Ádám Horváth
FRIDA: Free-Rider Detection using Privacy Attacks
Oct 07, 2024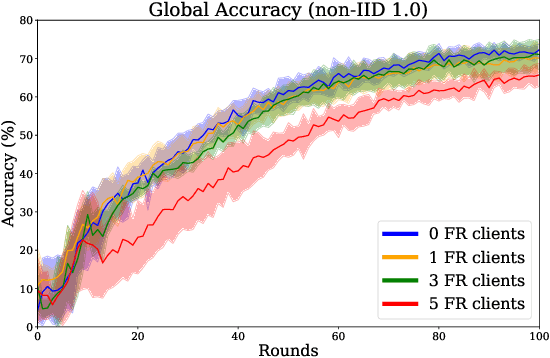
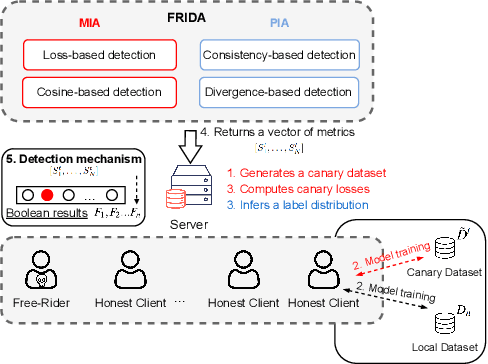
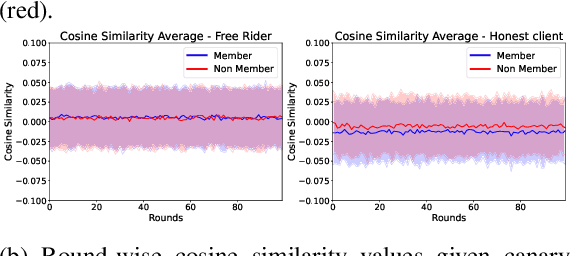
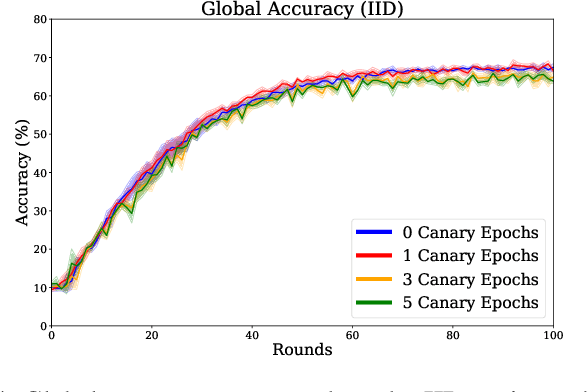
Abstract:Federated learning is increasingly popular as it enables multiple parties with limited datasets and resources to train a high-performing machine learning model collaboratively. However, similarly to other collaborative systems, federated learning is vulnerable to free-riders -- participants who do not contribute to the training but still benefit from the shared model. Free-riders not only compromise the integrity of the learning process but also slow down the convergence of the global model, resulting in increased costs for the honest participants. To address this challenge, we propose FRIDA: free-rider detection using privacy attacks, a framework that leverages inference attacks to detect free-riders. Unlike traditional methods that only capture the implicit effects of free-riding, FRIDA directly infers details of the underlying training datasets, revealing characteristics that indicate free-rider behaviour. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that membership and property inference attacks are effective for this purpose. Our evaluation shows that FRIDA outperforms state-of-the-art methods, especially in non-IID settings.
Forecasting Fold Bifurcations through Physics-Informed Convolutional Neural Networks
Dec 21, 2023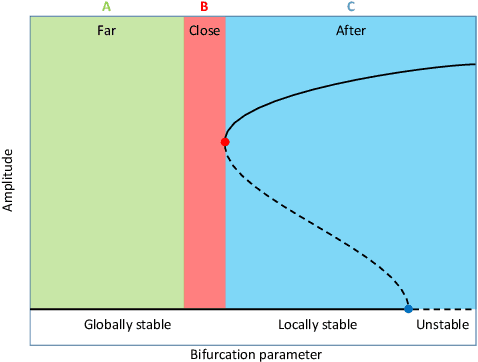
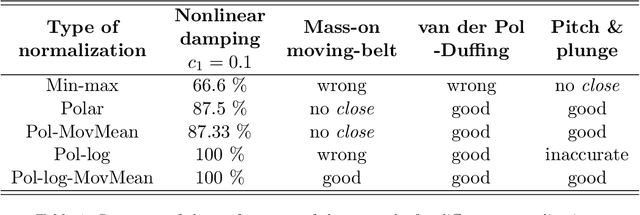
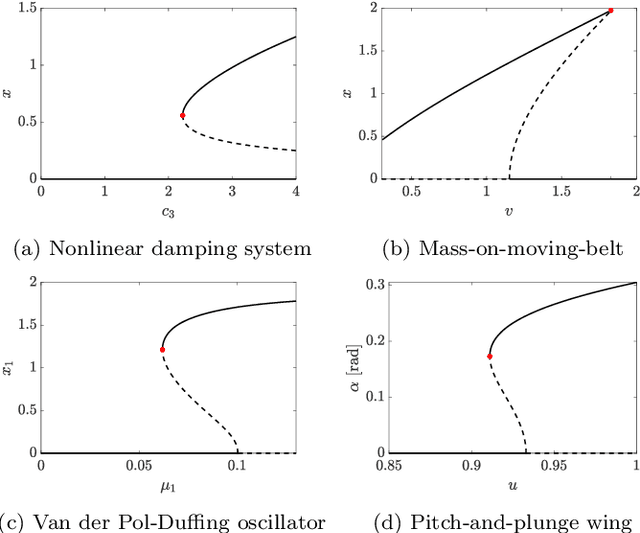
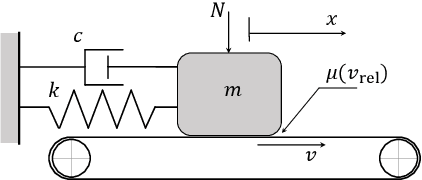
Abstract:This study proposes a physics-informed convolutional neural network (CNN) for identifying dynamical systems' time series near a fold bifurcation. The peculiarity of this work is that the CNN is trained with a relatively small amount of data and on a single, very simple system. In contrast, the CNN is validated on much more complicated systems. A similar task requires significant extrapolation capabilities, which are obtained by exploiting physics-based information. Physics-based information is provided through a specific pre-processing of the input data, consisting mostly of a transformation into polar coordinates, normalization, transformation into the logarithmic scale, and filtering through a moving mean. The results illustrate that such data pre-processing enables the CNN to grasp the important features related to approaching a fold bifurcation, namely, the trend of the oscillation amplitude, and neglect other characteristics that are not particularly relevant, such as the vibration frequency. The developed CNN was able to correctly classify trajectories near a fold for a mass-on-moving-belt system, a van der Pol-Duffing oscillator with an attached tuned mass damper, and a pitch-and-plunge wing profile. The results obtained pave the way for the development of similar CNNs effective in real-life applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge