Towards More Realistic Human-Robot Conversation: A Seq2Seq-based Body Gesture Interaction System
Paper and Code
May 05, 2019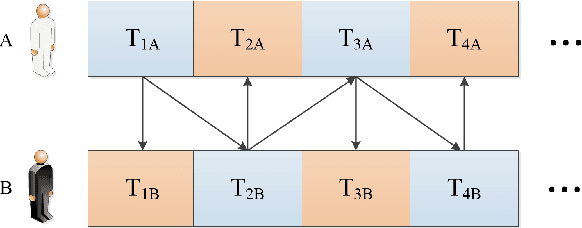

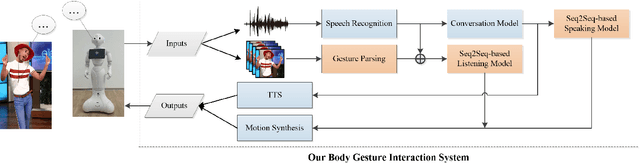
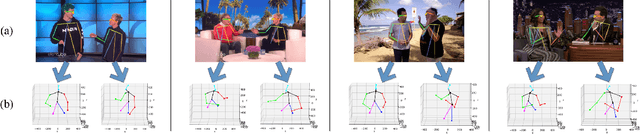
This paper presents a novel method to improve the conversational interaction abilities of intelligent robots to enable more realistic body gestures. The sequence-to-sequence (seq2seq) model is adapted for synthesizing the robots' body gestures represented by the movements of twelve upper-body keypoints in not only the speaking phase, but also the listening phase for which previous methods can hardly achieve. We collected and preprocessed substantial videos of human conversation from Youtube to train our seq2seq-based models and evaluated them by the mean squared error (MSE) and cosine similarity on the test set. The tuned models were implemented to drive a virtual avatar as well as a physical humanoid robot, to demonstrate the improvement on interaction abilities of our method in practice. With body gestures synthesized by our models, the avatar and Pepper exhibited more intelligently while communicating with humans.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge