Abdelrahman Younes
KITchen: A Real-World Benchmark and Dataset for 6D Object Pose Estimation in Kitchen Environments
Mar 24, 2024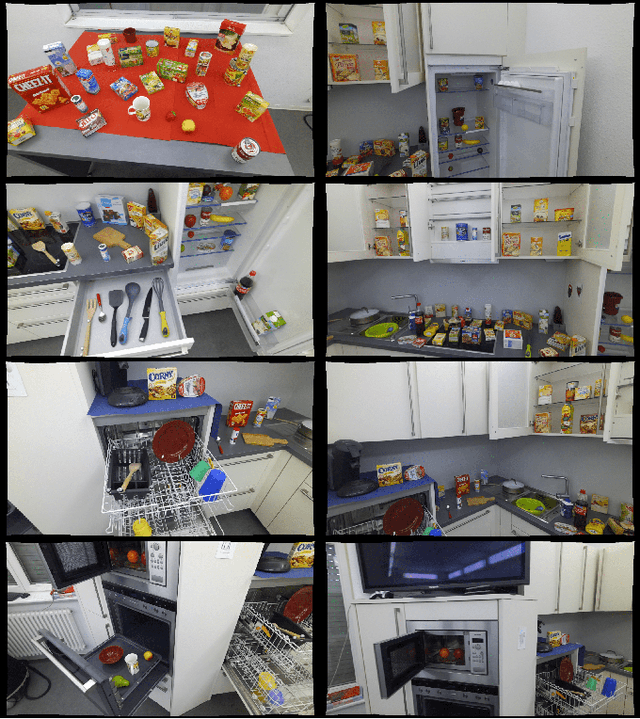



Abstract:Despite the recent progress on 6D object pose estimation methods for robotic grasping, a substantial performance gap persists between the capabilities of these methods on existing datasets and their efficacy in real-world mobile manipulation tasks, particularly when robots rely solely on their monocular egocentric field of view (FOV). Existing real-world datasets primarily focus on table-top grasping scenarios, where a robotic arm is placed in a fixed position and the objects are centralized within the FOV of fixed external camera(s). Assessing performance on such datasets may not accurately reflect the challenges encountered in everyday mobile manipulation tasks within kitchen environments such as retrieving objects from higher shelves, sinks, dishwashers, ovens, refrigerators, or microwaves. To address this gap, we present Kitchen, a novel benchmark designed specifically for estimating the 6D poses of objects located in diverse positions within kitchen settings. For this purpose, we recorded a comprehensive dataset comprising around 205k real-world RGBD images for 111 kitchen objects captured in two distinct kitchens, utilizing one humanoid robot with its egocentric perspectives. Subsequently, we developed a semi-automated annotation pipeline, to streamline the labeling process of such datasets, resulting in the generation of 2D object labels, 2D object segmentation masks, and 6D object poses with minimized human effort. The benchmark, the dataset, and the annotation pipeline are available at https://kitchen-dataset.github.io/KITchen.
AutoGPT+P: Affordance-based Task Planning with Large Language Models
Feb 16, 2024



Abstract:Recent advances in task planning leverage Large Language Models (LLMs) to improve generalizability by combining such models with classical planning algorithms to address their inherent limitations in reasoning capabilities. However, these approaches face the challenge of dynamically capturing the initial state of the task planning problem. To alleviate this issue, we propose AutoGPT+P, a system that combines an affordance-based scene representation with a planning system. Affordances encompass the action possibilities of an agent on the environment and objects present in it. Thus, deriving the planning domain from an affordance-based scene representation allows symbolic planning with arbitrary objects. AutoGPT+P leverages this representation to derive and execute a plan for a task specified by the user in natural language. In addition to solving planning tasks under a closed-world assumption, AutoGPT+P can also handle planning with incomplete information, e. g., tasks with missing objects by exploring the scene, suggesting alternatives, or providing a partial plan. The affordance-based scene representation combines object detection with an automatically generated object-affordance-mapping using ChatGPT. The core planning tool extends existing work by automatically correcting semantic and syntactic errors. Our approach achieves a success rate of 98%, surpassing the current 81% success rate of the current state-of-the-art LLM-based planning method SayCan on the SayCan instruction set. Furthermore, we evaluated our approach on our newly created dataset with 150 scenarios covering a wide range of complex tasks with missing objects, achieving a success rate of 79% on our dataset. The dataset and the code are publicly available at https://git.h2t.iar.kit.edu/birr/autogpt-p-standalone.
Dynamical Audio-Visual Navigation: Catching Unheard Moving Sound Sources in Unmapped 3D Environments
Jan 12, 2022
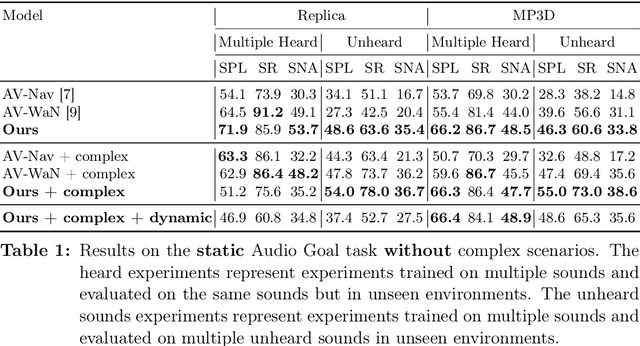
Abstract:Recent work on audio-visual navigation targets a single static sound in noise-free audio environments and struggles to generalize to unheard sounds. We introduce the novel dynamic audio-visual navigation benchmark in which an embodied AI agent must catch a moving sound source in an unmapped environment in the presence of distractors and noisy sounds. We propose an end-to-end reinforcement learning approach that relies on a multi-modal architecture that fuses the spatial audio-visual information from a binaural audio signal and spatial occupancy maps to encode the features needed to learn a robust navigation policy for our new complex task settings. We demonstrate that our approach outperforms the current state-of-the-art with better generalization to unheard sounds and better robustness to noisy scenarios on the two challenging 3D scanned real-world datasets Replica and Matterport3D, for the static and dynamic audio-visual navigation benchmarks. Our novel benchmark will be made available at http://dav-nav.cs.uni-freiburg.de.
Catch Me If You Hear Me: Audio-Visual Navigation in Complex Unmapped Environments with Moving Sounds
Nov 29, 2021



Abstract:Audio-visual navigation combines sight and hearing to navigate to a sound-emitting source in an unmapped environment. While recent approaches have demonstrated the benefits of audio input to detect and find the goal, they focus on clean and static sound sources and struggle to generalize to unheard sounds. In this work, we propose the novel dynamic audio-visual navigation benchmark which requires to catch a moving sound source in an environment with noisy and distracting sounds. We introduce a reinforcement learning approach that learns a robust navigation policy for these complex settings. To achieve this, we propose an architecture that fuses audio-visual information in the spatial feature space to learn correlations of geometric information inherent in both local maps and audio signals. We demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms the current state-of-the-art by a large margin across all tasks of moving sounds, unheard sounds, and noisy environments, on two challenging 3D scanned real-world environments, namely Matterport3D and Replica. The benchmark is available at http://dav-nav.cs.uni-freiburg.de.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge