Ali Asgari
Metamorphic Testing of Deep Code Models: A Systematic Literature Review
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:Large language models and deep learning models designed for code intelligence have revolutionized the software engineering field due to their ability to perform various code-related tasks. These models can process source code and software artifacts with high accuracy in tasks such as code completion, defect detection, and code summarization; therefore, they can potentially become an integral part of modern software engineering practices. Despite these capabilities, robustness remains a critical quality attribute for deep-code models as they may produce different results under varied and adversarial conditions (e.g., variable renaming). Metamorphic testing has become a widely used approach to evaluate models' robustness by applying semantic-preserving transformations to input programs and analyzing the stability of model outputs. While prior research has explored testing deep learning models, this systematic literature review focuses specifically on metamorphic testing for deep code models. By studying 45 primary papers, we analyze the transformations, techniques, and evaluation methods used to assess robustness. Our review summarizes the current landscape, identifying frequently evaluated models, programming tasks, datasets, target languages, and evaluation metrics, and highlights key challenges and future directions for advancing the field.
Towards a Safety Case for Hardware Fault Tolerance in Convolutional Neural Networks Using Activation Range Supervision
Aug 16, 2021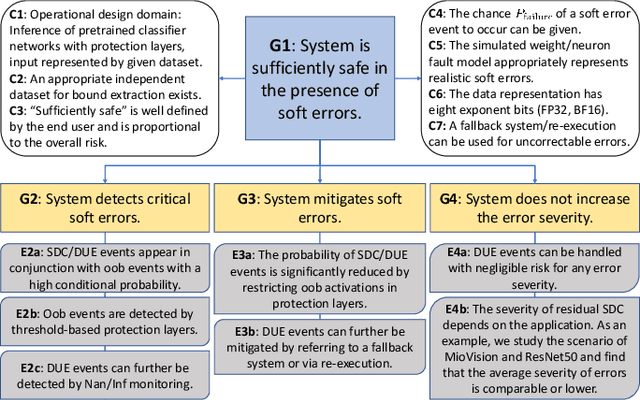
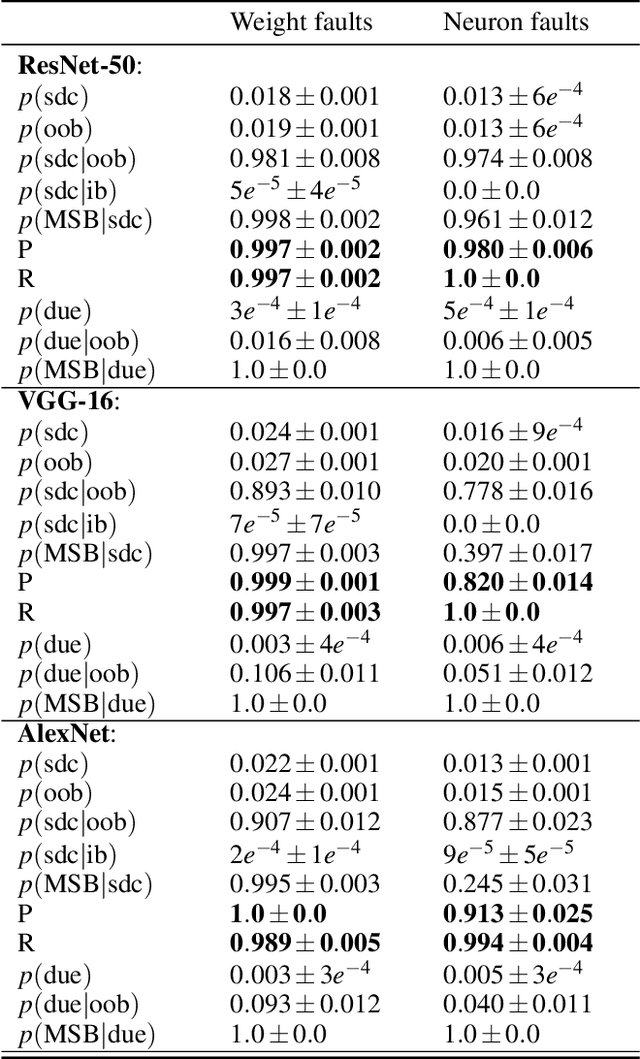
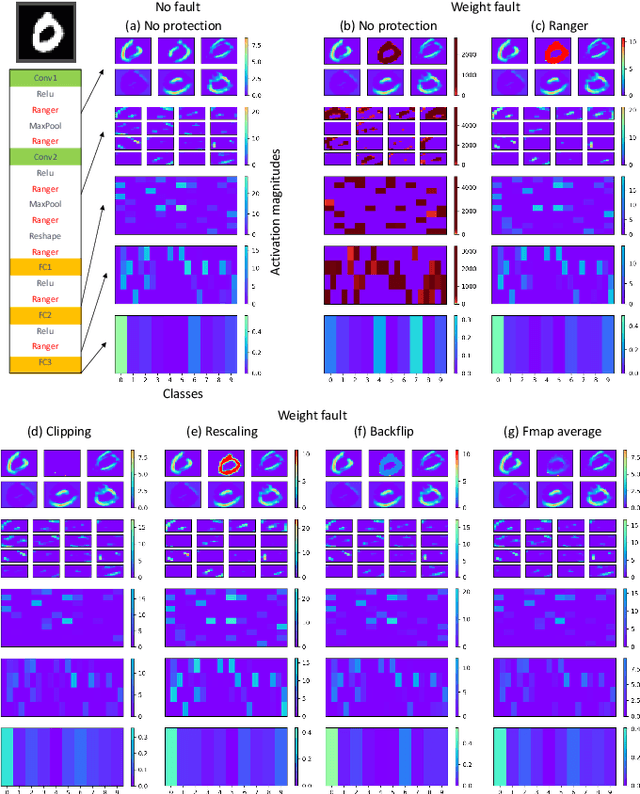
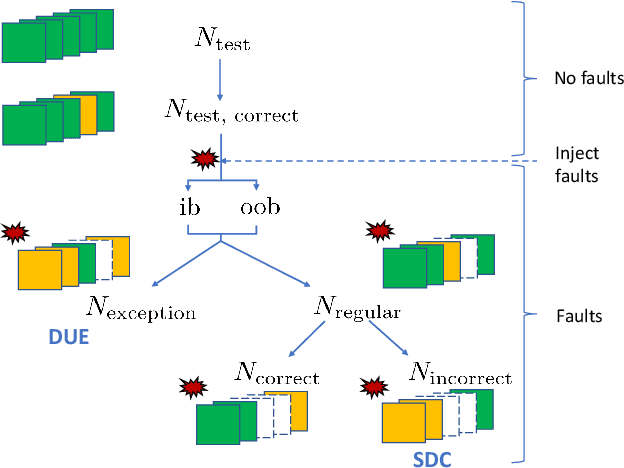
Abstract:Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have become an established part of numerous safety-critical computer vision applications, including human robot interactions and automated driving. Real-world implementations will need to guarantee their robustness against hardware soft errors corrupting the underlying platform memory. Based on the previously observed efficacy of activation clipping techniques, we build a prototypical safety case for classifier CNNs by demonstrating that range supervision represents a highly reliable fault detector and mitigator with respect to relevant bit flips, adopting an eight-exponent floating point data representation. We further explore novel, non-uniform range restriction methods that effectively suppress the probability of silent data corruptions and uncorrectable errors. As a safety-relevant end-to-end use case, we showcase the benefit of our approach in a vehicle classification scenario, using ResNet-50 and the traffic camera data set MIOVision. The quantitative evidence provided in this work can be leveraged to inspire further and possibly more complex CNN safety arguments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge