THC: Accelerating Distributed Deep Learning Using Tensor Homomorphic Compression
Paper and Code
Feb 16, 2023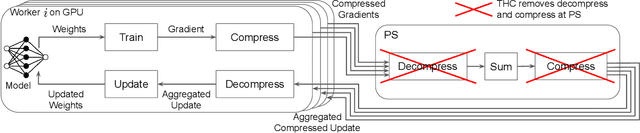

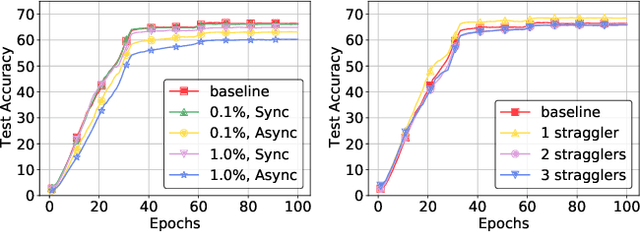
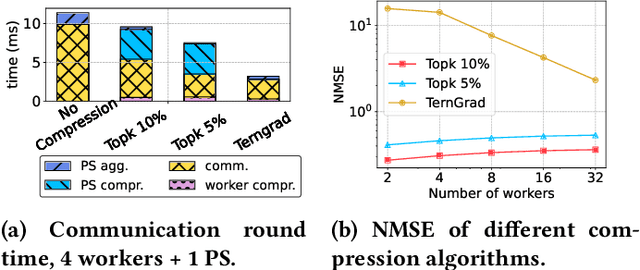
Deep neural networks (DNNs) are the de-facto standard for essential use cases, such as image classification, computer vision, and natural language processing. As DNNs and datasets get larger, they require distributed training on increasingly larger clusters. A main bottleneck is then the resulting communication overhead where workers exchange model updates (i.e., gradients) on a per-round basis. To address this bottleneck and accelerate training, a widely-deployed approach is compression. However, previous deployments often apply bi-directional compression schemes by simply using a uni-directional gradient compression scheme in each direction. This results in significant computational overheads at the parameter server and increased compression error, leading to longer training and lower accuracy. We introduce Tensor Homomorphic Compression (THC), a novel bi-directional compression framework that enables the direct aggregation of compressed values while optimizing the bandwidth to accuracy tradeoff, thus eliminating the aforementioned overheads. Moreover, THC is compatible with in-network aggregation (INA), which allows for further acceleration. Evaluation over a testbed shows that THC improves time-to-accuracy in comparison to alternatives by up to 1.32x with a software PS and up to 1.51x using INA. Finally, we demonstrate that THC is scalable and tolerant for acceptable packet-loss rates.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge