Alex Ho
DisCo-DSO: Coupling Discrete and Continuous Optimization for Efficient Generative Design in Hybrid Spaces
Dec 15, 2024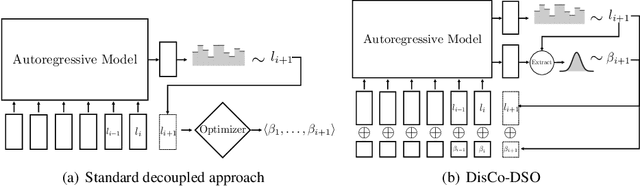
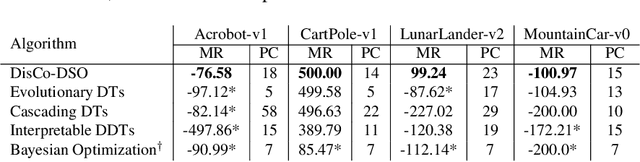
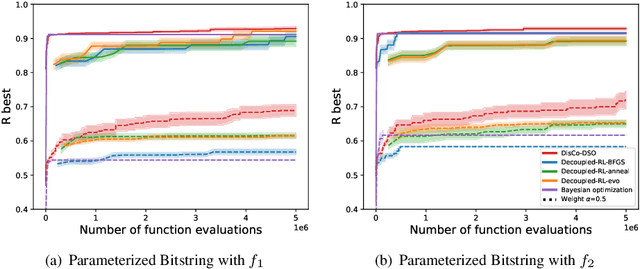
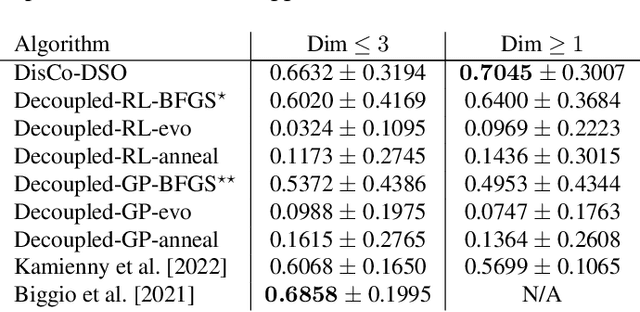
Abstract:We consider the challenge of black-box optimization within hybrid discrete-continuous and variable-length spaces, a problem that arises in various applications, such as decision tree learning and symbolic regression. We propose DisCo-DSO (Discrete-Continuous Deep Symbolic Optimization), a novel approach that uses a generative model to learn a joint distribution over discrete and continuous design variables to sample new hybrid designs. In contrast to standard decoupled approaches, in which the discrete and continuous variables are optimized separately, our joint optimization approach uses fewer objective function evaluations, is robust against non-differentiable objectives, and learns from prior samples to guide the search, leading to significant improvement in performance and sample efficiency. Our experiments on a diverse set of optimization tasks demonstrate that the advantages of DisCo-DSO become increasingly evident as the complexity of the problem increases. In particular, we illustrate DisCo-DSO's superiority over the state-of-the-art methods for interpretable reinforcement learning with decision trees.
Learning Temporally Causal Latent Processes from General Temporal Data
Oct 11, 2021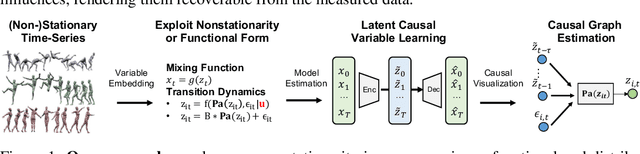
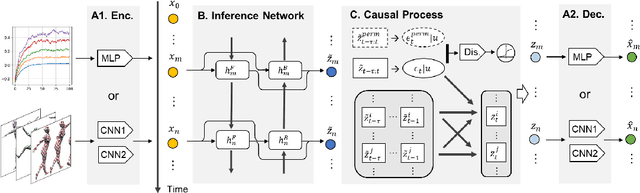
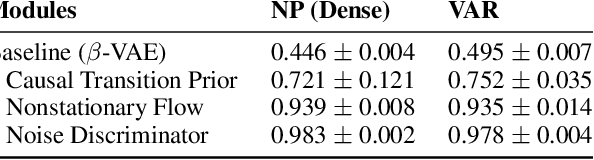
Abstract:Our goal is to recover time-delayed latent causal variables and identify their relations from measured temporal data. Estimating causally-related latent variables from observations is particularly challenging as the latent variables are not uniquely recoverable in the most general case. In this work, we consider both a nonparametric, nonstationary setting and a parametric setting for the latent processes and propose two provable conditions under which temporally causal latent processes can be identified from their nonlinear mixtures. We propose LEAP, a theoretically-grounded architecture that extends Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) by enforcing our conditions through proper constraints in causal process prior. Experimental results on various data sets demonstrate that temporally causal latent processes are reliably identified from observed variables under different dependency structures and that our approach considerably outperforms baselines that do not leverage history or nonstationarity information. This is one of the first works that successfully recover time-delayed latent processes from nonlinear mixtures without using sparsity or minimality assumptions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge