Alexey Kharlamov
High-Resolution Daytime Translation Without Domain Labels
Mar 23, 2020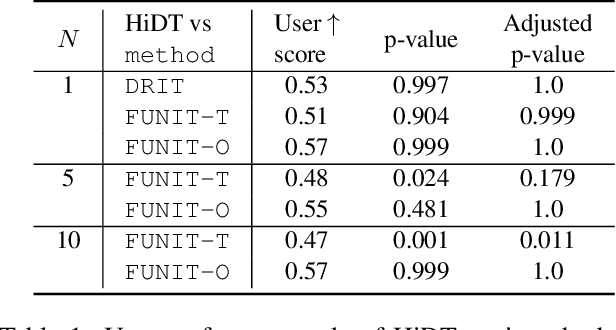
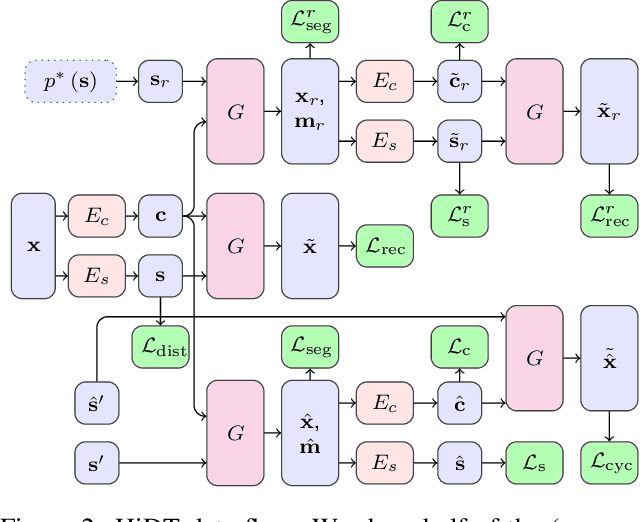
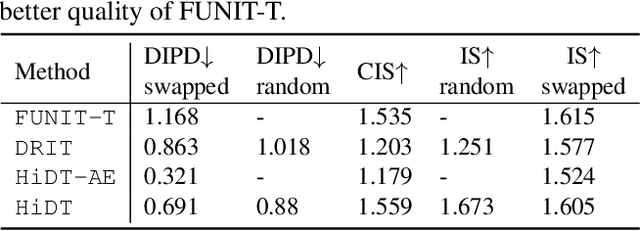
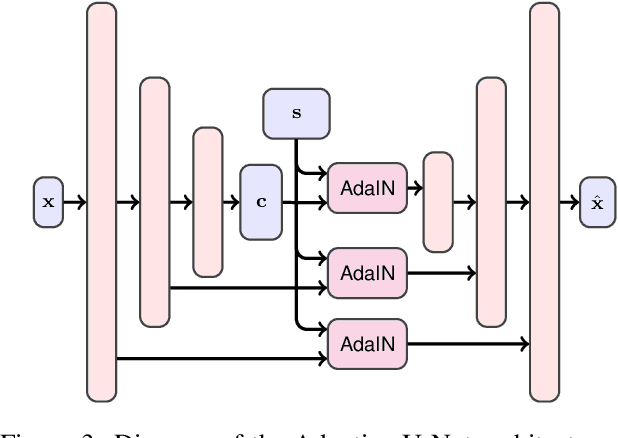
Abstract:Modeling daytime changes in high resolution photographs, e.g., re-rendering the same scene under different illuminations typical for day, night, or dawn, is a challenging image manipulation task. We present the high-resolution daytime translation (HiDT) model for this task. HiDT combines a generative image-to-image model and a new upsampling scheme that allows to apply image translation at high resolution. The model demonstrates competitive results in terms of both commonly used GAN metrics and human evaluation. Importantly, this good performance comes as a result of training on a dataset of still landscape images with no daytime labels available. Our results are available at https://saic-mdal.github.io/HiDT/.
Recognition of Russian traffic signs in winter conditions. Solutions of the "Ice Vision" competition winners
Sep 16, 2019

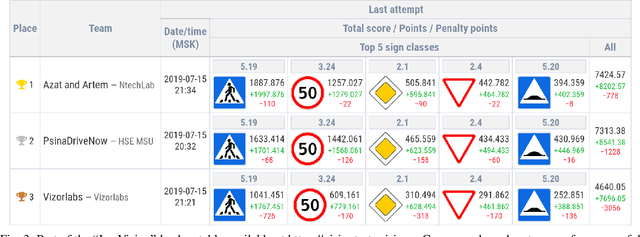
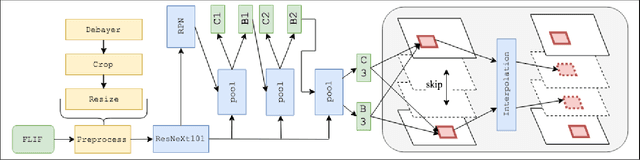
Abstract:With the advancements of various autonomous car projects aiming to achieve SAE Level 5, real-time detection of traffic signs in real-life scenarios has become a highly relevant problem for the industry. Even though a great progress has been achieved in this field, there is still no clear consensus on what the state-of-the-art in this field is. Moreover, it is important to develop and test systems in various regions and conditions. This is why the "Ice Vision" competition has focused on the detection of Russian traffic signs in winter conditions. The IceVisionSet dataset used for this competition features real-world collection of lossless frame sequences with traffic sign annotations. The sequences were collected in varying conditions, including: different weather, camera exposure, illumination and moving speeds. In this work we describe the competition and present the solutions of the 3 top teams.
A Machine-Synesthetic Approach To DDoS Network Attack Detection
Jan 13, 2019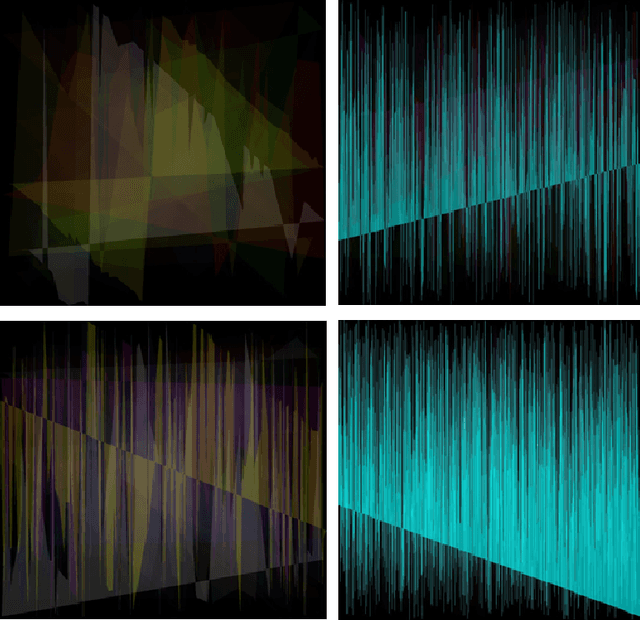

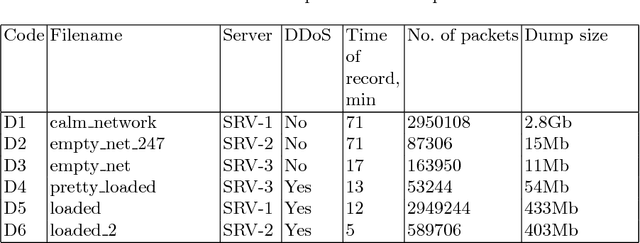
Abstract:In the authors' opinion, anomaly detection systems, or ADS, seem to be the most perspective direction in the subject of attack detection, because these systems can detect, among others, the unknown (zero-day) attacks. To detect anomalies, the authors propose to use machine synesthesia. In this case, machine synesthesia is understood as an interface that allows using image classification algorithms in the problem of detecting network anomalies, making it possible to use non-specialized image detection methods that have recently been widely and actively developed. The proposed approach is that the network traffic data is "projected" into the image. It can be seen from the experimental results that the proposed method for detecting anomalies shows high results in the detection of attacks. On a large sample, the value of the complex efficiency indicator reaches 97%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge