Aditya Bhattacharya
Explanatory Debiasing: Involving Domain Experts in the Data Generation Process to Mitigate Representation Bias in AI Systems
Dec 26, 2024Abstract:Representation bias is one of the most common types of biases in artificial intelligence (AI) systems, causing AI models to perform poorly on underrepresented data segments. Although AI practitioners use various methods to reduce representation bias, their effectiveness is often constrained by insufficient domain knowledge in the debiasing process. To address this gap, this paper introduces a set of generic design guidelines for effectively involving domain experts in representation debiasing. We instantiated our proposed guidelines in a healthcare-focused application and evaluated them through a comprehensive mixed-methods user study with 35 healthcare experts. Our findings show that involving domain experts can reduce representation bias without compromising model accuracy. Based on our findings, we also offer recommendations for developers to build robust debiasing systems guided by our generic design guidelines, ensuring more effective inclusion of domain experts in the debiasing process.
Cross-Domain Evaluation of Few-Shot Classification Models: Natural Images vs. Histopathological Images
Oct 11, 2024Abstract:In this study, we investigate the performance of few-shot classification models across different domains, specifically natural images and histopathological images. We first train several few-shot classification models on natural images and evaluate their performance on histopathological images. Subsequently, we train the same models on histopathological images and compare their performance. We incorporated four histopathology datasets and one natural images dataset and assessed performance across 5-way 1-shot, 5-way 5-shot, and 5-way 10-shot scenarios using a selection of state-of-the-art classification techniques. Our experimental results reveal insights into the transferability and generalization capabilities of few-shot classification models between diverse image domains. We analyze the strengths and limitations of these models in adapting to new domains and provide recommendations for optimizing their performance in cross-domain scenarios. This research contributes to advancing our understanding of few-shot learning in the context of image classification across diverse domains.
An Explanatory Model Steering System for Collaboration between Domain Experts and AI
May 17, 2024Abstract:With the increasing adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems in high-stake domains, such as healthcare, effective collaboration between domain experts and AI is imperative. To facilitate effective collaboration between domain experts and AI systems, we introduce an Explanatory Model Steering system that allows domain experts to steer prediction models using their domain knowledge. The system includes an explanation dashboard that combines different types of data-centric and model-centric explanations and allows prediction models to be steered through manual and automated data configuration approaches. It allows domain experts to apply their prior knowledge for configuring the underlying training data and refining prediction models. Additionally, our model steering system has been evaluated for a healthcare-focused scenario with 174 healthcare experts through three extensive user studies. Our findings highlight the importance of involving domain experts during model steering, ultimately leading to improved human-AI collaboration.
* Demo paper accepted for ACM UMAP 2024
EXMOS: Explanatory Model Steering Through Multifaceted Explanations and Data Configurations
Feb 01, 2024



Abstract:Explanations in interactive machine-learning systems facilitate debugging and improving prediction models. However, the effectiveness of various global model-centric and data-centric explanations in aiding domain experts to detect and resolve potential data issues for model improvement remains unexplored. This research investigates the influence of data-centric and model-centric global explanations in systems that support healthcare experts in optimising models through automated and manual data configurations. We conducted quantitative (n=70) and qualitative (n=30) studies with healthcare experts to explore the impact of different explanations on trust, understandability and model improvement. Our results reveal the insufficiency of global model-centric explanations for guiding users during data configuration. Although data-centric explanations enhanced understanding of post-configuration system changes, a hybrid fusion of both explanation types demonstrated the highest effectiveness. Based on our study results, we also present design implications for effective explanation-driven interactive machine-learning systems.
* This is a pre-print version only for early release. Please view the conference published version from ACM CHI 2024 to get the latest version of the paper
Lessons Learned from EXMOS User Studies: A Technical Report Summarizing Key Takeaways from User Studies Conducted to Evaluate The EXMOS Platform
Oct 03, 2023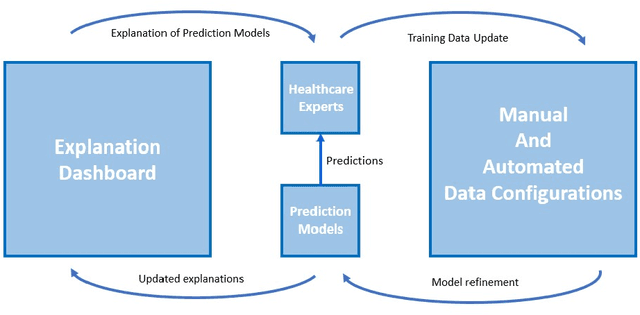
Abstract:In the realm of interactive machine-learning systems, the provision of explanations serves as a vital aid in the processes of debugging and enhancing prediction models. However, the extent to which various global model-centric and data-centric explanations can effectively assist domain experts in detecting and resolving potential data-related issues for the purpose of model improvement has remained largely unexplored. In this technical report, we summarise the key findings of our two user studies. Our research involved a comprehensive examination of the impact of global explanations rooted in both data-centric and model-centric perspectives within systems designed to support healthcare experts in optimising machine learning models through both automated and manual data configurations. To empirically investigate these dynamics, we conducted two user studies, comprising quantitative analysis involving a sample size of 70 healthcare experts and qualitative assessments involving 30 healthcare experts. These studies were aimed at illuminating the influence of different explanation types on three key dimensions: trust, understandability, and model improvement. Results show that global model-centric explanations alone are insufficient for effectively guiding users during the intricate process of data configuration. In contrast, data-centric explanations exhibited their potential by enhancing the understanding of system changes that occur post-configuration. However, a combination of both showed the highest level of efficacy for fostering trust, improving understandability, and facilitating model enhancement among healthcare experts. We also present essential implications for developing interactive machine-learning systems driven by explanations. These insights can guide the creation of more effective systems that empower domain experts to harness the full potential of machine learning
Directive Explanations for Monitoring the Risk of Diabetes Onset: Introducing Directive Data-Centric Explanations and Combinations to Support What-If Explorations
Feb 21, 2023Abstract:Explainable artificial intelligence is increasingly used in machine learning (ML) based decision-making systems in healthcare. However, little research has compared the utility of different explanation methods in guiding healthcare experts for patient care. Moreover, it is unclear how useful, understandable, actionable and trustworthy these methods are for healthcare experts, as they often require technical ML knowledge. This paper presents an explanation dashboard that predicts the risk of diabetes onset and explains those predictions with data-centric, feature-importance, and example-based explanations. We designed an interactive dashboard to assist healthcare experts, such as nurses and physicians, in monitoring the risk of diabetes onset and recommending measures to minimize risk. We conducted a qualitative study with 11 healthcare experts and a mixed-methods study with 45 healthcare experts and 51 diabetic patients to compare the different explanation methods in our dashboard in terms of understandability, usefulness, actionability, and trust. Results indicate that our participants preferred our representation of data-centric explanations that provide local explanations with a global overview over other methods. Therefore, this paper highlights the importance of visually directive data-centric explanation method for assisting healthcare experts to gain actionable insights from patient health records. Furthermore, we share our design implications for tailoring the visual representation of different explanation methods for healthcare experts.
Empirical Analysis of Image Caption Generation using Deep Learning
May 22, 2021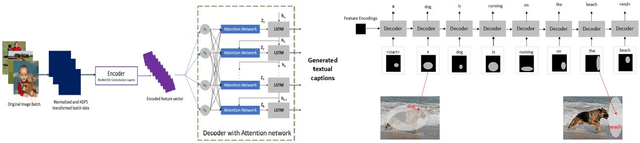
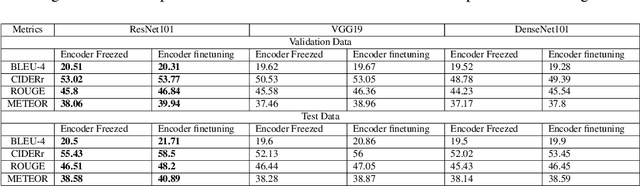

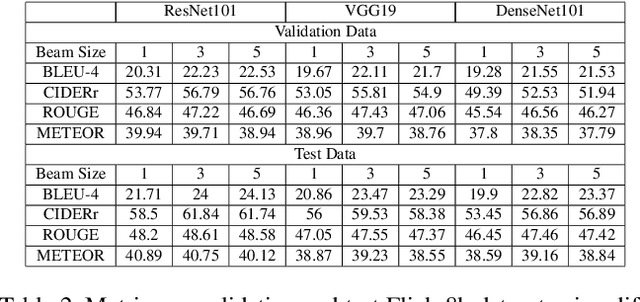
Abstract:Automated image captioning is one of the applications of Deep Learning which involves fusion of work done in computer vision and natural language processing, and it is typically performed using Encoder-Decoder architectures. In this project, we have implemented and experimented with various flavors of multi-modal image captioning networks where ResNet101, DenseNet121 and VGG19 based CNN Encoders and Attention based LSTM Decoders were explored. We have studied the effect of beam size and the use of pretrained word embeddings and compared them to baseline CNN encoder and RNN decoder architecture. The goal is to analyze the performance of each approach using various evaluation metrics including BLEU, CIDEr, ROUGE and METEOR. We have also explored model explainability using Visual Attention Maps (VAM) to highlight parts of the images which has maximum contribution for predicting each word of the generated caption.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge