Ahmed Rashed
EfficientVITON: An Efficient Virtual Try-On Model using Optimized Diffusion Process
Jan 20, 2025Abstract:Would not it be much more convenient for everybody to try on clothes by only looking into a mirror ? The answer to that problem is virtual try-on, enabling users to digitally experiment with outfits. The core challenge lies in realistic image-to-image translation, where clothing must fit diverse human forms, poses, and figures. Early methods, which used 2D transformations, offered speed, but image quality was often disappointing and lacked the nuance of deep learning. Though GAN-based techniques enhanced realism, their dependence on paired data proved limiting. More adaptable methods offered great visuals but demanded significant computing power and time. Recent advances in diffusion models have shown promise for high-fidelity translation, yet the current crop of virtual try-on tools still struggle with detail loss and warping issues. To tackle these challenges, this paper proposes EfficientVITON, a new virtual try-on system leveraging the impressive pre-trained Stable Diffusion model for better images and deployment feasibility. The system includes a spatial encoder to maintain clothings finer details and zero cross-attention blocks to capture the subtleties of how clothes fit a human body. Input images are carefully prepared, and the diffusion process has been tweaked to significantly cut generation time without image quality loss. The training process involves two distinct stages of fine-tuning, carefully incorporating a balance of loss functions to ensure both accurate try-on results and high-quality visuals. Rigorous testing on the VITON-HD dataset, supplemented with real-world examples, has demonstrated that EfficientVITON achieves state-of-the-art results.
Analyzing Fairness of Classification Machine Learning Model with Structured Dataset
Dec 13, 2024


Abstract:Machine learning (ML) algorithms have become integral to decision making in various domains, including healthcare, finance, education, and law enforcement. However, concerns about fairness and bias in these systems pose significant ethical and social challenges. This study investigates the fairness of ML models applied to structured datasets in classification tasks, highlighting the potential for biased predictions to perpetuate systemic inequalities. A publicly available dataset from Kaggle was selected for analysis, offering a realistic scenario for evaluating fairness in machine learning workflows. To assess and mitigate biases, three prominent fairness libraries; Fairlearn by Microsoft, AIF360 by IBM, and the What If Tool by Google were employed. These libraries provide robust frameworks for analyzing fairness, offering tools to evaluate metrics, visualize results, and implement bias mitigation strategies. The research aims to assess the extent of bias in the ML models, compare the effectiveness of these libraries, and derive actionable insights for practitioners. The findings reveal that each library has unique strengths and limitations in fairness evaluation and mitigation. By systematically comparing their capabilities, this study contributes to the growing field of ML fairness by providing practical guidance for integrating fairness tools into real world applications. These insights are intended to support the development of more equitable machine learning systems.
Analyzing Fairness of Computer Vision and Natural Language Processing Models
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:Machine learning (ML) algorithms play a crucial role in decision making across diverse fields such as healthcare, finance, education, and law enforcement. Despite their widespread adoption, these systems raise ethical and social concerns due to potential biases and fairness issues. This study focuses on evaluating and improving the fairness of Computer Vision and Natural Language Processing (NLP) models applied to unstructured datasets, emphasizing how biased predictions can reinforce existing systemic inequalities. A publicly available dataset from Kaggle was utilized to simulate a practical scenario for examining fairness in ML workflows. To address and mitigate biases, the study employed two leading fairness libraries: Fairlearn by Microsoft, and AIF360 by IBM. These tools offer comprehensive frameworks for fairness analysis, including metrics evaluation, result visualization, and bias mitigation techniques. The research aims to measure bias levels in ML models, compare the effectiveness of these fairness libraries, and provide actionable recommendations for practitioners. The results demonstrate that each library possesses distinct strengths and limitations in evaluating and mitigating fairness. By systematically analyzing these tools, the study contributes valuable insights to the growing field of ML fairness, offering practical guidance for integrating fairness solutions into real world applications. This research underscores the importance of building more equitable and responsible machine learning systems.
HMAR: Hierarchical Masked Attention for Multi-Behaviour Recommendation
Apr 29, 2024Abstract:In the context of recommendation systems, addressing multi-behavioral user interactions has become vital for understanding the evolving user behavior. Recent models utilize techniques like graph neural networks and attention mechanisms for modeling diverse behaviors, but capturing sequential patterns in historical interactions remains challenging. To tackle this, we introduce Hierarchical Masked Attention for multi-behavior recommendation (HMAR). Specifically, our approach applies masked self-attention to items of the same behavior, followed by self-attention across all behaviors. Additionally, we propose historical behavior indicators to encode the historical frequency of each items behavior in the input sequence. Furthermore, the HMAR model operates in a multi-task setting, allowing it to learn item behaviors and their associated ranking scores concurrently. Extensive experimental results on four real-world datasets demonstrate that our proposed model outperforms state-of-the-art methods. Our code and datasets are available here (https://github.com/Shereen-Elsayed/HMAR).
Context-Aware Sequential Model for Multi-Behaviour Recommendation
Dec 15, 2023Abstract:Sequential recommendation models are crucial for next-item recommendations in online platforms, capturing complex patterns in user interactions. However, many focus on a single behavior, overlooking valuable implicit interactions like clicks and favorites. Existing multi-behavioral models often fail to simultaneously capture sequential patterns. We propose CASM, a Context-Aware Sequential Model, leveraging sequential models to seamlessly handle multiple behaviors. CASM employs context-aware multi-head self-attention for heterogeneous historical interactions and a weighted binary cross-entropy loss for precise control over behavior contributions. Experimental results on four datasets demonstrate CASM's superiority over state-of-the-art approaches.
CARCA: Context and Attribute-Aware Next-Item Recommendation via Cross-Attention
Apr 04, 2022



Abstract:In sparse recommender settings, users' context and item attributes play a crucial role in deciding which items to recommend next. Despite that, recent works in sequential and time-aware recommendations usually either ignore both aspects or only consider one of them, limiting their predictive performance. In this paper, we address these limitations by proposing a context and attribute-aware recommender model (CARCA) that can capture the dynamic nature of the user profiles in terms of contextual features and item attributes via dedicated multi-head self-attention blocks that extract profile-level features and predicting item scores. Also, unlike many of the current state-of-the-art sequential item recommendation approaches that use a simple dot-product between the most recent item's latent features and the target items embeddings for scoring, CARCA uses cross-attention between all profile items and the target items to predict their final scores. This cross-attention allows CARCA to harness the correlation between old and recent items in the user profile and their influence on deciding which item to recommend next. Experiments on four real-world recommender system datasets show that the proposed model significantly outperforms all state-of-the-art models in the task of item recommendation and achieving improvements of up to 53% in Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain (NDCG) and Hit-Ratio. Results also show that CARCA outperformed several state-of-the-art dedicated image-based recommender systems by merely utilizing image attributes extracted from a pre-trained ResNet50 in a black-box fashion.
A.I. and Data-Driven Mobility at Volkswagen Financial Services AG
Feb 09, 2022Abstract:Machine learning is being widely adapted in industrial applications owing to the capabilities of commercially available hardware and rapidly advancing research. Volkswagen Financial Services (VWFS), as a market leader in vehicle leasing services, aims to leverage existing proprietary data and the latest research to enhance existing and derive new business processes. The collaboration between Information Systems and Machine Learning Lab (ISMLL) and VWFS serves to realize this goal. In this paper, we propose methods in the fields of recommender systems, object detection, and forecasting that enable data-driven decisions for the vehicle life-cycle at VWFS.
Do We Really Need Deep Learning Models for Time Series Forecasting?
Jan 06, 2021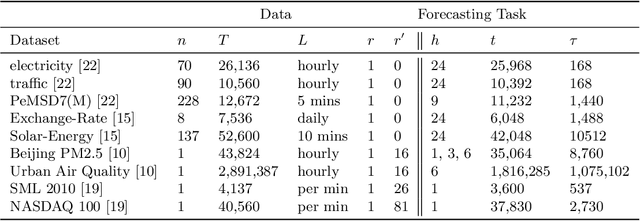

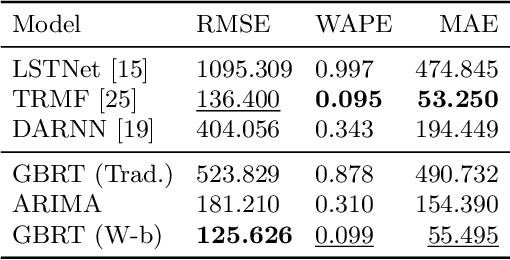
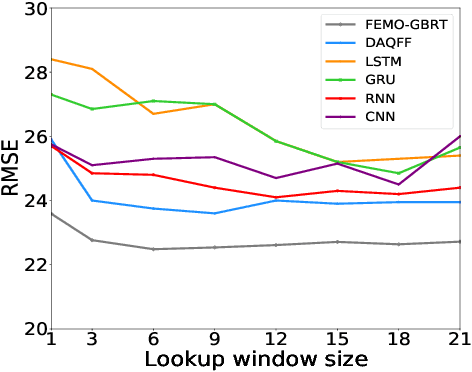
Abstract:Time series forecasting is a crucial task in machine learning, as it has a wide range of applications including but not limited to forecasting electricity consumption, traffic, and air quality. Traditional forecasting models relied on rolling averages, vector auto-regression and auto-regressive integrated moving averages. On the other hand, deep learning and matrix factorization models have been recently proposed to tackle the same problem with more competitive performance. However, one major drawback of such models is that they tend to be overly complex in comparison to traditional techniques. In this paper, we try to answer whether these highly complex deep learning models are without alternative. We aim to enrich the pool of simple but powerful baselines by revisiting the gradient boosting regression trees for time series forecasting. Specifically, we reconfigure the way time series data is handled by Gradient Tree Boosting models in a windowed fashion that is similar to the deep learning models. For each training window, the target values are concatenated with external features, and then flattened to form one input instance for a multi-output gradient boosting regression tree model. We conducted a comparative study on nine datasets for eight state-of-the-art deep-learning models that were presented at top-level conferences in the last years. The results demonstrated that the proposed approach outperforms all of the state-of-the-art models.
Multi-Label Network Classification via Weighted Personalized Factorizations
Feb 25, 2019



Abstract:Multi-label network classification is a well-known task that is being used in a wide variety of web-based and non-web-based domains. It can be formalized as a multi-relational learning task for predicting nodes labels based on their relations within the network. In sparse networks, this prediction task can be very challenging when only implicit feedback information is available such as in predicting user interests in social networks. Current approaches rely on learning per-node latent representations by utilizing the network structure, however, implicit feedback relations are naturally sparse and contain only positive observed feedbacks which mean that these approaches will treat all observed relations as equally important. This is not necessarily the case in real-world scenarios as implicit relations might have semantic weights which reflect the strength of those relations. If those weights can be approximated, the models can be trained to differentiate between strong and weak relations. In this paper, we propose a weighted personalized two-stage multi-relational matrix factorization model with Bayesian personalized ranking loss for network classification that utilizes basic transitive node similarity function for weighting implicit feedback relations. Experiments show that the proposed model significantly outperforms the state-of-art models on three different real-world web-based datasets and a biology-based dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge