Utilizing Large Language Models for Named Entity Recognition in Traditional Chinese Medicine against COVID-19 Literature: Comparative Study
Paper and Code
Aug 24, 2024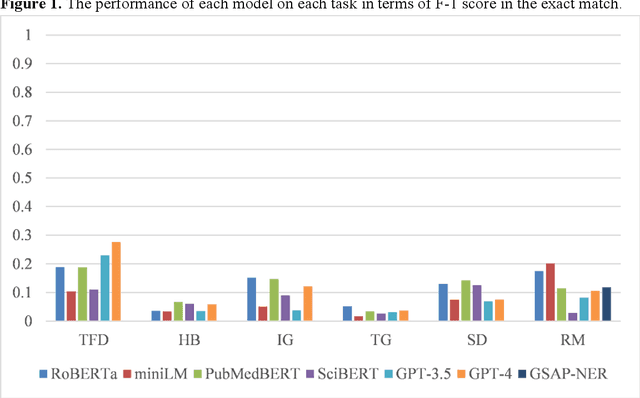
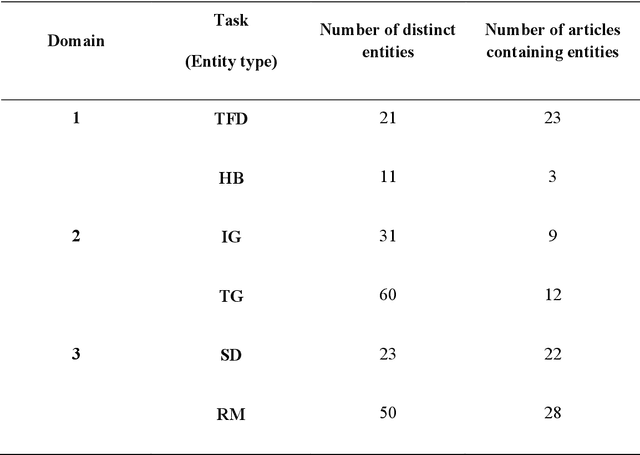
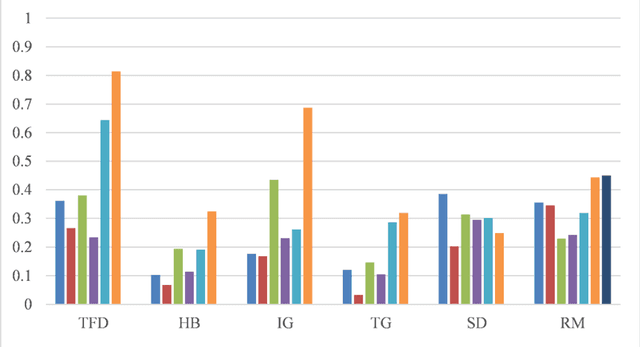
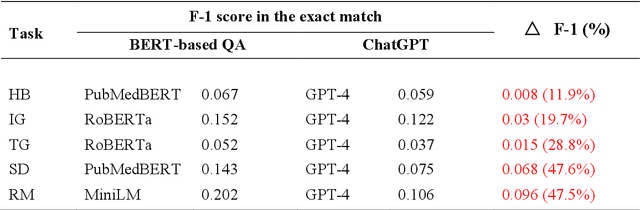
Objective: To explore and compare the performance of ChatGPT and other state-of-the-art LLMs on domain-specific NER tasks covering different entity types and domains in TCM against COVID-19 literature. Methods: We established a dataset of 389 articles on TCM against COVID-19, and manually annotated 48 of them with 6 types of entities belonging to 3 domains as the ground truth, against which the NER performance of LLMs can be assessed. We then performed NER tasks for the 6 entity types using ChatGPT (GPT-3.5 and GPT-4) and 4 state-of-the-art BERT-based question-answering (QA) models (RoBERTa, MiniLM, PubMedBERT and SciBERT) without prior training on the specific task. A domain fine-tuned model (GSAP-NER) was also applied for a comprehensive comparison. Results: The overall performance of LLMs varied significantly in exact match and fuzzy match. In the fuzzy match, ChatGPT surpassed BERT-based QA models in 5 out of 6 tasks, while in exact match, BERT-based QA models outperformed ChatGPT in 5 out of 6 tasks but with a smaller F-1 difference. GPT-4 showed a significant advantage over other models in fuzzy match, especially on the entity type of TCM formula and the Chinese patent drug (TFD) and ingredient (IG). Although GPT-4 outperformed BERT-based models on entity type of herb, target, and research method, none of the F-1 scores exceeded 0.5. GSAP-NER, outperformed GPT-4 in terms of F-1 by a slight margin on RM. ChatGPT achieved considerably higher recalls than precisions, particularly in the fuzzy match. Conclusions: The NER performance of LLMs is highly dependent on the entity type, and their performance varies across application scenarios. ChatGPT could be a good choice for scenarios where high recall is favored. However, for knowledge acquisition in rigorous scenarios, neither ChatGPT nor BERT-based QA models are off-the-shelf tools for professional practitioners.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge