Alex Tiong Heng Sia
oRetrieval Augmented Generation for 10 Large Language Models and its Generalizability in Assessing Medical Fitness
Oct 11, 2024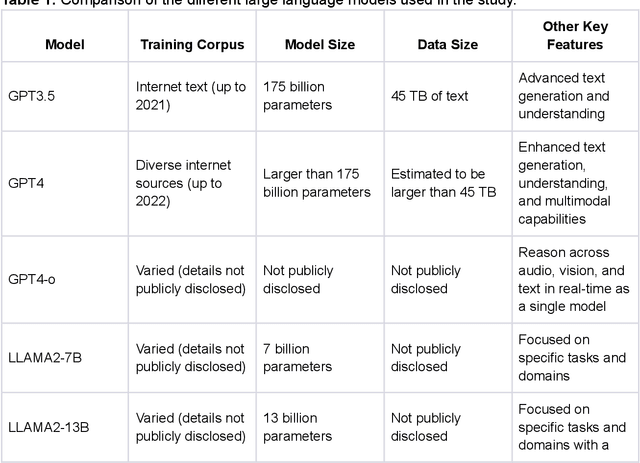



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) show potential for medical applications but often lack specialized clinical knowledge. Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) allows customization with domain-specific information, making it suitable for healthcare. This study evaluates the accuracy, consistency, and safety of RAG models in determining fitness for surgery and providing preoperative instructions. We developed LLM-RAG models using 35 local and 23 international preoperative guidelines and tested them against human-generated responses. A total of 3,682 responses were evaluated. Clinical documents were processed using Llamaindex, and 10 LLMs, including GPT3.5, GPT4, and Claude-3, were assessed. Fourteen clinical scenarios were analyzed, focusing on seven aspects of preoperative instructions. Established guidelines and expert judgment were used to determine correct responses, with human-generated answers serving as comparisons. The LLM-RAG models generated responses within 20 seconds, significantly faster than clinicians (10 minutes). The GPT4 LLM-RAG model achieved the highest accuracy (96.4% vs. 86.6%, p=0.016), with no hallucinations and producing correct instructions comparable to clinicians. Results were consistent across both local and international guidelines. This study demonstrates the potential of LLM-RAG models for preoperative healthcare tasks, highlighting their efficiency, scalability, and reliability.
Development and Testing of Retrieval Augmented Generation in Large Language Models -- A Case Study Report
Jan 29, 2024Abstract:Purpose: Large Language Models (LLMs) hold significant promise for medical applications. Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) emerges as a promising approach for customizing domain knowledge in LLMs. This case study presents the development and evaluation of an LLM-RAG pipeline tailored for healthcare, focusing specifically on preoperative medicine. Methods: We developed an LLM-RAG model using 35 preoperative guidelines and tested it against human-generated responses, with a total of 1260 responses evaluated. The RAG process involved converting clinical documents into text using Python-based frameworks like LangChain and Llamaindex, and processing these texts into chunks for embedding and retrieval. Vector storage techniques and selected embedding models to optimize data retrieval, using Pinecone for vector storage with a dimensionality of 1536 and cosine similarity for loss metrics. Human-generated answers, provided by junior doctors, were used as a comparison. Results: The LLM-RAG model generated answers within an average of 15-20 seconds, significantly faster than the 10 minutes typically required by humans. Among the basic LLMs, GPT4.0 exhibited the best accuracy of 80.1%. This accuracy was further increased to 91.4% when the model was enhanced with RAG. Compared to the human-generated instructions, which had an accuracy of 86.3%, the performance of the GPT4.0 RAG model demonstrated non-inferiority (p=0.610). Conclusions: In this case study, we demonstrated a LLM-RAG model for healthcare implementation. The pipeline shows the advantages of grounded knowledge, upgradability, and scalability as important aspects of healthcare LLM deployment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge