Aayush J Rana
Semi-supervised Active Learning for Video Action Detection
Dec 12, 2023



Abstract:In this work, we focus on label efficient learning for video action detection. We develop a novel semi-supervised active learning approach which utilizes both labeled as well as unlabeled data along with informative sample selection for action detection. Video action detection requires spatio-temporal localization along with classification, which poses several challenges for both active learning informative sample selection as well as semi-supervised learning pseudo label generation. First, we propose NoiseAug, a simple augmentation strategy which effectively selects informative samples for video action detection. Next, we propose fft-attention, a novel technique based on high-pass filtering which enables effective utilization of pseudo label for SSL in video action detection by emphasizing on relevant activity region within a video. We evaluate the proposed approach on three different benchmark datasets, UCF-101-24, JHMDB-21, and Youtube-VOS. First, we demonstrate its effectiveness on video action detection where the proposed approach outperforms prior works in semi-supervised and weakly-supervised learning along with several baseline approaches in both UCF101-24 and JHMDB-21. Next, we also show its effectiveness on Youtube-VOS for video object segmentation demonstrating its generalization capability for other dense prediction tasks in videos.
LARNet: Latent Action Representation for Human Action Synthesis
Oct 27, 2021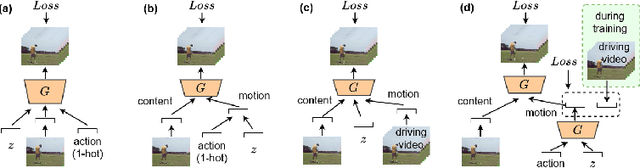
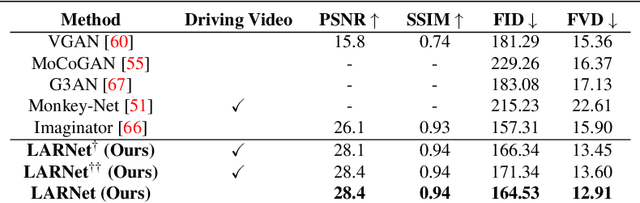
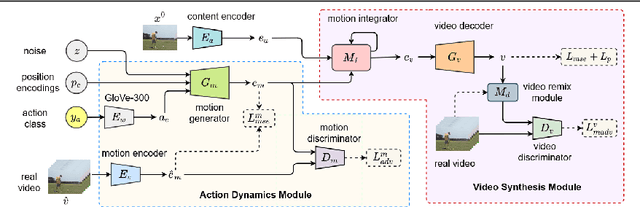
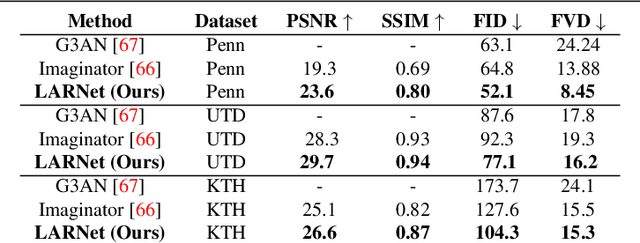
Abstract:We present LARNet, a novel end-to-end approach for generating human action videos. A joint generative modeling of appearance and dynamics to synthesize a video is very challenging and therefore recent works in video synthesis have proposed to decompose these two factors. However, these methods require a driving video to model the video dynamics. In this work, we propose a generative approach instead, which explicitly learns action dynamics in latent space avoiding the need of a driving video during inference. The generated action dynamics is integrated with the appearance using a recurrent hierarchical structure which induces motion at different scales to focus on both coarse as well as fine level action details. In addition, we propose a novel mix-adversarial loss function which aims at improving the temporal coherency of synthesized videos. We evaluate the proposed approach on four real-world human action datasets demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed approach in generating human actions. Code available at https://github.com/aayushjr/larnet.
TinyAction Challenge: Recognizing Real-world Low-resolution Activities in Videos
Jul 24, 2021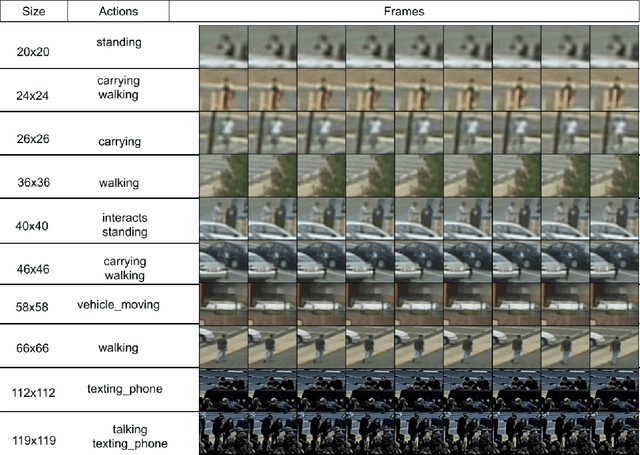
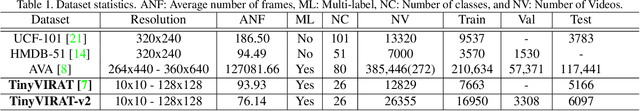
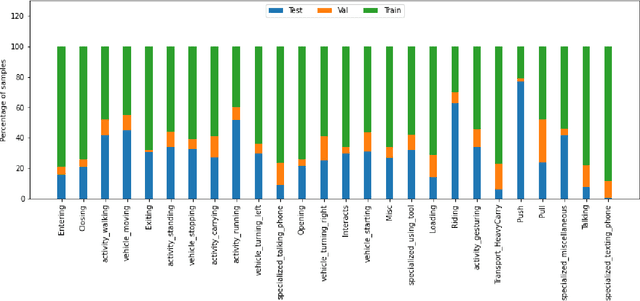
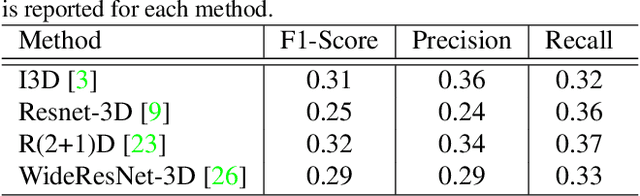
Abstract:This paper summarizes the TinyAction challenge which was organized in ActivityNet workshop at CVPR 2021. This challenge focuses on recognizing real-world low-resolution activities present in videos. Action recognition task is currently focused around classifying the actions from high-quality videos where the actors and the action is clearly visible. While various approaches have been shown effective for recognition task in recent works, they often do not deal with videos of lower resolution where the action is happening in a tiny region. However, many real world security videos often have the actual action captured in a small resolution, making action recognition in a tiny region a challenging task. In this work, we propose a benchmark dataset, TinyVIRAT-v2, which is comprised of naturally occuring low-resolution actions. This is an extension of the TinyVIRAT dataset and consists of actions with multiple labels. The videos are extracted from security videos which makes them realistic and more challenging. We use current state-of-the-art action recognition methods on the dataset as a benchmark, and propose the TinyAction Challenge.
We don't Need Thousand Proposals$\colon$ Single Shot Actor-Action Detection in Videos
Nov 22, 2020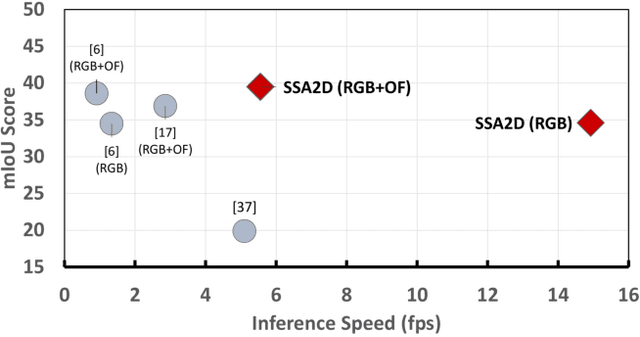
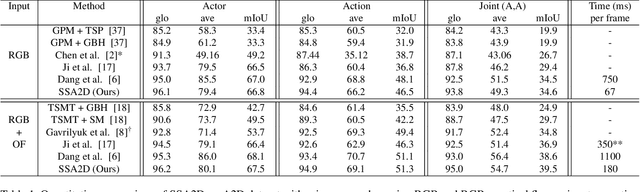
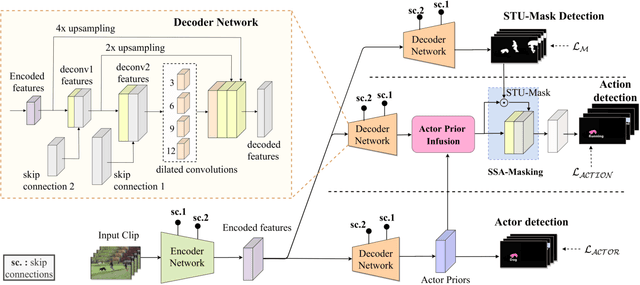
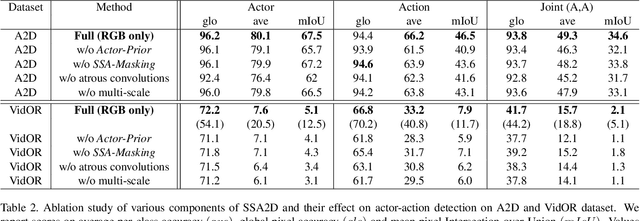
Abstract:We propose SSA2D, a simple yet effective end-to-end deep network for actor-action detection in videos. The existing methods take a top-down approach based on region-proposals (RPN), where the action is estimated based on the detected proposals followed by post-processing such as non-maximal suppression. While effective in terms of performance, these methods pose limitations in scalability for dense video scenes with a high memory requirement for thousands of proposals. We propose to solve this problem from a different perspective where we don't need any proposals. SSA2D is a unified network, which performs pixel level joint actor-action detection in a single-shot, where every pixel of the detected actor is assigned an action label. SSA2D has two main advantages: 1) It is a fully convolutional network which does not require any proposals and post-processing making it memory as well as time efficient, 2) It is easily scalable to dense video scenes as its memory requirement is independent of the number of actors present in the scene. We evaluate the proposed method on the Actor-Action dataset (A2D) and Video Object Relation (VidOR) dataset, demonstrating its effectiveness in multiple actors and action detection in a video. SSA2D is 11x faster during inference with comparable (sometimes better) performance and fewer network parameters when compared with the prior works.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge