What the DAAM: Interpreting Stable Diffusion Using Cross Attention
Paper and Code
Oct 11, 2022
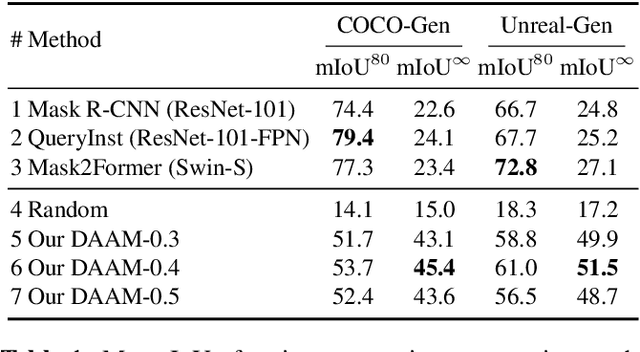
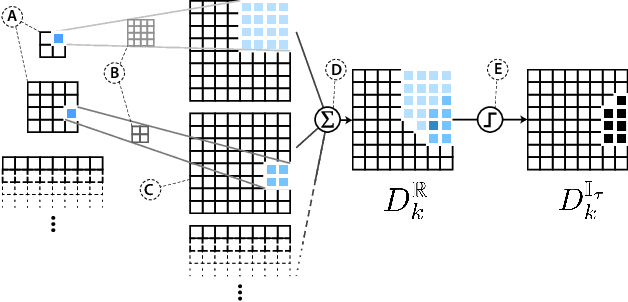

Large-scale diffusion neural networks represent a substantial milestone in text-to-image generation, with some performing similar to real photographs in human evaluation. However, they remain poorly understood, lacking explainability and interpretability analyses, largely due to their proprietary, closed-source nature. In this paper, to shine some much-needed light on text-to-image diffusion models, we perform a text-image attribution analysis on Stable Diffusion, a recently open-sourced large diffusion model. To produce pixel-level attribution maps, we propose DAAM, a novel method based on upscaling and aggregating cross-attention activations in the latent denoising subnetwork. We support its correctness by evaluating its unsupervised semantic segmentation quality on its own generated imagery, compared to supervised segmentation models. We show that DAAM performs strongly on COCO caption-generated images, achieving an mIoU of 61.0, and it outperforms supervised models on open-vocabulary segmentation, for an mIoU of 51.5. We further find that certain parts of speech, like punctuation and conjunctions, influence the generated imagery most, which agrees with the prior literature, while determiners and numerals the least, suggesting poor numeracy. To our knowledge, we are the first to propose and study word-pixel attribution for large-scale text-to-image diffusion models. Our code and data are at https://github.com/castorini/daam.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge