Vrinda Goel
FANVID: A Benchmark for Face and License Plate Recognition in Low-Resolution Videos
Jun 08, 2025

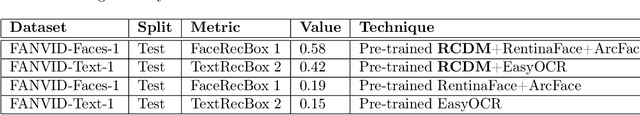
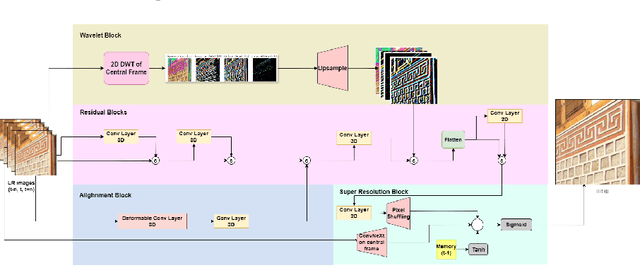
Abstract:Real-world surveillance often renders faces and license plates unrecognizable in individual low-resolution (LR) frames, hindering reliable identification. To advance temporal recognition models, we present FANVID, a novel video-based benchmark comprising nearly 1,463 LR clips (180 x 320, 20--60 FPS) featuring 63 identities and 49 license plates from three English-speaking countries. Each video includes distractor faces and plates, increasing task difficulty and realism. The dataset contains 31,096 manually verified bounding boxes and labels. FANVID defines two tasks: (1) face matching -- detecting LR faces and matching them to high-resolution mugshots, and (2) license plate recognition -- extracting text from LR plates without a predefined database. Videos are downsampled from high-resolution sources to ensure that faces and text are indecipherable in single frames, requiring models to exploit temporal information. We introduce evaluation metrics adapted from mean Average Precision at IoU > 0.5, prioritizing identity correctness for faces and character-level accuracy for text. A baseline method with pre-trained video super-resolution, detection, and recognition achieved performance scores of 0.58 (face matching) and 0.42 (plate recognition), highlighting both the feasibility and challenge of the tasks. FANVID's selection of faces and plates balances diversity with recognition challenge. We release the software for data access, evaluation, baseline, and annotation to support reproducibility and extension. FANVID aims to catalyze innovation in temporal modeling for LR recognition, with applications in surveillance, forensics, and autonomous vehicles.
Cross-Domain Evaluation of Few-Shot Classification Models: Natural Images vs. Histopathological Images
Oct 11, 2024Abstract:In this study, we investigate the performance of few-shot classification models across different domains, specifically natural images and histopathological images. We first train several few-shot classification models on natural images and evaluate their performance on histopathological images. Subsequently, we train the same models on histopathological images and compare their performance. We incorporated four histopathology datasets and one natural images dataset and assessed performance across 5-way 1-shot, 5-way 5-shot, and 5-way 10-shot scenarios using a selection of state-of-the-art classification techniques. Our experimental results reveal insights into the transferability and generalization capabilities of few-shot classification models between diverse image domains. We analyze the strengths and limitations of these models in adapting to new domains and provide recommendations for optimizing their performance in cross-domain scenarios. This research contributes to advancing our understanding of few-shot learning in the context of image classification across diverse domains.
HER2 and FISH Status Prediction in Breast Biopsy H&E-Stained Images Using Deep Learning
Aug 25, 2024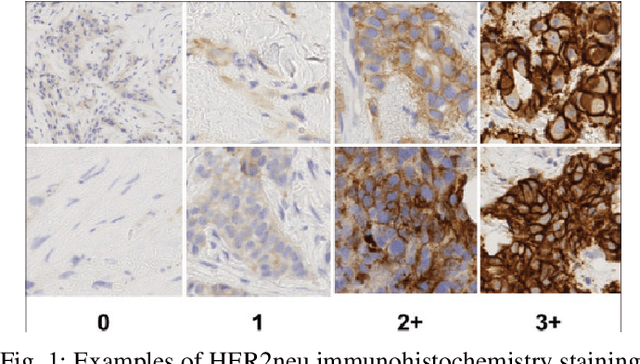
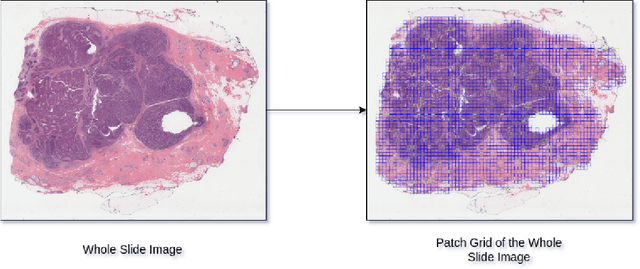

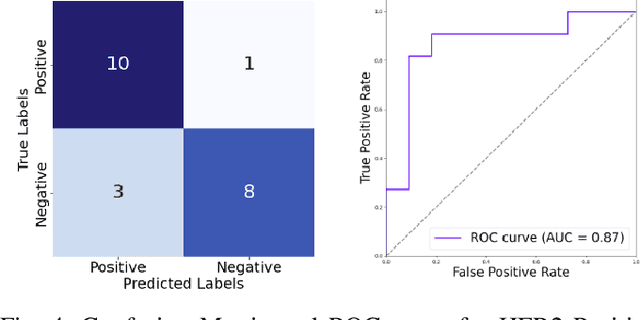
Abstract:The current standard for detecting human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) status in breast cancer patients relies on HER2 amplification, identified through fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) or immunohistochemistry (IHC). However, hematoxylin and eosin (H\&E) tumor stains are more widely available, and accurately predicting HER2 status using H\&E could reduce costs and expedite treatment selection. Deep Learning algorithms for H&E have shown effectiveness in predicting various cancer features and clinical outcomes, including moderate success in HER2 status prediction. In this work, we employed a customized weak supervision classification technique combined with MoCo-v2 contrastive learning to predict HER2 status. We trained our pipeline on 182 publicly available H&E Whole Slide Images (WSIs) from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), for which annotations by the pathology team at Yale School of Medicine are publicly available. Our pipeline achieved an Area Under the Curve (AUC) of 0.85 across four different test folds. Additionally, we tested our model on 44 H&E slides from the TCGA-BRCA dataset, which had an HER2 score of 2+ and included corresponding HER2 status and FISH test results. These cases are considered equivocal for IHC, requiring an expensive FISH test on their IHC slides for disambiguation. Our pipeline demonstrated an AUC of 0.81 on these challenging H&E slides. Reducing the need for FISH test can have significant implications in cancer treatment equity for underserved populations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge