Abir Bhowmick
Script Identification in Natural Scene Image and Video Frame using Attention based Convolutional-LSTM Network
Aug 07, 2018



Abstract:Script identification plays a significant role in analysing documents and videos. In this paper, we focus on the problem of script identification in scene text images and video scripts. Because of low image quality, complex background and similar layout of characters shared by some scripts like Greek, Latin, etc., text recognition in those cases become challenging. In this paper, we propose a novel method that involves extraction of local and global features using CNN-LSTM framework and weighting them dynamically for script identification. First, we convert the images into patches and feed them into a CNN-LSTM framework. Attention-based patch weights are calculated applying softmax layer after LSTM. Next, we do patch-wise multiplication of these weights with corresponding CNN to yield local features. Global features are also extracted from last cell state of LSTM. We employ a fusion technique which dynamically weights the local and global features for an individual patch. Experiments have been done in four public script identification datasets: SIW-13, CVSI2015, ICDAR-17 and MLe2e. The proposed framework achieves superior results in comparison to conventional methods.
Staff line Removal using Generative Adversarial Networks
Jun 05, 2018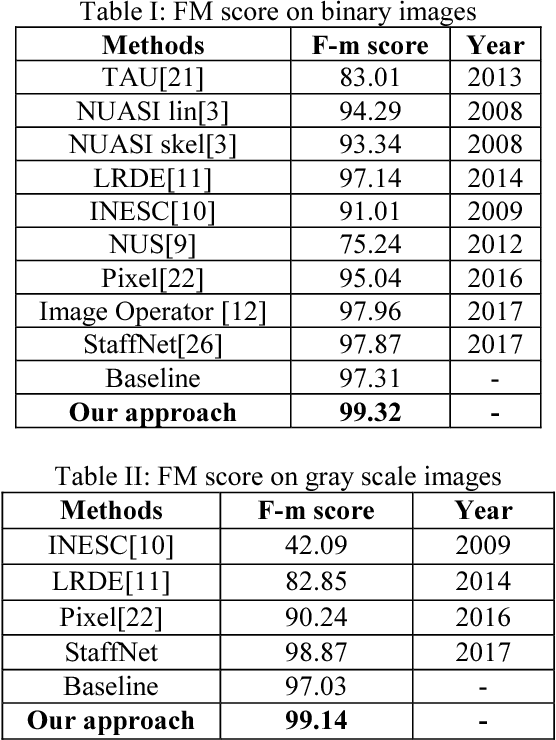

Abstract:Staff line removal is a crucial pre-processing step in Optical Music Recognition. It is a challenging task to simultaneously reduce the noise and also retain the quality of music symbol context in ancient degraded music score images. In this paper we propose a novel approach for staff line removal, based on Generative Adversarial Networks. We convert staff line images into patches and feed them into a U-Net, used as Generator. The Generator intends to produce staff-less images at the output. Then the Discriminator does binary classification and differentiates between the generated fake staff-less image and real ground truth staff less image. For training, we use a Loss function which is a weighted combination of L2 loss and Adversarial loss. L2 loss minimizes the difference between real and fake staff-less image. Adversarial loss helps to retrieve more high quality textures in generated images. Thus our architecture supports solutions which are closer to ground truth and it reflects in our results. For evaluation we consider the ICDAR/GREC 2013 staff removal database. Our method achieves superior performance in comparison to other conventional approaches.
Handwriting Trajectory Recovery using End-to-End Deep Encoder-Decoder Network
Jun 03, 2018
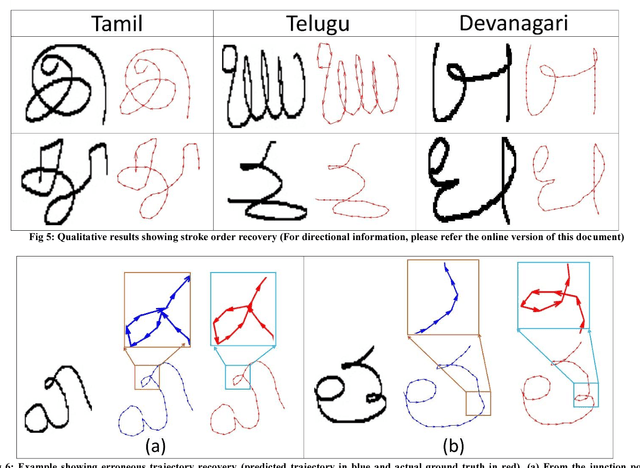
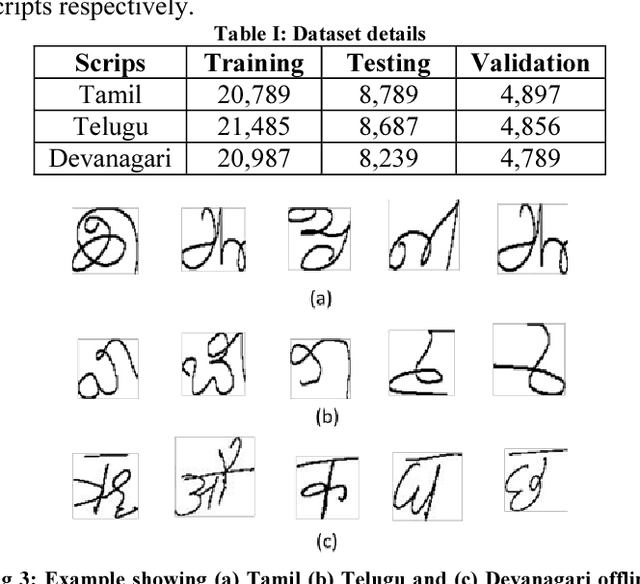

Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a novel technique to recover the pen trajectory of offline characters which is a crucial step for handwritten character recognition. Generally, online acquisition approach has more advantage than its offline counterpart as the online technique keeps track of the pen movement. Hence, pen tip trajectory retrieval from offline text can bridge the gap between online and offline methods. Our proposed framework employs sequence to sequence model which consists of an encoder-decoder LSTM module. Our encoder module consists of Convolutional LSTM network, which takes an offline character image as the input and encodes the feature sequence to a hidden representation. The output of the encoder is fed to a decoder LSTM and we get the successive coordinate points from every time step of the decoder LSTM. Although the sequence to sequence model is a popular paradigm in various computer vision and language translation tasks, the main contribution of our work lies in designing an end-to-end network for a decade old popular problem in Document Image Analysis community. Tamil, Telugu and Devanagari characters of LIPI Toolkit dataset are used for our experiments. Our proposed method has achieved superior performance compared to the other conventional approaches.
Word Level Font-to-Font Image Translation using Convolutional Recurrent Generative Adversarial Networks
May 24, 2018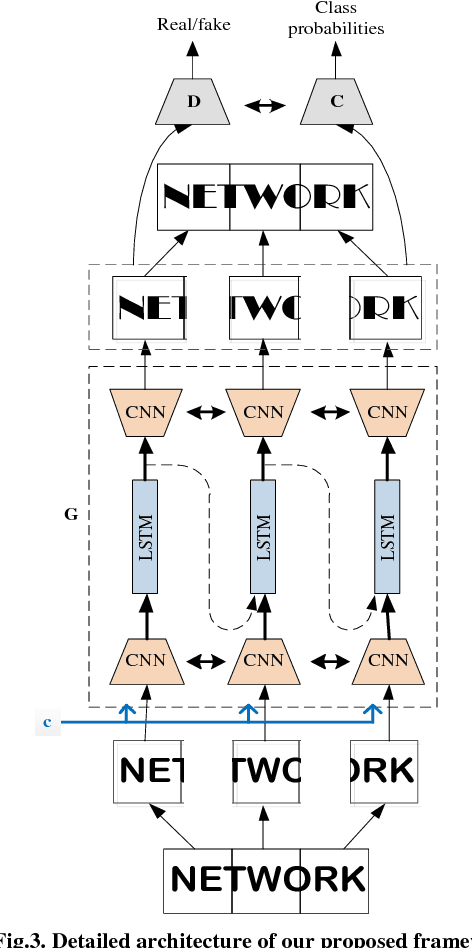
Abstract:Conversion of one font to another font is very useful in real life applications. In this paper, we propose a Convolutional Recurrent Generative model to solve the word level font transfer problem. Our network is able to convert the font style of any printed text images from its current font to the required font. The network is trained end-to-end for the complete word images. Thus it eliminates the necessary pre-processing steps, like character segmentations. We extend our model to conditional setting that helps to learn one-to-many mapping function. We employ a novel convolutional recurrent model architecture in the Generator that efficiently deals with the word images of arbitrary width. It also helps to maintain the consistency of the final images after concatenating the generated image patches of target font. Besides, the Generator and the Discriminator network, we employ a Classification network to classify the generated word images of converted font style to their subsequent font categories. Most of the earlier works related to image translation are performed on square images. Our proposed architecture is the first work which can handle images of varying widths. Word images generally have varying width depending on the number of characters present. Hence, we test our model on a synthetically generated font dataset. We compare our method with some of the state-of-the-art methods for image translation. The superior performance of our network on the same dataset proves the ability of our model to learn the font distributions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge