Alessio Zappone
CNIT and University of Cassino and Southern Lazio, Cassino, Italy
Holographic & Channel-Aware Distributed Detection of a Non-cooperative Target
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:This work investigates Distributed Detection (DD) in Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs), where spatially distributed sensors transmit binary decisions over a shared flat-fading channel. To enhance fusion efficiency, a reconfigurable metasurface is positioned in the near-field of a few receive antennas, enabling a holographic architecture that harnesses large-aperture gains with minimal RF hardware. A generalized likelihood ratio test is derived for fixed metasurface settings, and two low-complexity joint design strategies are proposed to optimize both fusion and metasurface configuration. These suboptimal schemes achieve a balance between performance, complexity, and system knowledge. The goal is to ensure reliable detection of a localized phenomenon at the fusion center, under energy-efficient constraints aligned with IoT requirements. Simulation results validate the effectiveness of the proposed holographic fusion, even under simplified designs.
Design of RIS-aided mMTC+ Networks for Rate Maximization under the Finite Blocklength Regime with Imperfect Channel Knowledge
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Within the context of massive machine-type communications+, reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) represent a promising technology to boost system performance in scenarios with poor channel conditions. Considering single-antenna sensors transmitting short data packets to a multiple-antenna collector node, we introduce and design an RIS to maximize the weighted sum rate (WSR) of the system working in the finite blocklength regime. Due to the large number of reflecting elements and their passive nature, channel estimation errors may occur. In this letter, we then propose a robust RIS optimization to combat such a detrimental issue. Based on concave bounds and approximations, the nonconvex WSR problem for the RIS response is addressed via successive convex optimization (SCO). Numerical experiments validate the performance and complexity of the SCO solutions.
* This work has been accepted for publication in IEEE Communications Letters. The final published version is available via IEEE Xplore
Energy Efficiency Maximization of MIMO Systems through Reconfigurable Holographic Beamforming
Jan 02, 2026Abstract:This study considers a point-to-point wireless link, in which both the transmitter and receiver are equipped with multiple antennas. In addition, two reconfigurable metasurfaces are deployed, one in the immediate vicinity of the transmit antenna array, and one in the immediate vicinity of the receive antenna array. The resulting architecture implements a holographic beamforming structure at both the transmitter and receiver. In this scenario, the system energy efficiency is optimized with respect to the transmit covariance matrix, and the reflection matrices of the two metasurfaces. A low-complexity algorithm is developed, which is guaranteed to converge to a first-order optimal point of the energy efficiency maximization problem. Moreover, closed-form expressions are derived for the metasurface matrices in the special case of single-antenna or single-stream transmission. The two metasurfaces are considered to be nearly-passive and subject to global reflection constraints. A numerical performance analysis is conducted to assess the performance of the proposed optimization methods, showing, in particular, that the use of holographic beamforming by metasurfaces can provide significant energy efficiency gains compared to fully digital beamforming architectures, even when the latter achieve substantial multiplexing gains.
Channel-Aware Holographic Decision Fusion
May 27, 2025Abstract:This work investigates Distributed Detection (DD) in Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) utilizing channel-aware binary-decision fusion over a shared flat-fading channel. A reconfigurable metasurface, positioned in the near-field of a limited number of receive antennas, is integrated to enable a holographic Decision Fusion (DF) system. This approach minimizes the need for multiple RF chains while leveraging the benefits of a large array. The optimal fusion rule for a fixed metasurface configuration is derived, alongside two suboptimal joint fusion rule and metasurface design strategies. These suboptimal approaches strike a balance between reduced complexity and lower system knowledge requirements, making them practical alternatives. The design objective focuses on effectively conveying the information regarding the phenomenon of interest to the FC while promoting energy-efficient data analytics aligned with the Internet of Things (IoT) paradigm. Simulation results underscore the viability of holographic DF, demonstrating its advantages even with suboptimal designs and highlighting the significant energy-efficiency gains achieved by the proposed system.
Rate Optimization for RIS-Aided mMTC Networks in the Finite Blocklength Regime
Dec 10, 2024
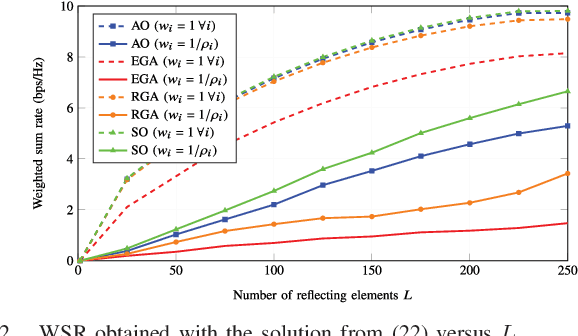
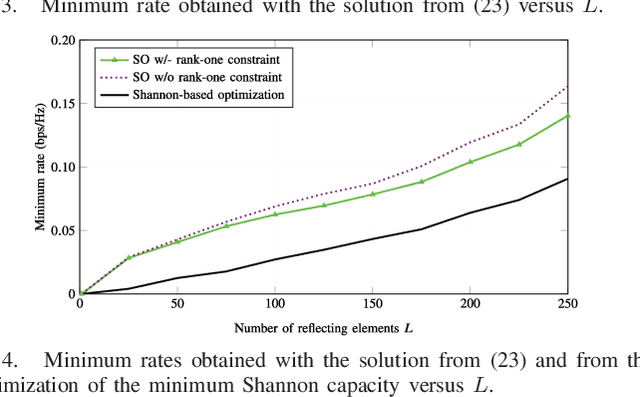
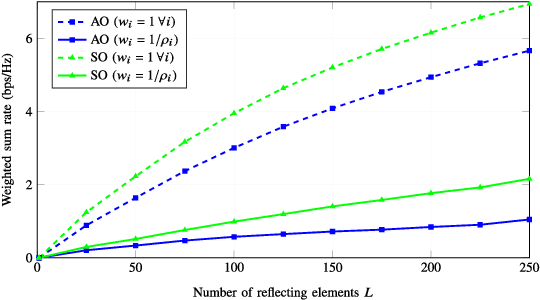
Abstract:Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) have become a promising candidate for the development of future mobile systems. In the context of massive machine-type communications (mMTC), a RIS can be used to support the transmission from a group of sensors to a collector node. Due to the short data packets, we focus on the design of the RIS for maximizing the weighted sum and minimum rates in the finite blocklength regime. Under the assumption of non-orthogonal multiple access, successive interference cancelation is considered as a decoding scheme to mitigate interference. Accordingly, we formulate the optimizations as non-convex problems and propose two sub-optimal solutions based on gradient ascent (GA) and sequential optimization (SO) with semi-definite relaxation (SDR). In the GA, we distinguish between Euclidean and Riemannian gradients. For the SO, we derive a concave lower bound for the throughput and maximize it sequentially applying SDR. Numerical results show that the SO can outperform the GA and that strategies relying on the optimization of the classical Shannon capacity might be inadequate for mMTC networks.
* Paper accepted to be published at IEEE Communications Letters
Rate Region of RIS-Aided URLLC Broadcast Channels: Diagonal versus Beyond Diagonal Globally Passive RIS
Oct 28, 2024
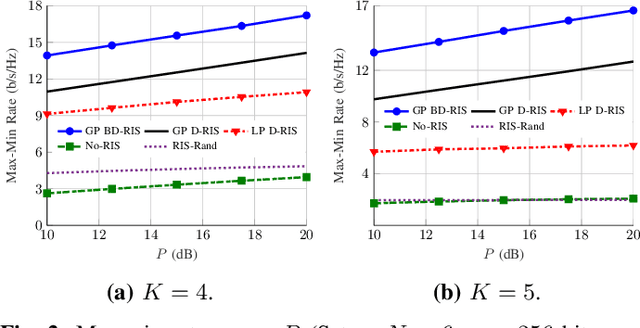
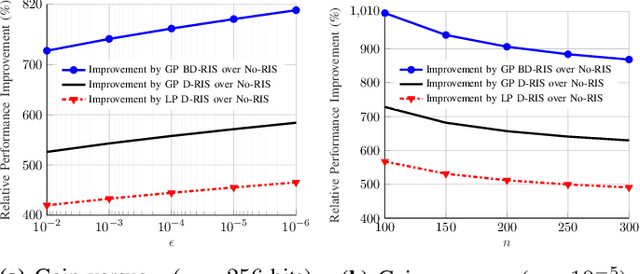
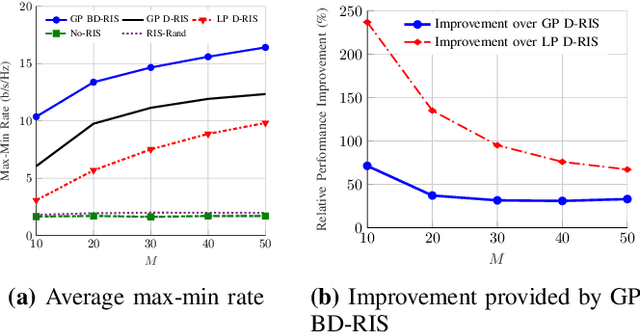
Abstract:We analyze the finite-block-length rate region of wireless systems aided by reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs), employing treating interference as noise. We consider three nearly passive RIS architectures, including locally passive (LP) diagonal (D), globally passive (GP) D, and GP beyond diagonal (BD) RISs. In a GP RIS, the power constraint is applied globally to the whole surface, while some elements may amplify the incident signal locally. The considered RIS architectures provide substantial performance gains compared with systems operating without RIS. GP BD-RIS outperforms, at the price of increasing the complexity, LP and GP D-RIS as it enlarges the feasible set of allowed solutions. However, the gain provided by BD-RIS decreases with the number of RIS elements. Additionally, deploying RISs provides higher gains as the reliability/latency requirement becomes more stringent.
Secrecy Energy Efficiency Maximization in RIS-Aided Wireless Networks
Jun 11, 2024



Abstract:This work proposes a provably convergent and low complexity optimization algorithm for the maximization of the secrecy energy efficiency in the uplink of a wireless network aided by a Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS), in the presence of an eavesdropper. The mobil users' transmit powers and the RIS reflection coefficients are optimized. Numerical results show the performance of the proposed methods and compare the use of active and nearly-passive RISs from an energy-efficient perspective.
Energy Efficiency in RIS-Aided Wireless Networks: Active or Passive RIS?
Mar 08, 2023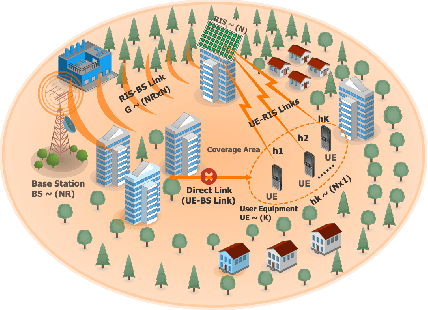
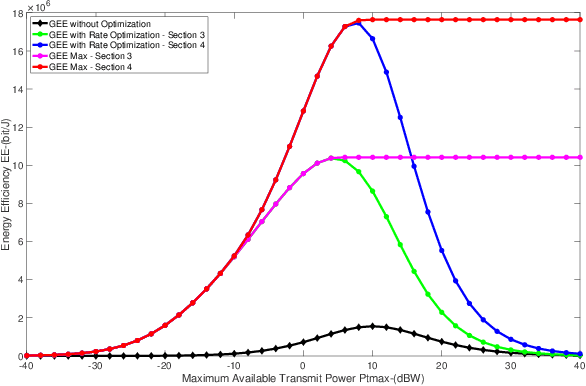
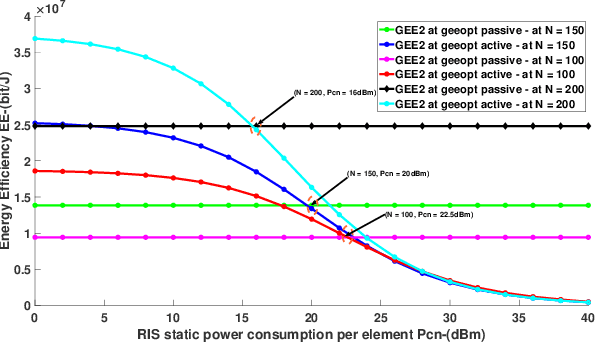
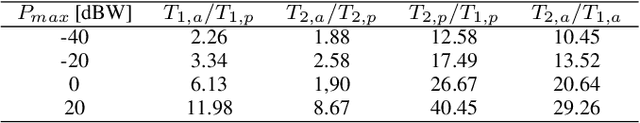
Abstract:This work addresses the comparison between active and passive RISs in wireless networks, with reference to the system energy efficiency (EE). To provably convergent and computationally-friendly EE maximization algorithms are developed, which optimize the reflection coefficients of the RIS, the transmit powers, and the linear receive filters. Numerical results show the performance of the proposed methods and discuss the operating points in which active or passive RISs should be preferred from an energy-efficient perspective.
Energy Efficiency Maximization in RIS-Aided Networks with Global Reflection Constraints
Mar 06, 2023



Abstract:This work addresses the issue of energy efficiency maximization in a multi-user network aided by reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) with global reflection capabilities. Two optimization methods are proposed to optimize the mobile users' powers, the RIS coefficients and the linear receive filters. Both methods are provably convergent and require only the solution of convex optimization problems. The numerical results show that the proposed methods largely outperform heuristic resource allocation schemes.
Digital Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces: On the Impact of Realistic Reradiation Models
May 19, 2022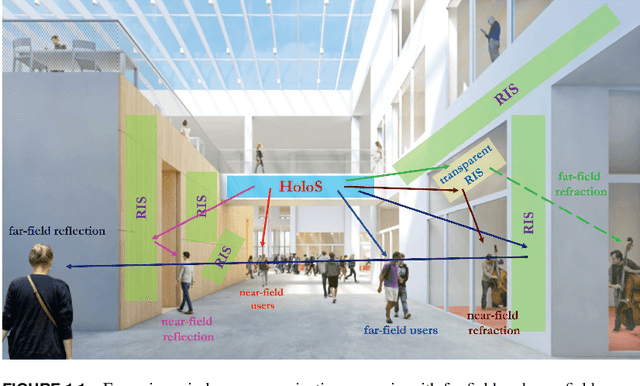
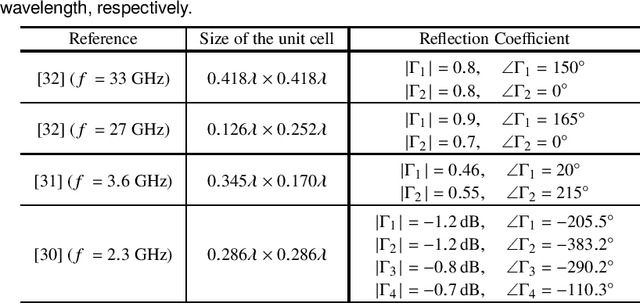
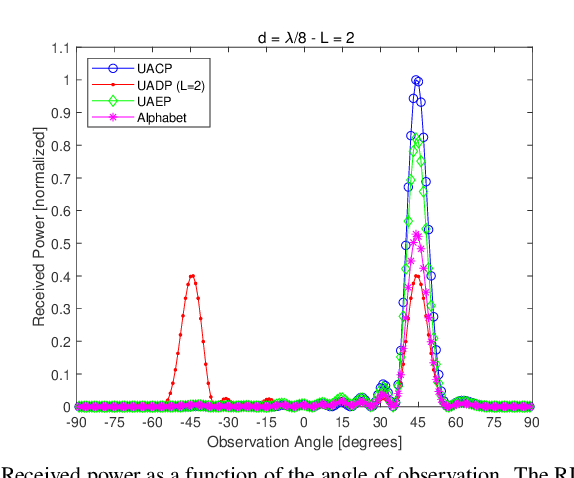
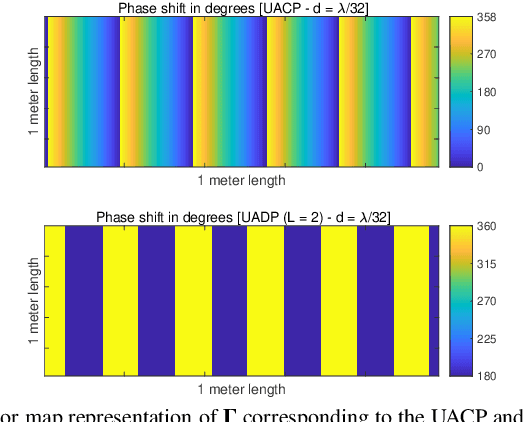
Abstract:Reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) is an emerging technology that is under investigation for different applications in wireless communications. RISs are often analyzed and optimized by considering simplified electromagnetic reradiation models. In this chapter, we aim to study the impact of realistic reradiation models for RISs as a function of the sub-wavelength inter-distance between nearby elements of the RIS, the quantization levels of the reflection coefficients, the interplay between the amplitude and phase of the reflection coefficients, and the presence of electromagnetic interference. We consider both case studies in which the users may be located in the far-field and near-field regions of an RIS. Our study shows that, due to design constraints, such as the need of using quantized reflection coefficients or the inherent interplay between the phase and the amplitude of the reflection coefficients, an RIS may reradiate power towards unwanted directions that depend on the intended and interfering electromagnetic waves. Therefore, it is in general important to optimize an RIS by considering the entire reradiation pattern by design to maximize the reradiated power towards the desired directions of reradiation while keeping the power reradiated towards other unwanted directions at a low level. Our study shows that a 2-bit digitally controllable RIS with an almost constant reflection amplitude as a function of the applied phase shift, and whose scattering elements have a size and an inter-distance between (1/8)th and (1/4)th of the signal wavelength may be a good tradeoff between performance, implementation complexity and cost. However, the presented results are preliminary and pave the way for further research into the performance of RISs based on accurate and realistic electromagnetic reradiation models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge