Aisling O'Kane
University of Bristol
Artificial Intelligence for Collective Intelligence: A National-Scale Research Strategy
Nov 09, 2024



Abstract:Advances in artificial intelligence (AI) have great potential to help address societal challenges that are both collective in nature and present at national or trans-national scale. Pressing challenges in healthcare, finance, infrastructure and sustainability, for instance, might all be productively addressed by leveraging and amplifying AI for national-scale collective intelligence. The development and deployment of this kind of AI faces distinctive challenges, both technical and socio-technical. Here, a research strategy for mobilising inter-disciplinary research to address these challenges is detailed and some of the key issues that must be faced are outlined.
Model-Based Reinforcement Learning for Type 1Diabetes Blood Glucose Control
Oct 13, 2020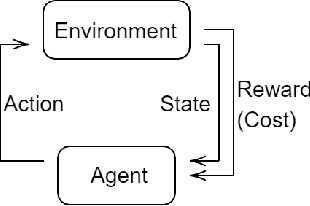
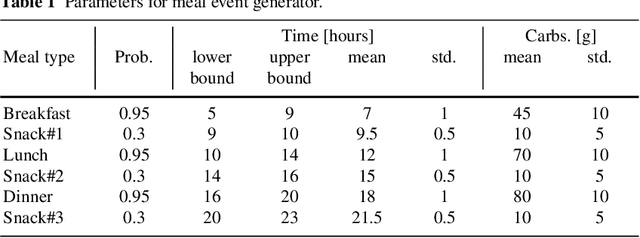
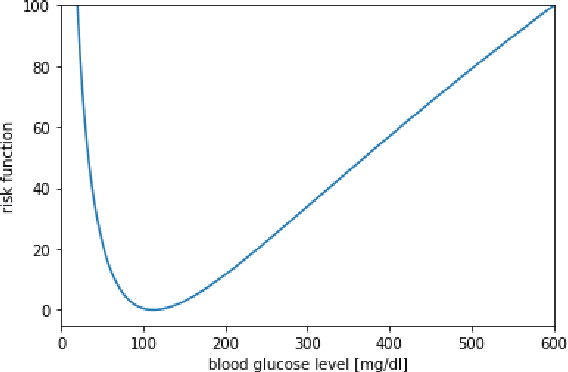
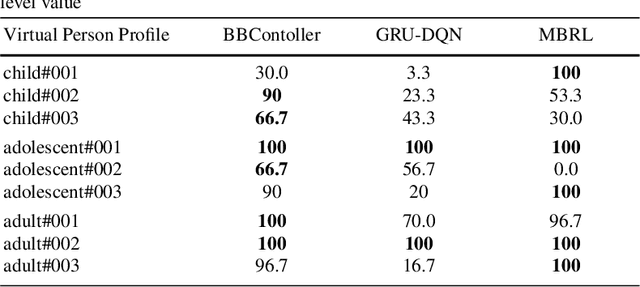
Abstract:In this paper we investigate the use of model-based reinforcement learning to assist people with Type 1 Diabetes with insulin dose decisions. The proposed architecture consists of multiple Echo State Networks to predict blood glucose levels combined with Model Predictive Controller for planning. Echo State Network is a version of recurrent neural networks which allows us to learn long term dependencies in the input of time series data in an online manner. Additionally, we address the quantification of uncertainty for a more robust control. Here, we used ensembles of Echo State Networks to capture model (epistemic) uncertainty. We evaluated the approach with the FDA-approved UVa/Padova Type 1 Diabetes simulator and compared the results against baseline algorithms such as Basal-Bolus controller and Deep Q-learning. The results suggest that the model-based reinforcement learning algorithm can perform equally or better than the baseline algorithms for the majority of virtual Type 1 Diabetes person profiles tested.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge