VICON: Vision In-Context Operator Networks for Multi-Physics Fluid Dynamics Prediction
Paper and Code
Nov 25, 2024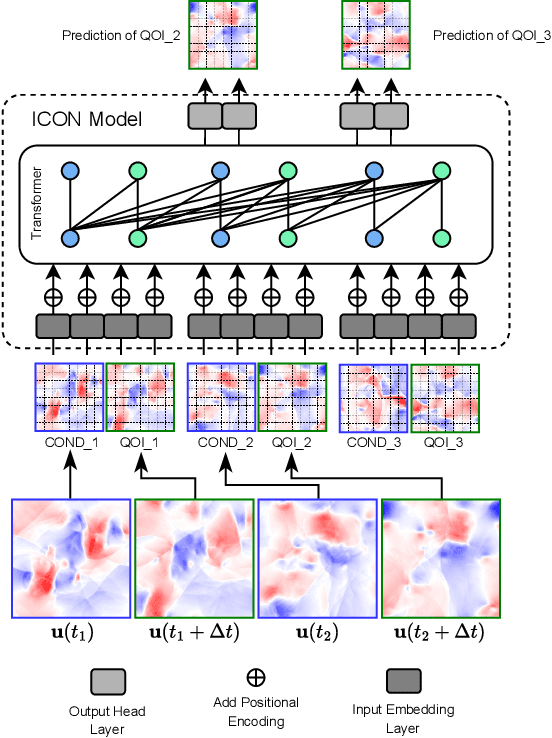
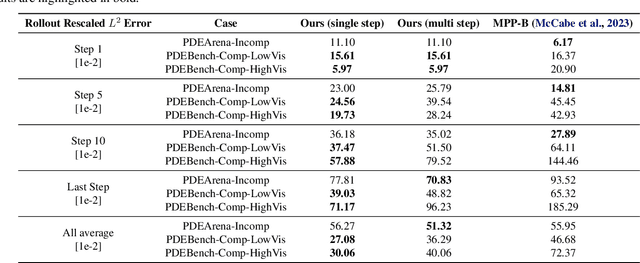
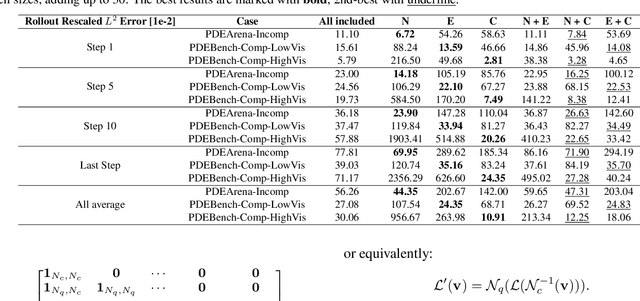
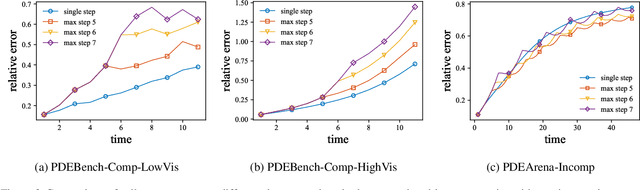
In-Context Operator Networks (ICONs) are models that learn operators across different types of PDEs using a few-shot, in-context approach. Although they show successful generalization to various PDEs, existing methods treat each data point as a single token, and suffer from computational inefficiency when processing dense data, limiting their application in higher spatial dimensions. In this work, we propose Vision In-Context Operator Networks (VICON), incorporating a vision transformer architecture that efficiently processes 2D functions through patch-wise operations. We evaluated our method on three fluid dynamics datasets, demonstrating both superior performance (reducing scaled $L^2$ error by $40\%$ and $61.6\%$ for two benchmark datasets for compressible flows, respectively) and computational efficiency (requiring only one-third of the inference time per frame) in long-term rollout predictions compared to the current state-of-the-art sequence-to-sequence model with fixed timestep prediction: Multiple Physics Pretraining (MPP). Compared to MPP, our method preserves the benefits of in-context operator learning, enabling flexible context formation when dealing with insufficient frame counts or varying timestep values.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge