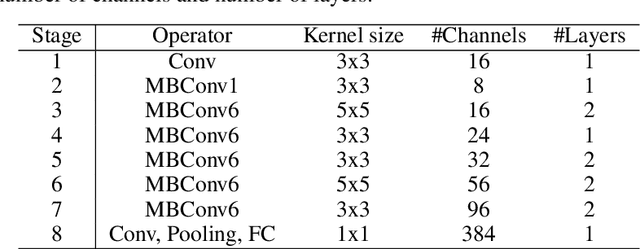

Abstract:Keyword spotting is a process of finding some specific words or phrases in recorded speeches by computers. Deep neural network algorithms, as a powerful engine, can handle this problem if they are trained over an appropriate dataset. To this end, the football keyword dataset (FKD), as a new keyword spotting dataset in Persian, is collected with crowdsourcing. This dataset contains nearly 31000 samples in 18 classes. The continuous speech synthesis method proposed to made FKD usable in the practical application which works with continuous speeches. Besides, we proposed a lightweight architecture called EfficientNet-A0 (absolute zero) by applying the compound scaling method on EfficientNet-B0 for keyword spotting task. Finally, the proposed architecture is evaluated with various models. It is realized that EfficientNet-A0 and Resnet models outperform other models on this dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge